Acetyl-CoA C-acyltransferase
Thiolases form a ubiquitous family of enzymes found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Thiolases catalyse the reversible two step cleavage of acyl-CoA into CoA and acetyl-CoA. There are two classes of thiolases, I and II. This entry represents the Class II thiolases. Class II only acts upon acetoacetyl-CoA and its main function is to synthesise this compound in a Claisen condensation reaction important in several biosynthetic pathways.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P27796
 (2.3.1.16)
(2.3.1.16)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288c (Baker's yeast)

- PDB
-
1afw
- THE 1.8 ANGSTROM CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE DIMERIC PEROXISOMAL THIOLASE OF SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE
(1.8 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.47.10
 (see all for 1afw)
(see all for 1afw)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.3.1.16)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
His375 deprotonates Cys125 to activate it as a nucleophile. Cys125 attacks the carbonyl of the acyl-CoA in an addition reaction, forming an oxyanion transition state. This is stabilised by the main-chain amide of Gly405. The oxyanion collapses, eliminating CoA with concomitant deprotonation of Cys403. Cys403 then deprotonates the methyl group of the acetyl CoA with concomitant double bond rearrangement. The acetyl-CoA oxyanion collapses, initiating a nucleophilic attack on the acylated Cys125 in an addition reaction. The oxyanion collapses eliminating Cys125 with concomitant deprotonation of His375, restoring the enzyme to its native state.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1afw) | ||
| His375 | His375(351)A | Deprotonates Cys125 to activate it as a nucleophile. May also stabilise the negatively charged transition state, when in the positively charged protonated state. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys403 | Cys403(379)A | Donates a proton to the leaving group. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly405 (main-N) | Gly405(381)A (main-N) | Stabilises the oxyanion transition states. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys125 | Cys125(101)A | Deprotonated cysteine is the nucleophile in both the forward and reverse forms of this reaction. It is acylated by the substrate, and remains covalently bound throughout the reaction. | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor, nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, aldol addition, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Modis Y et al. (2000), J Mol Biol, 297, 1171-1182. Crystallographic analysis of the reaction pathway of Zoogloea ramigera biosynthetic thiolase11Edited by I. A. Wilson. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2000.3638. PMID:10764581.
- Schaefer CM et al. (2015), Structure, 23, 21-33. FadA5 a Thiolase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis: A Steroid-Binding Pocket Reveals the Potential for Drug Development against Tuberculosis. DOI:10.1016/j.str.2014.10.010. PMID:25482540.
- Nesbitt NM et al. (2010), Infect Immun, 78, 275-282. A Thiolase of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Is Required for Virulence and Production of Androstenedione and Androstadienedione from Cholesterol. DOI:10.1128/iai.00893-09. PMID:19822655.
- Modis Y et al. (1999), Structure, 7, 1279-1290. A biosynthetic thiolase in complex with a reaction intermediate: the crystal structure provides new insights into the catalytic mechanism. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(00)80061-1. PMID:10545327.
- Mathieu M et al. (1997), J Mol Biol, 273, 714-728. The 1.8 Å crystal structure of the dimeric peroxisomal 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: implications for substrate binding and reaction mechanism. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1997.1331. PMID:9402066.
- Mathieu M et al. (1994), Structure, 2, 797-808. The 2.8å Crystal Structure of peroxisomal 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae : a five-layered αβαβα structure constructed from two core domains of identical topology. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(94)00081-6.
- Gilbert LR et al. (1976), Anal Biochem, 72, 480-484. Optimal conditions for the iodination of fibrinogen using immobilized lactoperoxidase. DOI:doi:10.1016/0003-2697(76)90557-1. PMID:942066.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His375(351)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys125(101)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His375(351)A | proton acceptor |
| Cys125(101)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer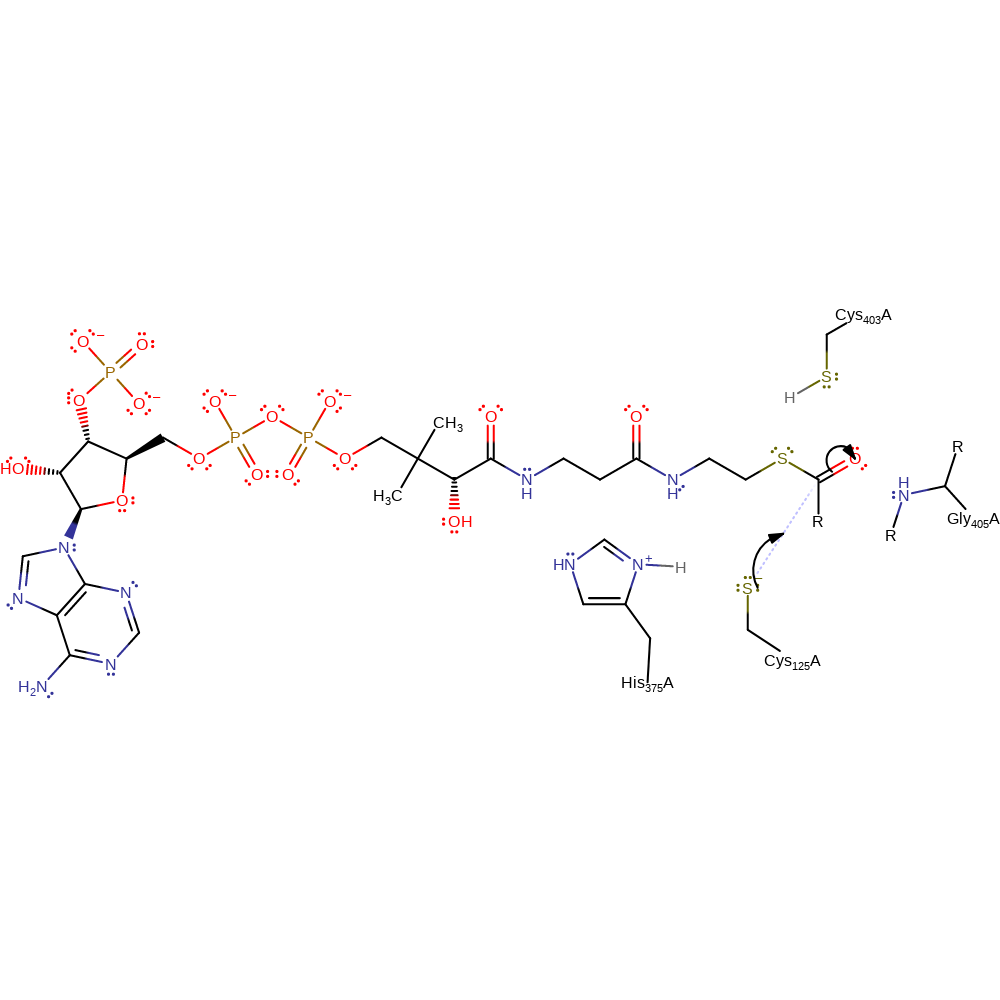
Step 2. Cys125 initiates a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of the acyl-CoA in an addition reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly405(381)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys403(379)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys125(101)A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used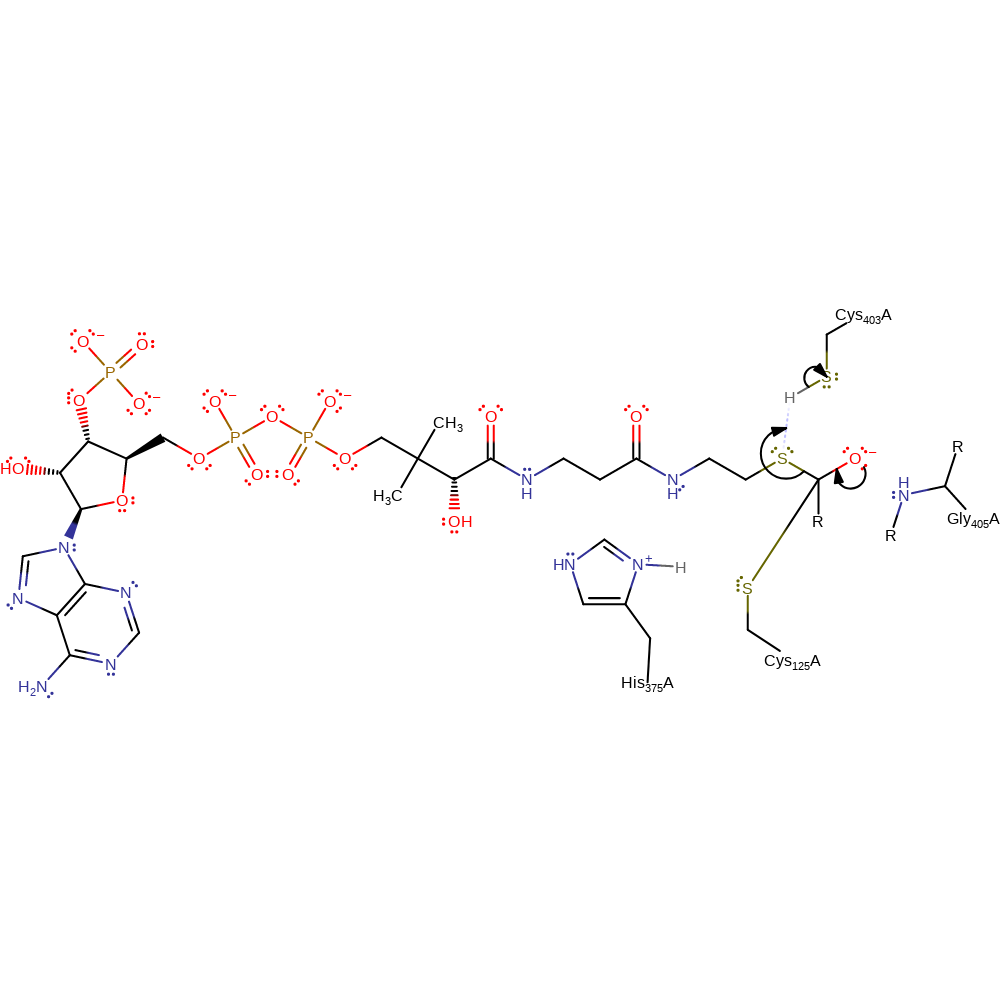
Step 3. The oxyanion collapses, eliminating CoA with concomitant deprotonation of Cys403.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly405(381)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys125(101)A | covalently attached |
| Cys403(379)A | hydrogen bond donor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation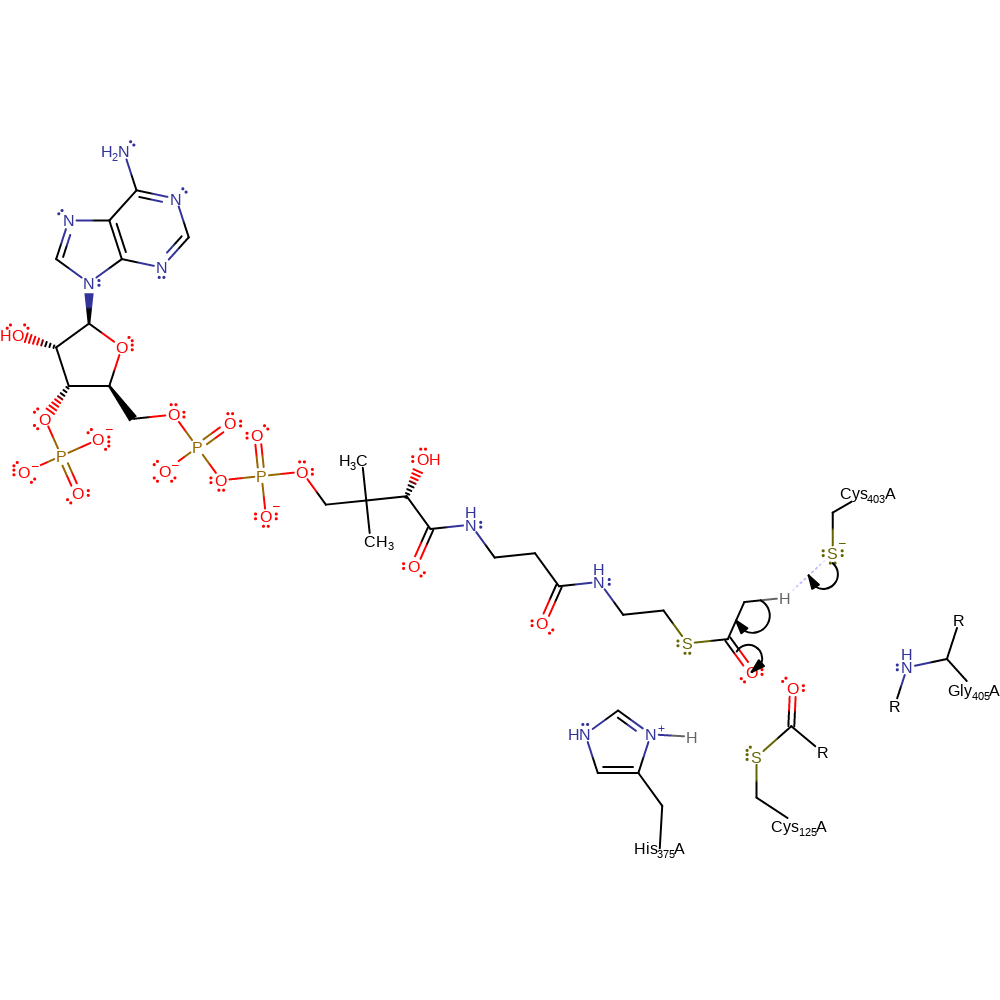
Step 4. Cys403 deprotonates the CH3 of the acetyl-CoA, with concomitant double bond rearrangement.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly405(381)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| His375(351)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys125(101)A | covalently attached |
| Cys403(379)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, overall reactant used, intermediate formation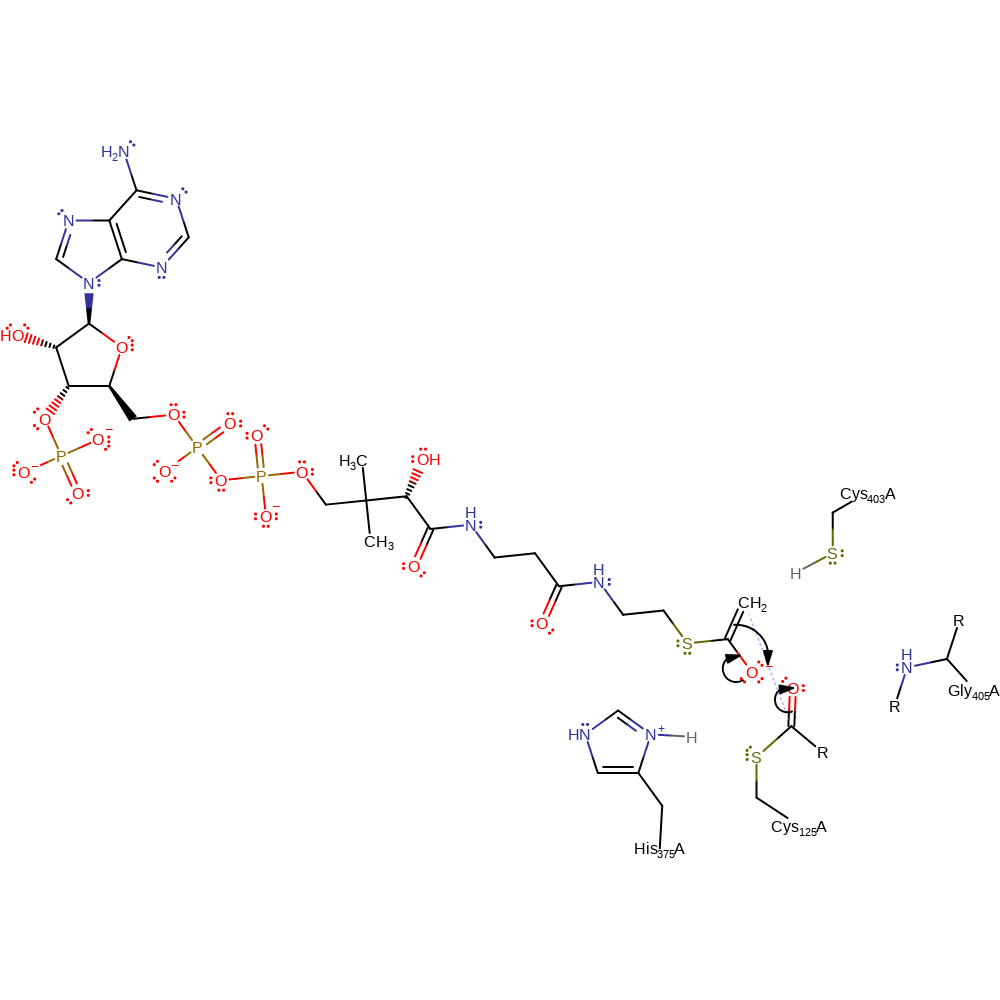
Step 5. The acetyl-CoA oxyanion collapses, initiating a nucleophilic attack on the acylated Cys125 in an addition reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly405(381)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His375(351)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys125(101)A | covalently attached |
| Cys403(379)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
aldol addition, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation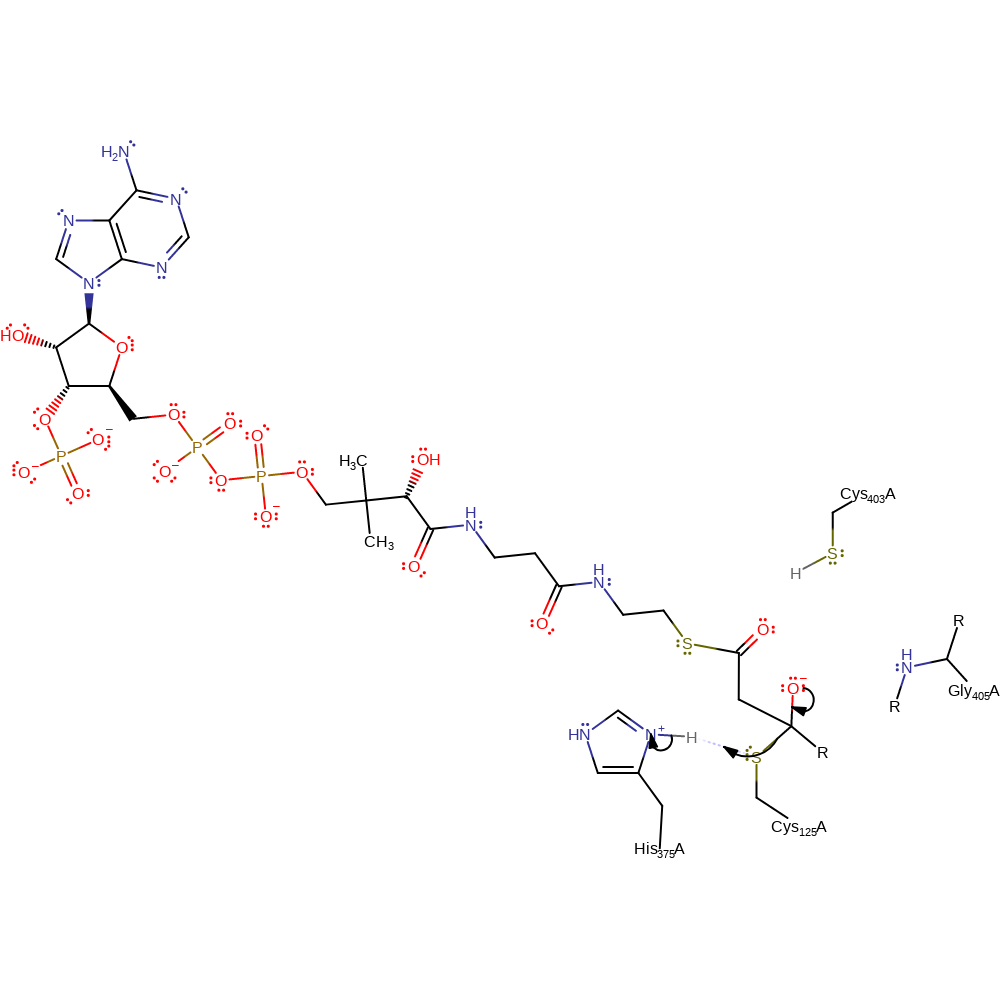
Step 6. The oxyanion collapses eliminating Cys125 with concomitant deprotonation of His375.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly405(381)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His375(351)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys125(101)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys403(379)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His375(351)A | proton donor |
| Cys125(101)A | proton acceptor, nucleofuge |




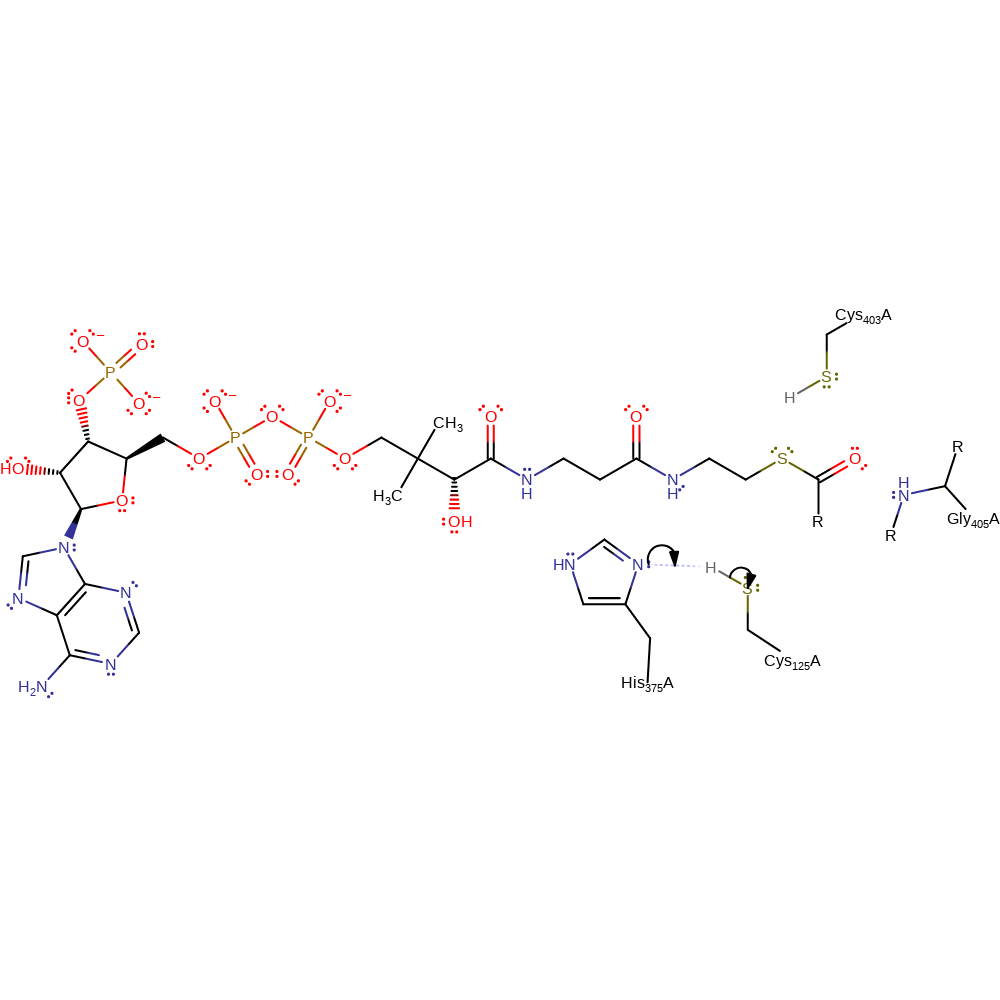
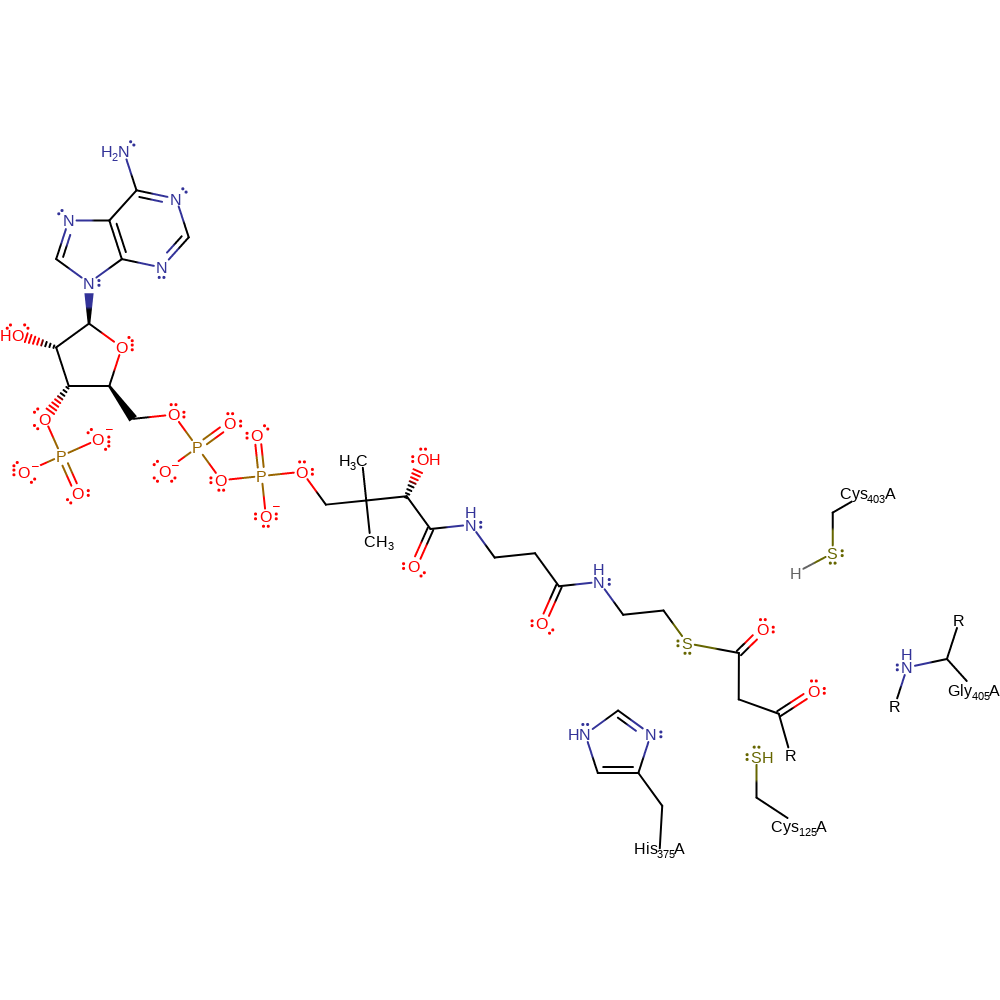 Download:
Download: