Amidophosphoribosyltransferase
Glutamine phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amido transferase (GPATase) catalyses the transfer of the glutamine amide nitrogen to phosphoribosylpyrophosphate to generate phosphoribosylamine, pyrophosphate and glutamate. The enzyme is a member of a family of proteins which utilise the amide nitrogen of glutamate for the biosynthesis of amino acids, nucleotides, amino sugars and coenzymes. The coupling of phosphoribosyl transferase and glutaminase actities in an enzyme is not frequently seen but required for de novo purine synthesis.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P0AG16
 (2.4.2.14)
(2.4.2.14)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1ecf
- ESCHERICHIA COLI GLUTAMINE PHOSPHORIBOSYLPYROPHOSPHATE (PRPP) AMIDOTRANSFERASE
(2.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.60.20.10
 (see all for 1ecf)
(see all for 1ecf)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.4.2.14)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The enzyme is described as complex; its reaction is catyalysed as two half reactions, each occurring at separate catalytic sites along a single polypeptide chain. The two sites are highly coupled, facilitating the transfer of NH3 between them. The N terminal domain is a member of the Ntn hydrolase family and catalyses the hydrolysis of glutamine to glutamate and ammonia, while the C terminal domain, the ammonia acceptor domain, a member of the phophoribosyltransferase (PRTase) family is responsible for the coupling of ammonia to phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP). The PRTase active site is described as non classical, since no catalytic residues have been identified. However, it has been suggested by analogy with a homologue mechanism that the main function of the enzyme is not to promote catalysis, but rather to bring the reactants together appropriately and preventing unwanted side reactions.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1ecf) | ||
| Cys2 | Cys1A | The side chain sulphur acts as a nucleophile towards the glutamine substrate, forming a thioester intermediate and a proton donor towards the leaving group, forming ammonia. A binding pocket recognises glutamine specifically and orientates the substrate so that the amide group binds with carbonyl group located in the oxyanion hole, its carbon atom aligned for attack from the sulphur and the departing NH2 group close enough to the residue to receive a proton and depart as NH3. | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Gly103 (main-N), Asn102 | Gly102A (main-N), Asn101A | The residue forms an oxyanion hole in the active site pocket, stabilising the anionic thioester intermediate. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys2 (N-term) | Cys1A (N-term) | The N-terminus of the protein acts as a general acid/base. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Gly28 (main-C) | Gly27A (main-C) | Stabilises and activates the N-terminus of Cys1. | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr259 | Tyr258A | Stabilises and activates the substrate in the PRTase domain. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton relay, enzyme-substrate complex formation, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, deamination, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, intermediate terminated, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, native state of enzyme regenerated, dephosphorylationReferences
- Smith JL (1998), Curr Opin Struct Biol, 8, 686-694. Glutamine PRPP amidotransferase: snapshots of an enzyme in action. DOI:10.1016/s0959-440x(98)80087-0. PMID:9914248.
- Hove-Jensen B et al. (2017), Microbiol Mol Biol Rev, 81,Phosphoribosyl Diphosphate (PRPP): Biosynthesis, Enzymology, Utilization, and Metabolic Significance. DOI:10.1128/MMBR.00040-16. PMID:28031352.
- Muchmore CR et al. (1998), Protein Sci, 7, 39-51. Crystal structure of glutamine phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase fromEscherichia coli. DOI:10.1002/pro.5560070104. PMID:9514258.

Step 1. Reaction occurs in the glutaminase domain (CATH code 3.60.20.10). The glutamine will only bind if the 5-phospho-alpha-D-ribose-1-diphosphate is bound first [PMID:9914248]. The N-terminus of Cys1 deprotonates the thiol group of Cys1, which attacks the amino carbon in a nucleophilic addition.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn101A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys1A (N-term) | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Gly102A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly27A (main-C) | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys1A | nucleophile |
| Cys1A (N-term) | proton acceptor |
| Cys1A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton relay, enzyme-substrate complex formation, overall reactant used, intermediate formation
Step 2. The oxyanion initiates an elimination that cleaves ammonia from the bound L-Glutamine substrate. Ammonia deprotonates the N-terminus of Cys1. The ammonia formed here goes onto the next domain via an intramolecular channel.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn101A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys1A (N-term) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly102A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly27A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys1A | covalently attached |
| Cys1A (N-term) | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, proton relay, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, deamination, intermediate collapse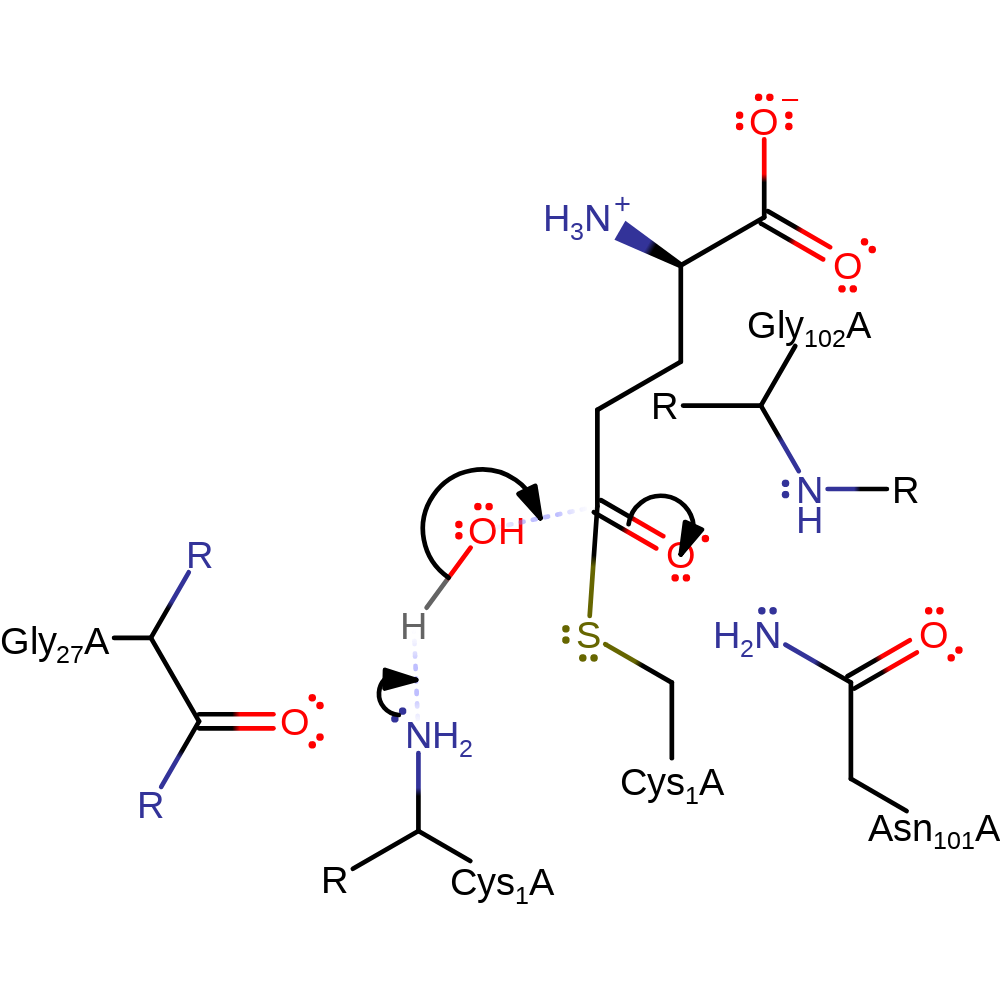
Step 3. The N-terminus of Cys1 deprotonates water, which attacks the carbonyl carbon of the covalently bound intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn101A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys1A (N-term) | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly102A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly27A (main-C) | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys1A | covalently attached |
| Cys1A (N-term) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, proton relay, intermediate formation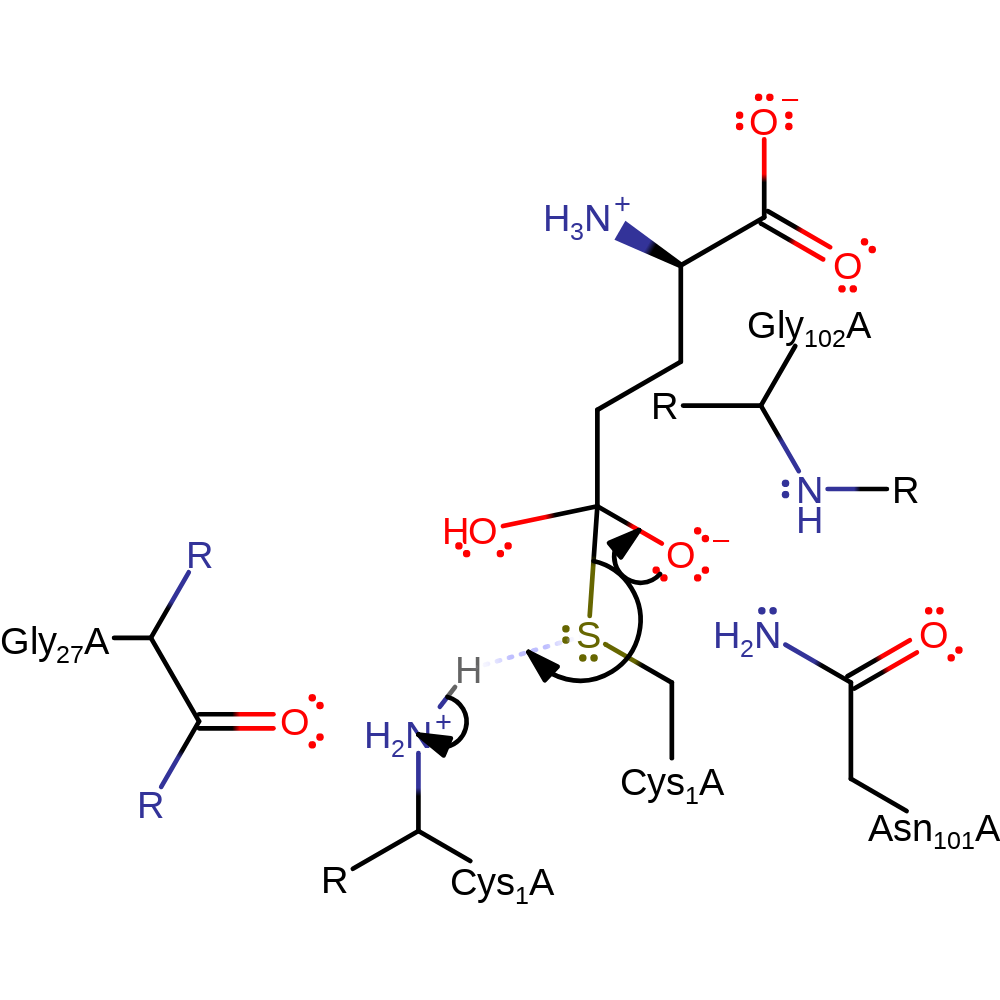
Step 4. The oxyanion initiates an elimination that cleaves the C-S bond, the thiolate of Cys1 deprotonates the N-terminus of Cys1
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn101A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys1A (N-term) | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Gly102A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Gly27A (main-C) | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys1A | nucleofuge, proton acceptor |
| Cys1A (N-term) | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, intermediate terminated, proton relay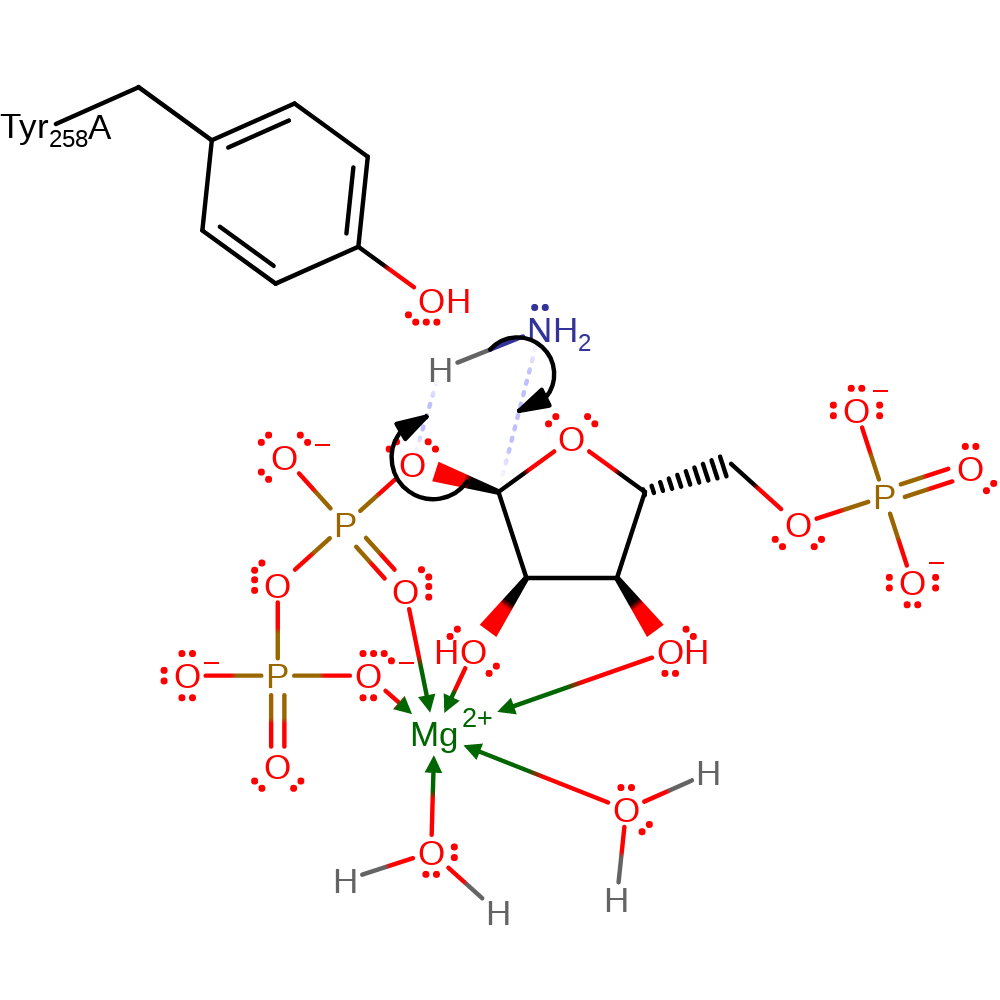
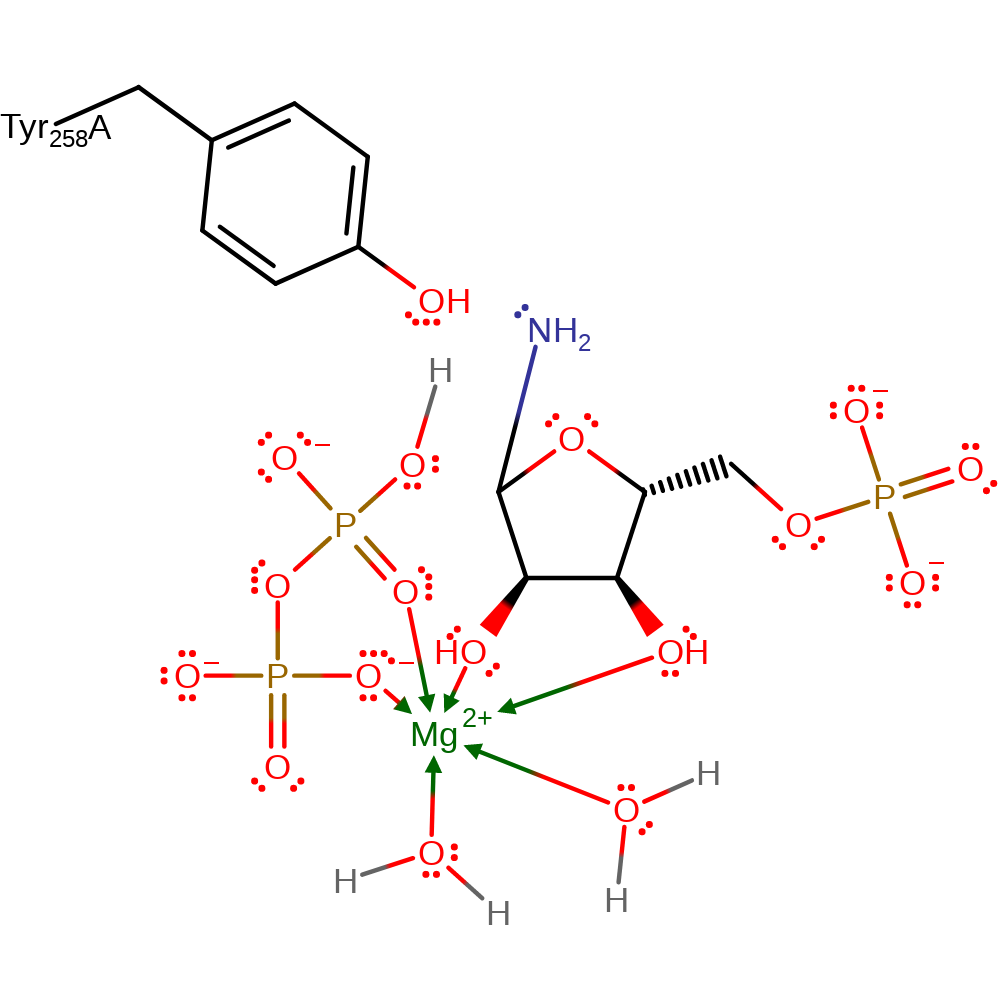
Step 5. Reaction occurs in the PRTase Domain. The conformation of the enzyme-bound Mn-cPRPP for catalysis as it favours the formation of a tri- or pentavalent intermediate with some double bond character in the ribose C1-O4 bond. . The step is described as an in-line displacement in which ammonia attacks the C1 of the 5-Phospho-alpha-D-ribose-1-diphosphate substrate in a nucleophilic substitution. The product pyrophosphate deprotonates the newly attached ammonia. However, it is unclear whether the intermediate is actually a transition state. There are no residues that are essential for catalytic activity, however the Tyr258 is probably stabilising [PMID:9914248].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr258A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |

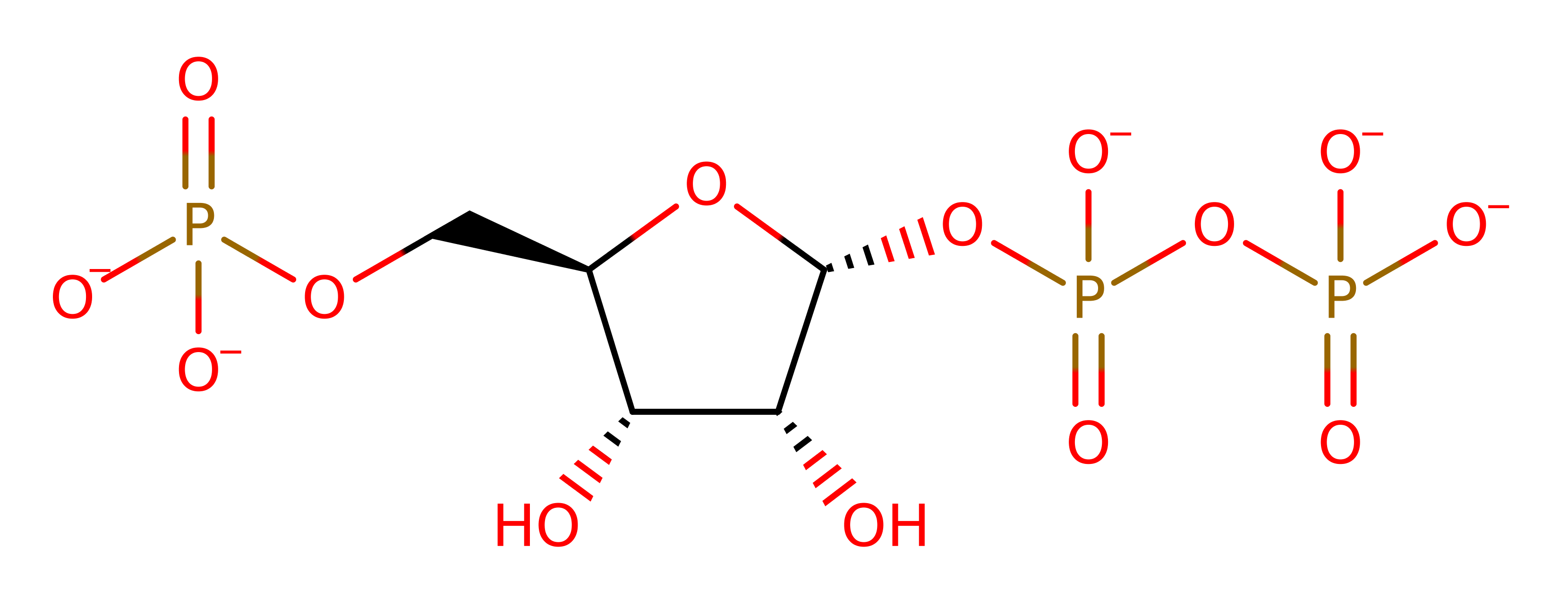




 Download:
Download: