Dethiobiotin synthase
Dethiobiotin synthase is the penultimate enzyme in the biotin synthesis pathway in E. coli and other microorganisms. The enzyme catalyses the formation of the ureido ring of dethiobiotin from (7R,8S)-7,8-diaminononanic acid (DAPA) and carbon dioxide. The enzyme requires ATP and divalent cations as cofactors. The enzyme represents a third enzymatic mechanism for carboxylation reactions, after the biotin-dependent carboxylases and ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P13000
 (6.3.3.3)
(6.3.3.3)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1bs1
- DETHIOBIOTIN SYNTHETASE COMPLEXED WITH DETHIOBIOTIN, ADP , INORGANIC PHOSPHATE AND MAGNESIUM
(1.8 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.300
 (see all for 1bs1)
(see all for 1bs1)
- Cofactors
- Water (1), Magnesium(2+) (2) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:6.3.3.3)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Detailed mechanistic information is sparse. However, speculations can be made on the basis of site-directed mutagenesis and crystal structures. The first step in the reaction is the formation of a carbamate of the substrate DAPA. Evidence is conflicting over whether this is on the N7 or N8 position of the substrate. The second step is the formation of a carbamic-phosphoric mixed anhydride as a second intermediate, followed by ring closure. This is most likely to occur via nucleophilic attack of the activated carbamate with a substrate nitrogen, with release of inorganic phosphate.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1bs1) | ||
| Glu13 | Glu12A | Forms part of the magnesium 1 binding site. | metal ligand |
| Thr12, Lys38, Lys16, Ser42 (main-N), Glu13, Ser42 | Thr11A, Lys37A, Lys15A, Ser41A (main-N), Glu12A, Ser41A | Helps to stabilise the reactive intermediates. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp55, Thr17, Glu116 | Asp54A, Thr16A, Glu115A | Forms part of the magnesium 2 binding site. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall product formed, intramolecular nucleophilic addition, cyclisation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, dephosphorylation, intermediate terminated, intermediate collapseReferences
- Yang G et al. (1997), Biochemistry, 36, 4751-4760. Active Site Mutants ofEscherichia coliDethiobiotin Synthetase: Effects of Mutations on Enzyme Catalytic and Structural Properties. DOI:10.1021/bi9631677. PMID:9125495.
- Lin S et al. (2011), Mol Biosyst, 7, 1811-. Closing in on complete pathways of biotin biosynthesis. DOI:10.1039/c1mb05022b. PMID:21437340.
- Dey S et al. (2010), Biochemistry, 49, 6746-6760. Structural Characterization of theMycobacterium tuberculosisBiotin Biosynthesis Enzymes 7,8-Diaminopelargonic Acid Synthase and Dethiobiotin Synthetase,. DOI:10.1021/bi902097j. PMID:20565114.
- Sandalova T et al. (1999), Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, 55, 610-624. Structure of dethiobiotin synthetase at 0.97 A resolution. PMID:10089457.
- Käck H et al. (1998), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 95, 5495-5500. Snapshot of a phosphorylated substrate intermediate by kinetic crystallography. DOI:10.1073/pnas.95.10.5495. PMID:9576910.
- Käck H et al. (1998), Protein Sci, 7, 2560-2566. Crystal structure of two quaternary complexes of dethiobiotin synthetase, enzyme-MgADP-AlF3-diaminopelargonic acid and enzyme-MgADP-dethiobiotin-phosphate; implications for catalysis. DOI:10.1002/pro.5560071209. PMID:9865950.
- Schneider G et al. (1997), Methods Enzymol, 376-385. [40] Structure of ATP-dependent carboxylase, dethiobiotin synthase. DOI:10.1016/s0076-6879(97)79042-6.
- Huang W et al. (1995), Biochemistry, 34, 10985-10995. Mechanism of an ATP-dependent carboxylase, dethiobiotin synthetase, based on crystallographic studies of complexes with substrates and a reaction intermediate. PMID:7669756.
- Alexeev D et al. (1995), Structure, 3, 1207-1215. Substrate binding and carboxylation by dethiobiotin synthetase--a kinetic and X-ray study. PMID:8591031.
- Alexeev D et al. (1994), Structure, 2, 1061-1072. Mechanistic implications and family relationships from the structure of dethiobiotin synthetase. PMID:7881906.
- Baxter RL et al. (1994), J Chem Soc Chem Commun, 559-560. Mechanism of dethiobiotin synthetase—characterisation of the 8-aminocarbamate of (7R,8S)-7,8 diaminononanoate as an enzyme-bound intermediate. DOI:10.1039/c39940000559.
- Baxter RL et al. (1994), J Chem Soc Chem Commun, 0, 759-760. The mechanism of Escherichia coli dethiobiotin synthetase—the closure of the ureido ring of dethiobiotin involves formation of a carbamic-phosphate mixed anhydride. DOI:10.1039/c39940000759.
- Huang W et al. (1994), Structure, 2, 407-414. Crystal structure of an ATP-dependent carboxylase, dethiobiotin synthetase, at 1.65 A resolution. PMID:8081756.
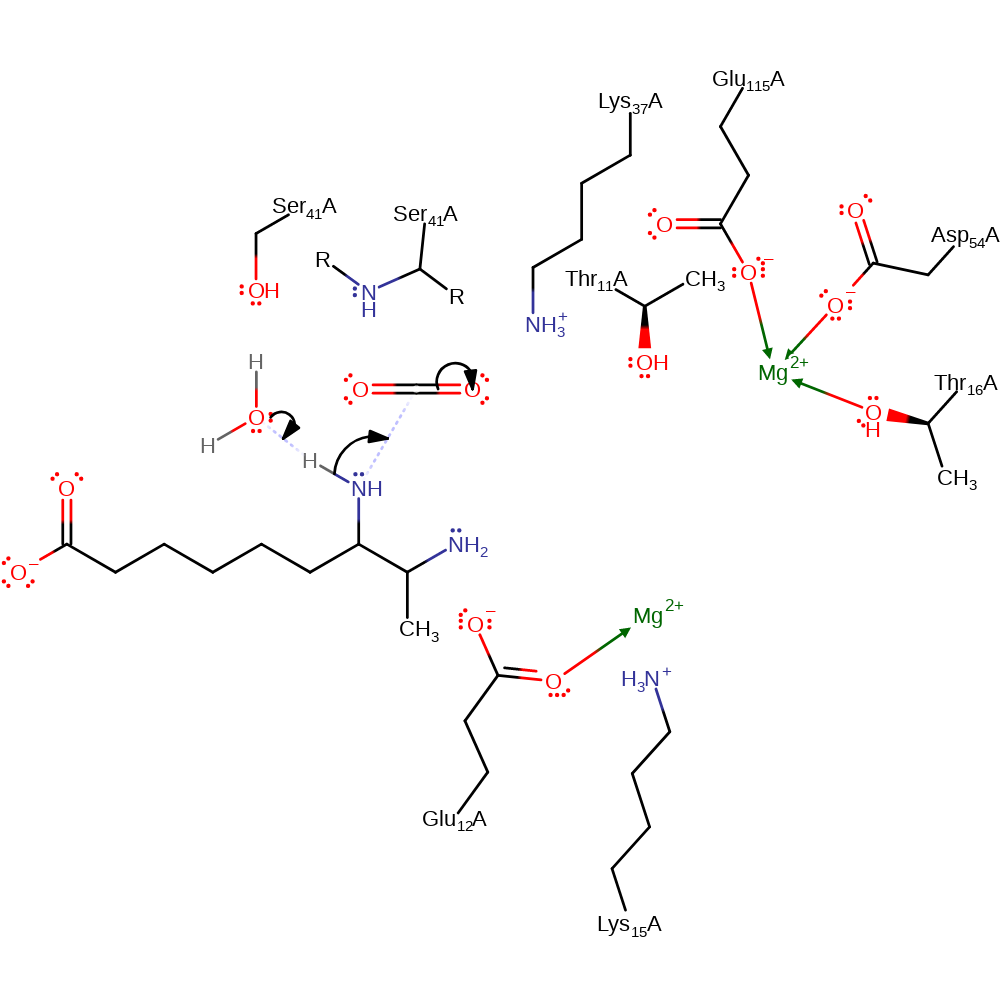
Step 1. Water deprotonates the 7,8-diaminononanoate substrate, activating it for a nucleophilic attack upon the carbon dioxide in an addition reaction. Lys37 stabilises the formation of the negatively charged intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys37A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser41A | increase basicity |
| Glu115A | metal ligand |
| Asp54A | metal ligand |
| Glu12A | metal ligand |
| Thr16A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation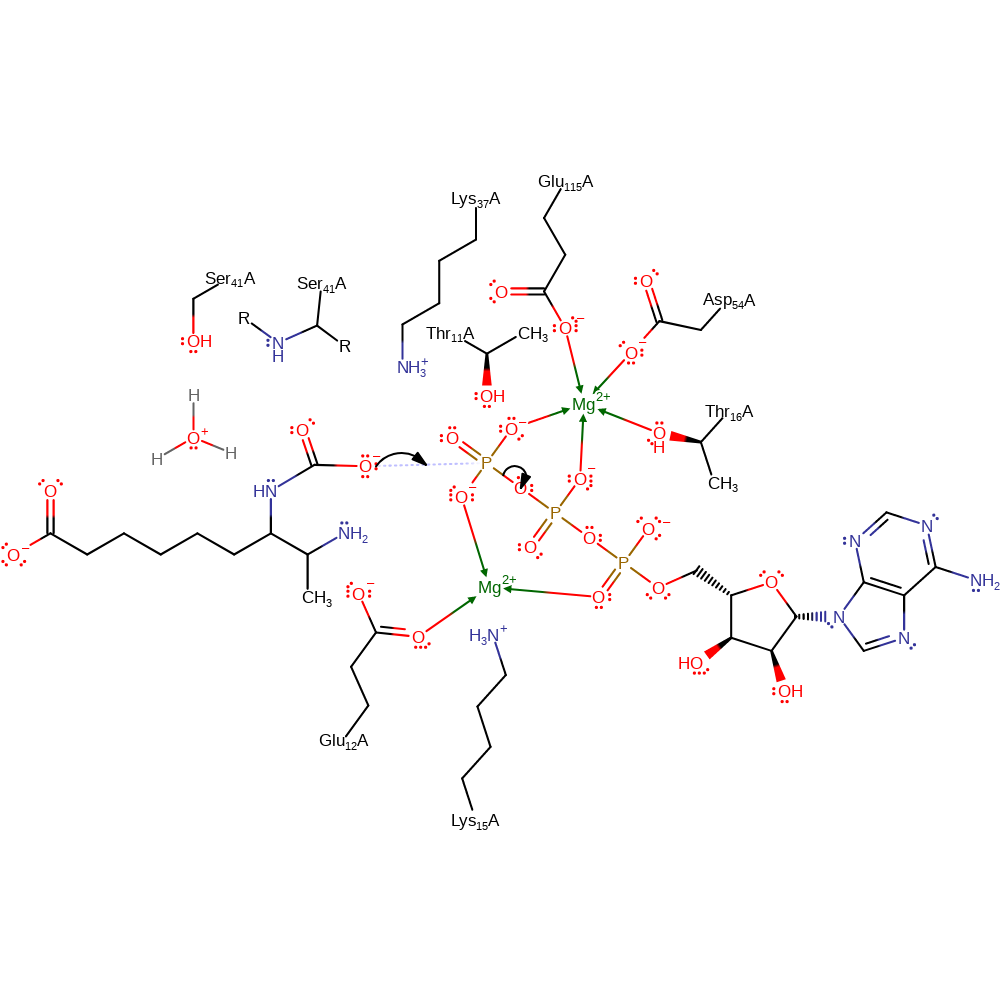
Step 2. The carboxylated intermediate acts as a nucleophile and attacks the gamma phosphate of ATP in a substitution reaction. Lys37, Lys15 and two Mg(II) ions stabilise the intermediates.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys37A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser41A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys15A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Thr11A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser41A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu115A | metal ligand |
| Asp54A | metal ligand |
| Glu12A | metal ligand |
| Thr16A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, overall product formed, intermediate formation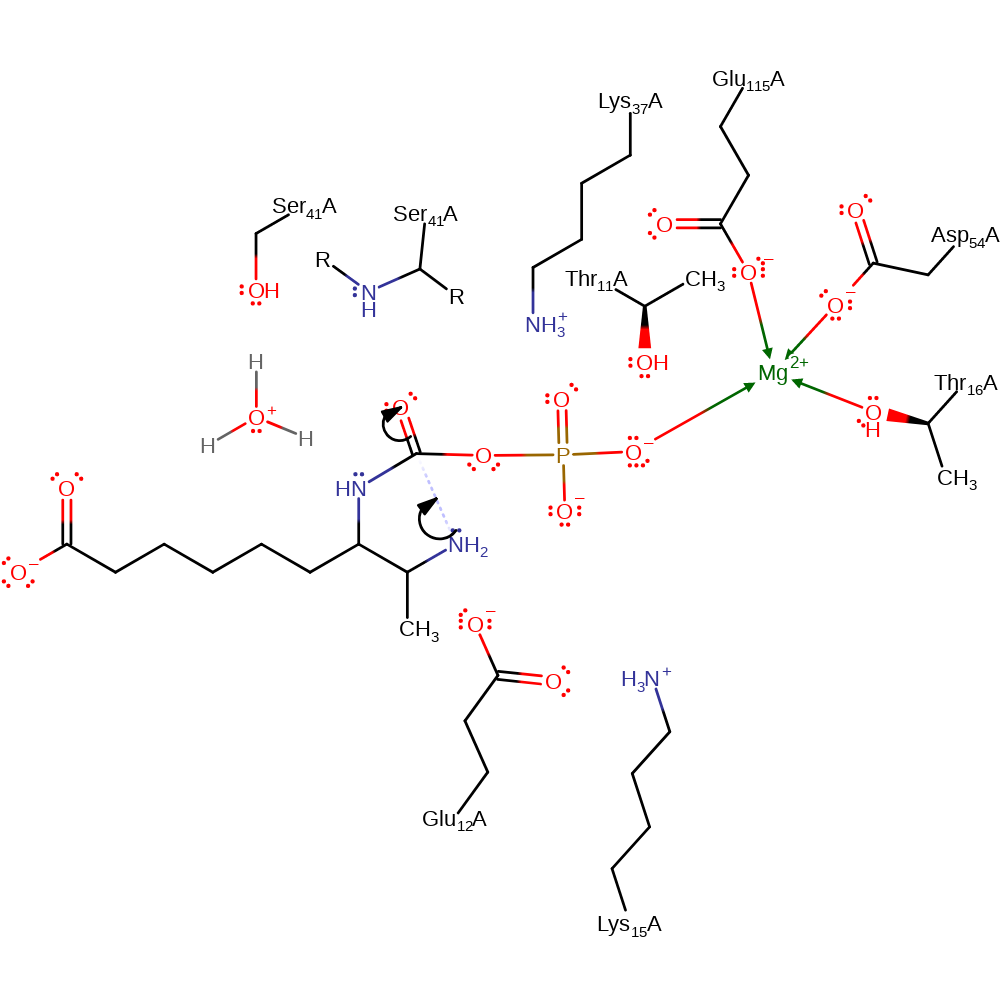
Step 3. The newly attached phosphate group deprotonates the terminal primary amine, which in turn acts as a nucleophile to attack the phosphorylated carbonyl carbon in an internal addition reaction. Lys37, Lys15 and the main chain amide of Ser41 all stabilise the intermediates.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys37A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser41A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys15A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Thr11A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser41A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu115A | metal ligand |
| Asp54A | metal ligand |
| Thr16A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: intramolecular nucleophilic addition, cyclisation, intermediate formation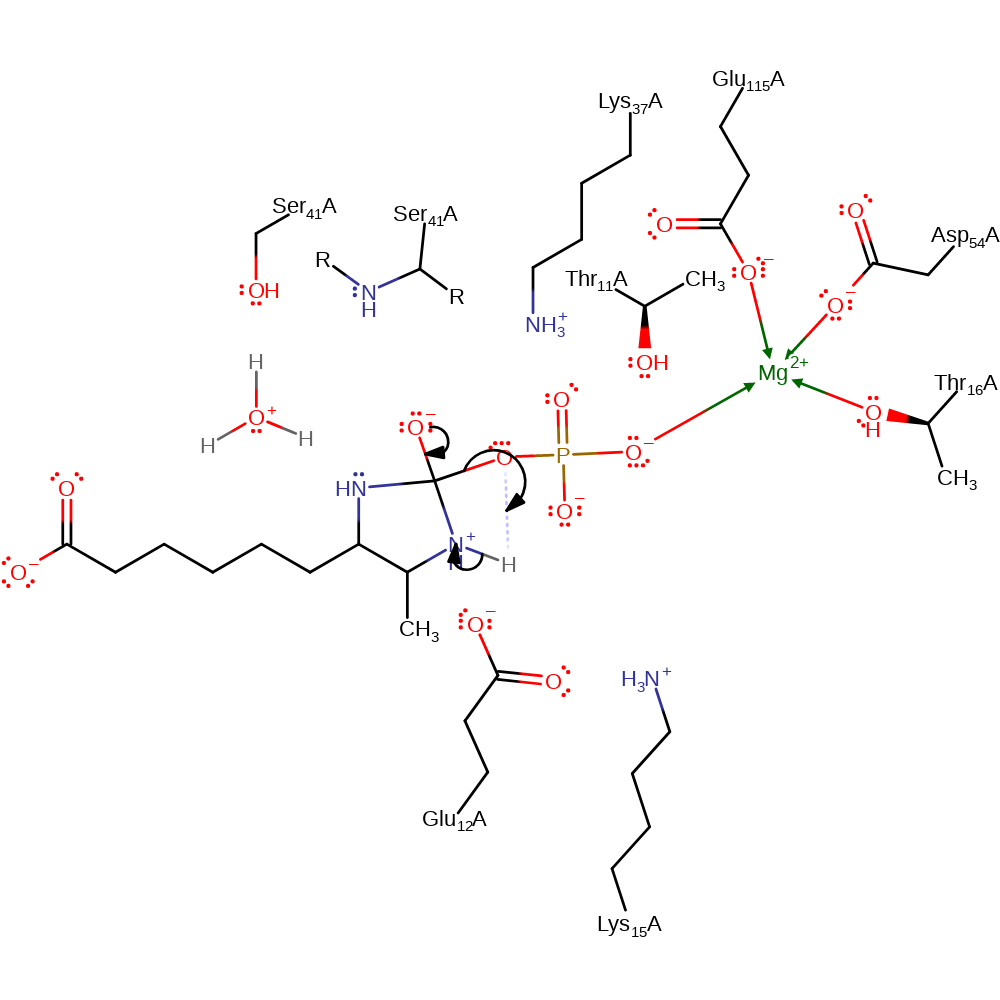
Step 4. The oxyanion formed re-forms the carbonyl group, cleaving the P-O bond in a conjugate base elimination reaction. The leaving phosphate group deprotonates the newly formed secondary amine. Lys15, Lys37 and the main chain amide of Ser41 all stabilise the intermediates.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys37A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys15A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser41A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Thr11A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser41A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu115A | metal ligand |
| Asp54A | metal ligand |
| Thr16A | metal ligand |







 Download:
Download: