 |
PDBsum entry 1eog

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of pi class glutathione transferase
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Glutathione s-transferase. Chain: a, b. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562. Expression_system_organ: liver.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
Dimer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.10Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.204
|
R-free:
|
0.238
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.Rossjohn,W.J.Mckinstry,A.J.Oakley,M.W.Parker,G.Stenberg, B.Mannervik,B.Dragani,R.Cocco,A.Aceto
|
Key ref:

|
 |
J.Rossjohn
et al.
(2000).
Structures of thermolabile mutants of human glutathione transferase P1-1.
J Mol Biol,
302,
295-302.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
22-Mar-00
|
Release date:
|
18-Oct-00
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P09211
(GSTP1_HUMAN) -
Glutathione S-transferase P from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
210 a.a.
208 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.5.1.18
- glutathione transferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
RX + glutathione = an S-substituted glutathione + a halide anion + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
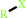 RX
RX
|
+
|
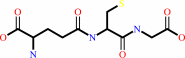 glutathione
glutathione
|
=
|
S-substituted glutathione
|
+
|
halide anion
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
302:295-302
(2000)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structures of thermolabile mutants of human glutathione transferase P1-1.
|
|
J.Rossjohn,
W.J.McKinstry,
A.J.Oakley,
M.W.Parker,
G.Stenberg,
B.Mannervik,
B.Dragani,
R.Cocco,
A.Aceto.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
An N-capping box motif (Ser/Thr-Xaa-Xaa-Asp) is strictly conserved at the
beginning of helix alpha6 in the core of virtually all glutathione transferases
(GST) and GST-related proteins. It has been demonstrated that this local motif
is important in determining the alpha-helical propensity of the isolated
alpha6-peptide and plays a crucial role in the folding and stability of GSTs.
Its removal by site-directed mutagenesis generated temperature-sensitive folding
mutants unable to refold at physiological temperature (37 degrees C). In the
present work, variants of human GSTP1-1 (S150A and D153A), in which the capping
residues have been substituted by alanine, have been generated and purified for
structural analysis. Thus, for the first time, temperature-sensitive folding
mutants of an enzyme, expressed at a permissive temperature, have been
crystallized and their three-dimensional structures determined by X-ray
crystallography. The crystal structures of human pi class GST
temperature-sensitive mutants provide a basis for understanding the structural
origin of the dramatic effects observed on the overall stability of the enzyme
at higher temperatures upon single substitution of a capping residue.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. Ribbon picture of a monomer of human pi class
GST. The location of helix a6, the GST motif II (the conserved
sequence motif consisting of helix a6 and the preceding long
loop), GSH and the sites of mutation (shown in ball-and-stick)
are indicated. This Figure was produced using MOLSCRIPT [Kraulis
1991].
|
 |
Figure 2.
Figure 2. Stereoviews of the region in GST P1-1 about the
sites of mutation. The N-terminal end of helix a6 is shown in
ribbon representation and key residues are shown as
ball-and-stick. (a) Wild-type structure (9GSS; [Oakley et al
1997]), (b) S150A and (c) D153A. The Figure was produced using
MOLSCRIPT [Kraulis 1991].
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2000,
302,
295-302)
copyright 2000.
|
|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
P.Winayanuwattikun,
and
A.J.Ketterman
(2005).
An electron-sharing network involved in the catalytic mechanism is functionally conserved in different glutathione transferase classes.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
31776-31782.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.K.Kong,
G.Polekhina,
W.J.McKinstry,
M.W.Parker,
B.Dragani,
A.Aceto,
D.Paludi,
D.R.Principe,
B.Mannervik,
and
G.Stenberg
(2003).
Contribution of glycine 146 to a conserved folding module affecting stability and refolding of human glutathione transferase p1-1.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
1291-1302.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

