 |
PDBsum entry 1a2v

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Amine oxidase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1a2v
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.4.3.21
- primary-amine oxidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a primary methyl amine + O2 + H2O = an aldehyde + H2O2 + NH4+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
primary methyl amine
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
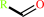 aldehyde
aldehyde
|
+
|
 H2O2
H2O2
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
53:364-370
(1997)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystallographic study of yeast copper amine oxidase.
|
|
R.Li,
L.Chen,
D.Cai,
J.P.Klinman,
F.S.Mathews.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The copper-containing amine oxidase from the yeast Hansenula polymorpha (YAO)
has been crystallized and partially solved by molecular replacement. It
catalyzes the oxidative deamination of primary amines by molecular oxygen to the
corresponding aldehydes, ammonia and hydrogen peroxide. It contains a covalently
bound redox cofactor, topa quinone, generated by post-translational modification
of a single tyrosine side chain. The crystals of YAO are orthorhombic, with
space-group symmetry P2(1)2(1)2(1) and unit-cell dimensions a = 138.8, b =
148.2, c = 234.0 A and diffract X-rays beyond 2.0 A resolution. Solution by
molecular replacement using the E. coli amine oxidase structure [Parsons,
Convery, Wilmot, Yadav, Blakeley, Corner, Philips, McPherson & Knowles
(1995). Structure, 3, 1171-1184] as a search model reveals that there are three
dimers in the asymmetric unit in a trigonal arrangement having 32 point-group
symmetry. The solution agrees well with the self-rotation function of YAO. The
non-crystallographic threefold axis lies parallel to a crystallographic twofold
screw axis and each dimer has twofold symmetry. Phases from the refined model
based on the molecular-replacement solution were used to solve one heavy-atom
derivative. Model building from the unbiased isomorphous replacement phases is
in progress.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Fig. 1. Crystals of yeast copper amine oxidase. There ae four polymorphs observed under the same crystallization conditions: (a) and (b are
monoclinic crystls and (c) and (d) are orthorhombic crystals.
|
 |
Figure 3.
Fig. 3. Schematic drawing of the crystallographic asymmetric unit
based on the molecularreplacement solution. The asymmetric unit
consists of a trigonal arrangement of dimers and has pointgroup
symmetry D3 (32), with the local threefold axis parallel to the
crystallographic a axis. The directions of the dyads in each dimer
(the monomers are ditinguished by thin and thick lines) are
indicated with respect to the crystallographic b and c axes.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the IUCr:
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
(1997,
53,
364-370)
copyright 1997.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
R.Li,
J.P.Klinman,
and
F.S.Mathews
(1998).
Copper amine oxidase from Hansenula polymorpha: the crystal structure determined at 2.4 A resolution reveals the active conformation.
|
| |
Structure,
6,
293-307.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

