 |
PDBsum entry 1a27

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Dehydrogenase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1a27
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.51
- 3(or 17)beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
testosterone + NAD+ = androst-4-ene-3,17-dione + NADH + H+
|
|
2.
|
testosterone + NADP+ = androst-4-ene-3,17-dione + NADPH + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
testosterone
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 91.67% similarity
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 95.24% similarity
|
=
|
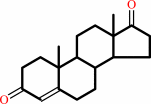 androst-4-ene-3,17-dione
androst-4-ene-3,17-dione
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
testosterone
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 95.24% similarity
|
=
|
 androst-4-ene-3,17-dione
androst-4-ene-3,17-dione
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.62
- 17beta-estradiol 17-dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
17beta-estradiol + NAD+ = estrone + NADH + H+
|
|
2.
|
17beta-estradiol + NADP+ = estrone + NADPH + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
17beta-estradiol
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 91.67% similarity
|
=
|
estrone
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
17beta-estradiol
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
estrone
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
J Mol Biol
244:114-116
(1994)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystallization and X-ray crystallographic analysis of recombinant chicken poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase catalytic domain produced in Sf9 insect cells.
|
|
S.Jung,
E.A.Miranda,
J.M.de Murcia,
C.Niedergang,
M.Delarue,
G.E.Schulz,
G.M.de Murcia.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) participates in the immediate response in
mammalian cells exposed to DNA-damaging agents. Recombinant baculovirus
harboring the cDNA of the chicken PARP catalytic domain (40 kDa) have been used
to infect Spodoptera frugiperda (Sf9) insect cells. The recombinant polypeptide
(30 mg per 1 x 10(9) cells) was purified to homogeneity by 3-aminobenzamide
affinity chromatography. The enzymatic properties of the recombinant domain were
similar to those of the native fragment. Crystals of the purified recombinant
catalytic domain were grown by vapor diffusion. The crystals belong to space
group P2(1)2(1)2(1) with unit cell dimensions of a = 59.2 A, b = 65.0 A, c =
96.9 A. They are suitable for X-ray analysis and diffract to 2.0 A.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.R.Morrison,
J.Moss,
L.A.Stevens,
J.E.Evans,
C.Farrell,
E.Merithew,
D.G.Lambright,
D.L.Greiner,
J.P.Mordes,
A.A.Rossini,
and
R.Bortell
(2006).
ART2, a T cell surface mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase, generates extracellular poly(ADP-ribose).
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
33363-33372.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.R.Calabrese,
R.Almassy,
S.Barton,
M.A.Batey,
A.H.Calvert,
S.Canan-Koch,
B.W.Durkacz,
Z.Hostomsky,
R.A.Kumpf,
S.Kyle,
J.Li,
K.Maegley,
D.R.Newell,
E.Notarianni,
I.J.Stratford,
D.Skalitzky,
H.D.Thomas,
L.Z.Wang,
S.E.Webber,
K.J.Williams,
and
N.J.Curtin
(2004).
Anticancer chemosensitization and radiosensitization by the novel poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibitor AG14361.
|
| |
J Natl Cancer Inst,
96,
56-67.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.C.Amé,
V.Rolli,
V.Schreiber,
C.Niedergang,
F.Apiou,
P.Decker,
S.Muller,
T.Höger,
J.Ménissier-de Murcia,
and
G.de Murcia
(1999).
PARP-2, A novel mammalian DNA damage-dependent poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
17860-17868.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Ruf,
G.de Murcia,
and
G.E.Schulz
(1998).
Inhibitor and NAD+ binding to poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase as derived from crystal structures and homology modeling.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
3893-3900.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Decker,
J.P.Briand,
G.de Murcia,
R.W.Pero,
D.A.Isenberg,
and
S.Muller
(1998).
Zinc is an essential cofactor for recognition of the DNA binding domain of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase by antibodies in autoimmune rheumatic and bowel diseases.
|
| |
Arthritis Rheum,
41,
918-926.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Ruf,
J.Mennissier de Murcia,
G.de Murcia,
and
G.E.Schulz
(1996).
Structure of the catalytic fragment of poly(AD-ribose) polymerase from chicken.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
93,
7481-7485.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Lindahl,
M.S.Satoh,
G.G.Poirier,
and
A.Klungland
(1995).
Post-translational modification of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase induced by DNA strand breaks.
|
| |
Trends Biochem Sci,
20,
405-411.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

