 |
PDBsum entry 1db3

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.47
- GDP-mannose 4,6-dehydratase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
GDP-L-Fucose and GDP-mannose Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
GDP-alpha-D-mannose = GDP-4-dehydro-alpha-D-rhamnose + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
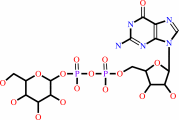 GDP-mannose
GDP-mannose
|
=
|
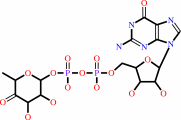 GDP-4-dehydro-6-deoxy-D-mannose
GDP-4-dehydro-6-deoxy-D-mannose
|
+
|
H(2)O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
NAD(+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Structure
8:123-135
(2000)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural and kinetic analysis of Escherichia coli GDP-mannose 4,6 dehydratase provides insights into the enzyme's catalytic mechanism and regulation by GDP-fucose.
|
|
J.R.Somoza,
S.Menon,
H.Schmidt,
D.Joseph-McCarthy,
A.Dessen,
M.L.Stahl,
W.S.Somers,
F.X.Sullivan.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Background: GDP-mannose 4,6 dehydratase (GMD) catalyzes the conversion of
GDP-(D)-mannose to GDP-4-keto, 6-deoxy-(D)-mannose. This is the first and
regulatory step in the de novo biosynthesis of GDP-(L)-fucose. Fucose forms part
of a number of glycoconjugates, including the ABO blood groups and the selectin
ligand sialyl Lewis X. Defects in GDP-fucose metabolism have been linked to
leukocyte adhesion deficiency type II (LADII). Results: The structure of the
GDP-mannose 4,6 dehydratase apo enzyme has been determined and refined using
data to 2.3 A resolution. GMD is a homodimeric protein with each monomer
composed of two domains. The larger N-terminal domain binds the NADP(H) cofactor
in a classical Rossmann fold and the C-terminal domain harbors the
sugar-nucleotide binding site. We have determined the GMD dissociation constants
for NADP, NADPH and GDP-mannose. Each GMD monomer binds one cofactor and one
substrate molecule, suggesting that both subunits are catalytically competent.
GDP-fucose acts as a competitive inhibitor, suggesting that it binds to the same
site as GDP-mannose, providing a mechanism for the feedback inhibition of fucose
biosynthesis. Conclusions: The X-ray structure of GMD reveals that it is a
member of the short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR) family of proteins. We
have modeled the binding of NADP and GDP-mannose to the enzyme and mutated four
of the active-site residues to determine their function. The combined modeling
and mutagenesis data suggests that at position 133 threonine substitutes serine
as part of the serine-tyrosine-lysine catalytic triad common to the SDR family
and Glu 135 functions as an active-site base.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. GDP-fucose biosynthesis. NADP bound to GMD is
reduced and then oxidized during the course of the reaction. GFS
catalyzes two distinct reactions: the epimerization of the
GDP-4-keto, 6-deoxymannose at C3 and C5 followed by the
subsequent reduction at C4 to yield GDP-fucose.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figure is
reprinted
by permission from Cell Press:
Structure
(2000,
8,
123-135)
copyright 2000.
|
|
| |
Figure was
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.D.King,
K.K.Poon,
N.A.Webb,
E.M.Anderson,
D.J.McNally,
J.R.Brisson,
P.Messner,
R.M.Garavito,
and
J.S.Lam
(2009).
The structural basis for catalytic function of GMD and RMD, two closely related enzymes from the GDP-D-rhamnose biosynthesis pathway.
|
| |
FEBS J,
276,
2686-2700.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.L.Chen,
Y.H.Chen,
Y.C.Lin,
K.C.Tsai,
and
H.T.Chiu
(2009).
Functional characterization and substrate specificity of spinosyn rhamnosyltransferase by in vitro reconstitution of spinosyn biosynthetic enzymes.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
7352-7363.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Liu,
Y.A.Knirel,
L.Feng,
A.V.Perepelov,
S.N.Senchenkova,
Q.Wang,
P.R.Reeves,
and
L.Wang
(2008).
Structure and genetics of Shigella O antigens.
|
| |
FEMS Microbiol Rev,
32,
627-653.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Fruscione,
L.Sturla,
G.Duncan,
J.L.Van Etten,
P.Valbuzzi,
A.De Flora,
E.Di Zanni,
and
M.Tonetti
(2008).
Differential role of NADP+ and NADPH in the activity and structure of GDP-D-mannose 4,6-dehydratase from two chlorella viruses.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
184-193.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.D.Barrows,
S.M.Haslam,
L.J.Bischof,
H.R.Morris,
A.Dell,
and
R.V.Aroian
(2007).
Resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxin in Caenorhabditis elegans from loss of fucose.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
3302-3311.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Oka,
T.Nemoto,
and
Y.Jigami
(2007).
Functional analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana RHM2/MUM4, a multidomain protein involved in UDP-D-glucose to UDP-L-rhamnose conversion.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
5389-5403.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Rhomberg,
C.Fuchsluger,
D.Rendić,
K.Paschinger,
V.Jantsch,
P.Kosma,
and
I.B.Wilson
(2006).
Reconstitution in vitro of the GDP-fucose biosynthetic pathways of Caenorhabditis elegans and Drosophila melanogaster.
|
| |
FEBS J,
273,
2244-2256.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.M.Koropatkin,
and
H.M.Holden
(2005).
Structure of CDP-D-glucose 4,6-dehydratase from Salmonella typhi complexed with CDP-D-xylose.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
61,
365-373.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.C.Price,
Y.M.Zhang,
C.O.Rock,
and
S.W.White
(2004).
Cofactor-induced conformational rearrangements establish a catalytically competent active site and a proton relay conduit in FabG.
|
| |
Structure,
12,
417-428.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.A.Webb,
A.M.Mulichak,
J.S.Lam,
H.L.Rocchetta,
and
R.M.Garavito
(2004).
Crystal structure of a tetrameric GDP-D-mannose 4,6-dehydratase from a bacterial GDP-D-rhamnose biosynthetic pathway.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
13,
529-539.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.A.Wolucka,
and
M.Van Montagu
(2003).
GDP-mannose 3',5'-epimerase forms GDP-L-gulose, a putative intermediate for the de novo biosynthesis of vitamin C in plants.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
47483-47490.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.M.Koropatkin,
H.W.Liu,
and
H.M.Holden
(2003).
High resolution x-ray structure of tyvelose epimerase from Salmonella typhi.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
20874-20881.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
X.M.He,
and
H.W.Liu
(2002).
Formation of unusual sugars: mechanistic studies and biosynthetic applications.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
71,
701-754.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.A.Wolucka,
G.Persiau,
J.Van Doorsselaere,
M.W.Davey,
H.Demol,
J.Vandekerckhove,
M.Van Montagu,
M.Zabeau,
and
W.Boerjan
(2001).
Partial purification and identification of GDP-mannose 3",5"-epimerase of Arabidopsis thaliana, a key enzyme of the plant vitamin C pathway.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
98,
14843-14848.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.F.Giraud,
and
J.H.Naismith
(2000).
The rhamnose pathway.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
10,
687-696.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

