 |
PDBsum entry 1c4t

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Catalytic domain from trimeric dihydrolipoamide succinyltransferase
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Protein (dihydrolipoamide succinyltransferase). Chain: a, b, c. Fragment: catalytic domain, residues 172 - 404. Synonym: e2o. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli. Organism_taxid: 469008. Strain: bl21(de3). Cellular_location: mitochondria. Gene: sucb. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Hexamer (from
)
Hexamer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
3.00Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.257
|
R-free:
|
0.286
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.E.Knapp,D.Carroll,J.E.Lawson,S.R.Ernst,L.J.Reed,M.L.Hackert
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
J.E.Knapp
et al.
(2000).
Expression, purification, and structural analysis of the trimeric form of the catalytic domain of the Escherichia coli dihydrolipoamide succinyltransferase.
Protein Sci,
9,
37-48.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
22-Sep-99
|
Release date:
|
18-Feb-00
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P0AFG6
(ODO2_ECOLI) -
Dihydrolipoyllysine-residue succinyltransferase component of 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex from Escherichia coli (strain K12)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
405 a.a.
226 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.3.1.61
- dihydrolipoyllysine-residue succinyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Citric acid cycle
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N6-[(R)-dihydrolipoyl]-L-lysyl-[protein] + succinyl-CoA = N6-[(R)- S(8)-succinyldihydrolipoyl]-L-lysyl-[protein] + CoA
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
N(6)-[(R)-dihydrolipoyl]-L-lysyl-[protein]
|
+
|
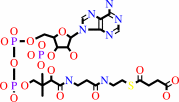 succinyl-CoA
succinyl-CoA
|
=
|
N(6)-[(R)- S(8)-succinyldihydrolipoyl]-L-lysyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 CoA
CoA
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Protein Sci
9:37-48
(2000)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Expression, purification, and structural analysis of the trimeric form of the catalytic domain of the Escherichia coli dihydrolipoamide succinyltransferase.
|
|
J.E.Knapp,
D.Carroll,
J.E.Lawson,
S.R.Ernst,
L.J.Reed,
M.L.Hackert.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The dihydrolipoamide succinyltransferase (E2o) component of the
alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex catalyzes the transfer of a succinyl
group from the S-succinyldihydrolipoyl moiety to coenzyme A. E2o is normally a
24-mer, but is found as a trimer when E2o is expressed with a C-terminal [His]6
tag. The crystal structure of the trimeric form of the catalytic domain (CD) of
the Escherichia coli E2o has been solved to 3.0 A resolution using the Molecular
Replacement method. The refined model contains an intact trimer in the
asymmetric unit and has an R-factor of 0.257 (Rfree = 0.286) for 18,699
reflections between 10.0 and 3.0 A resolution. The core of tE2oCD (residues
187-396) superimposes onto that of the cubic E2oCD with an RMS difference of 0.4
A for all main-chain atoms. The C-terminal end of tE2oCD (residues 397-404)
rotates by an average of 37 degrees compared to cubic E2oCD, disrupting the
normal twofold interface. Despite the alteration of quaternary structure, the
active site of tE2oCD shows no significant differences from that of the cubic
E2oCD, although several side chains in the active site are more ordered in the
trimeric form of E2oCD. Analysis of the available sequence data suggests that
the majority of E2 components have active sites that resemble that of E. coli
E2oCD. The remaining E2 components can be divided into three groups based on
active-site sequence similarity. Analysis of the surface properties of both
crystal forms of E. coli E2oCD suggests key residues that may be involved in the
protein-protein contacts that occur between the catalytic and lipoyl domains of
E2o.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
G.E.Homanics,
K.Skvorak,
C.Ferguson,
S.Watkins,
and
H.S.Paul
(2006).
Production and characterization of murine models of classic and intermediate maple syrup urine disease.
|
| |
BMC Med Genet,
7,
33.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Kato,
R.M.Wynn,
J.L.Chuang,
C.A.Brautigam,
M.Custorio,
and
D.T.Chuang
(2006).
A synchronized substrate-gating mechanism revealed by cubic-core structure of the bovine branched-chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex.
|
| |
EMBO J,
25,
5983-5994.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Rey,
J.L.Gardy,
and
F.S.Brinkman
(2005).
Assessing the precision of high-throughput computational and laboratory approaches for the genome-wide identification of protein subcellular localization in bacteria.
|
| |
BMC Genomics,
6,
162.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.F.Hengeveld,
C.P.van Mierlo,
H.W.van den Hooven,
A.J.Visser,
and
A.de Kok
(2002).
Functional and structural characterization of a synthetic peptide representing the N-terminal domain of prokaryotic pyruvate dehydrogenase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
41,
7490-7500.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

