 |
PDBsum entry 1a80

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1a80
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Native 2,5-diketo-d-gluconic acid reductase a from corynbacterium sp. Complexed with NADPH
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
2,5-diketo-d-gluconic acid reductase a. Chain: a. Synonym: 2,5-dkg reductase a. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Corynebacterium sp.. Organism_taxid: 1720. Variant: a. Gene: 2 5-diketo-d-gluconic acid. Expressed in: pantoea citrea. Expression_system_taxid: 53336.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.10Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.191
|
R-free:
|
0.288
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
S.Khurana,D.B.Powers,S.Anderson,M.Blaber
|
Key ref:

|
 |
S.Khurana
et al.
(1998).
Crystal structure of 2,5-diketo-D-gluconic acid reductase A complexed with NADPH at 2.1-A resolution.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
95,
6768-6773.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
31-Mar-98
|
Release date:
|
30-Mar-99
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P06632
(DKGA_CORSC) -
2,5-diketo-D-gluconic acid reductase A from Corynebacterium sp. (strain ATCC 31090)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
278 a.a.
277 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.346
- 2,5-didehydrogluconate reductase (2-dehydro-L-gulonate-forming).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
2-dehydro-L-idonate + NADP+ = 2,5-didehydro-D-gluconate + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
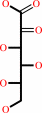 2-dehydro-L-idonate
2-dehydro-L-idonate
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
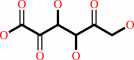 2,5-didehydro-D-gluconate
2,5-didehydro-D-gluconate
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
95:6768-6773
(1998)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of 2,5-diketo-D-gluconic acid reductase A complexed with NADPH at 2.1-A resolution.
|
|
S.Khurana,
D.B.Powers,
S.Anderson,
M.Blaber.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The three-dimensional structure of Corynebacterium 2, 5-diketo-D-gluconic acid
reductase A (2,5-DKGR A; EC 1.1.1.-), in complex with cofactor NADPH, has been
solved by using x-ray crystallographic data to 2.1-A resolution. This enzyme
catalyzes stereospecific reduction of 2,5-diketo-D-gluconate (2,5-DKG) to
2-keto-L-gulonate. Thus the three-dimensional structure has now been solved for
a prokaryotic example of the aldo-keto reductase superfamily. The details of the
binding of the NADPH cofactor help to explain why 2,5-DKGR exhibits lower
binding affinity for cofactor than the related human aldose reductase does.
Furthermore, changes in the local loop structure near the cofactor suggest that
2,5-DKGR will not exhibit the biphasic cofactor binding characteristics observed
in aldose reductase. Although the crystal structure does not include substrate,
the two ordered water molecules present within the substrate-binding pocket are
postulated to provide positional landmarks for the substrate 5-keto and
4-hydroxyl groups. The structural basis for several previously described
active-site mutants of 2,5-DKGR A is also proposed. Recent research efforts have
described a novel approach to the synthesis of L-ascorbate (vitamin C) by using
a genetically engineered microorganism that is capable of synthesizing 2,5-DKG
from glucose and subsequently is transformed with the gene for 2,5-DKGR. These
modifications create a microorganism capable of direct production of
2-keto-L-gulonate from D-glucose, and the gulonate can subsequently be converted
into vitamin C. In economic terms, vitamin C is the single most important
specialty chemical manufactured in the world. Understanding the structural
determinants of specificity, catalysis, and stability for 2,5-DKGR A is of
substantial commercial interest.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Fig. 1. Structures of 2,5-diketo-D-gluconate (2,5-DKG),
2-keto-L-gulonate (2-KLG), and L-ascorbate (vitamin C). The
uppermost carbon is C1.
|
 |
Figure 4.
Fig. 4. Noncovalent interactions between the NADPH
cofactor and 2,5-DKGR A. In addition to hydrogen bonding and
electrostatic interactions, the side chain of Trp-187 is
involved in an aromatic stacking interaction with the
nicotinamide ring of the NADPH cofactor.
|
 |
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.G.Olsen,
L.Pedersen,
C.L.Christensen,
O.Olsen,
and
A.Henriksen
(2008).
Barley aldose reductase: structure, cofactor binding, and substrate recognition in the aldo/keto reductase 4C family.
|
| |
Proteins,
71,
1572-1581.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Machielsen,
A.R.Uria,
S.W.Kengen,
and
J.van der Oost
(2006).
Production and characterization of a thermostable alcohol dehydrogenase that belongs to the aldo-keto reductase superfamily.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
72,
233-238.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Jeudy,
V.Monchois,
C.Maza,
J.M.Claverie,
and
C.Abergel
(2006).
Crystal structure of Escherichia coli DkgA, a broad-specificity aldo-keto reductase.
|
| |
Proteins,
62,
302-307.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.F.Couture,
K.P.de Jésus-Tran,
A.M.Roy,
L.Cantin,
P.L.Côté,
P.Legrand,
V.Luu-The,
F.Labrie,
and
R.Breton
(2005).
Comparison of crystal structures of human type 3 3alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase reveals an "induced-fit" mechanism and a conserved basic motif involved in the binding of androgen.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
14,
1485-1497.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Sanli,
S.Banta,
S.Anderson,
and
M.Blaber
(2004).
Structural alteration of cofactor specificity in Corynebacterium 2,5-diketo-D-gluconic acid reductase.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
13,
504-512.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Ehrensberger,
and
D.K.Wilson
(2003).
Expression, crystallization and activities of the two family 11 aldo-keto reductases from Bacillus subtilis.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
59,
375-377.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.M.Ellis
(2002).
Microbial aldo-keto reductases.
|
| |
FEMS Microbiol Lett,
216,
123-131.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Kim,
S.I.Blaber,
and
M.Blaber
(2002).
Alternative type I and I' turn conformations in the beta8/beta9 beta-hairpin of human acidic fibroblast growth factor.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
11,
459-466.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Banta,
B.A.Swanson,
S.Wu,
A.Jarnagin,
and
S.Anderson
(2002).
Optimizing an artificial metabolic pathway: engineering the cofactor specificity of Corynebacterium 2,5-diketo-D-gluconic acid reductase for use in vitamin C biosynthesis.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
41,
6226-6236.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Zhou,
F.Yan,
and
H.H.Tai
(2001).
C-Terminal region of human NAD+-dependent 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase is involved in the interaction with prostaglandin substrates.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
268,
3368-3374.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.H.Eschenfeldt,
L.Stols,
H.Rosenbaum,
Z.S.Khambatta,
E.Quaite-Randall,
S.Wu,
D.C.Kilgore,
J.D.Trent,
and
M.I.Donnelly
(2001).
DNA from uncultured organisms as a source of 2,5-diketo-D-gluconic acid reductases.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
67,
4206-4214.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.J.Pujol,
and
C.I.Kado
(2000).
Genetic and biochemical characterization of the pathway in Pantoea citrea leading to pink disease of pineapple.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
182,
2230-2237.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Hur,
and
D.K.Wilson
(2000).
Crystallization and aldo-keto reductase activity of Gcy1p from Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
56,
763-765.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Khurana,
G.Sanli,
D.B.Powers,
S.Anderson,
and
M.Blaber
(2000).
Molecular modeling of substrate binding in wild-type and mutant Corynebacteria 2,5-diketo-D-gluconate reductases.
|
| |
Proteins,
39,
68-75.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Y.Yum,
B.Y.Lee,
and
J.G.Pan
(1999).
Identification of the yqhE and yafB genes encoding two 2, 5-diketo-D-gluconate reductases in Escherichia coli.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
65,
3341-3346.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

