Long-chain-fatty-acid-CoA ligase
Long chain fatty acid coenzyme-A synthetase (LC-FACS) participates in the first reaction step of long chain fatty acid degradation. These enzymes act on a wide range of long-chain saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, but the enzymes from different tissues and species show some variation in specificity. For example, the liver enzyme acts on acids from C6 to C20, that from brain shows high activity up to C24, and the enzyme from Thermus thermophilus acts on C12 to C22 fatty acids. LC-FACS catalyses the conversion of long chain fatty acids into fatty-acyl-CoA, creating AMP and pyrophosphate as bi-products. LC-FACS is responsible for physiological regulation of cellular functions, as well as fatty acid degradation.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q5SKN9
 (6.2.1.3)
(6.2.1.3)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Thermus thermophilus HB8 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1v25
- Crystal structure of tt0168 from Thermus thermophilus HB8
(2.3 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.12780
 3.30.300.310
3.30.300.310  (see all for 1v25)
(see all for 1v25)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:6.2.1.3)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Trp 444 hydrogen bonds to the alpha-phosphorus atom, making the alpha-phosphorus electron deficient, and a better electrophile. This is helped by the electrostatic interaction of Mg(II). The carbonyl oxygen of the fatty acid nucleophilically attacks the alpha-phosphorus atom, forming a negatively charged, penta-coordinated intermediate. This intermediate is stabilised through interactions between the O1A atom of the substrate and the indole ring of Trp 444. As the intermediate collapses, the scissile P-O bond is broken, resulting in a fatty-acyl-AMP, and a pyrophosphate leaving group.
Lys 439 hydrogen bonds to the carbonyl oxygen atom of the fatty-acyl-AMP, and the O1A atom of the alpha-phosphorus, generating an electron deficient carbonyl carbon, making it more electrophilic. The S atom of CoA nucleophilically attacks the fatty-acyl-AMP carbonyl carbon, breaking the C-O ester bond. This forms the fatty-acyl-CoA product, and a negatively charged AMP, which is stabilised by Lys 439.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1v25) | ||
| Trp444 | Trp444A | Acts to make the alpha-phosphorus atom more electrophilic. stabilises the negatively charged intermediate. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys439 | Lys439A | Acts to make the carbonyl carbon atom of fatty-acyl-AMP more electrophilic. Also stabilises the negatively charged AMP leaving group. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr184, Glu328 | Thr184A, Glu328A | Forms part of the magnesium binding site. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic addition, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transferReferences
- Hisanaga Y et al. (2004), J Biol Chem, 279, 31717-31726. Structural Basis of the Substrate-specific Two-step Catalysis of Long Chain Fatty Acyl-CoA Synthetase Dimer. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m400100200. PMID:15145952.
- Soupene E et al. (2008), Exp Biol Med (Maywood), 233, 507-521. Mammalian Long-Chain Acyl-CoA Synthetases. DOI:10.3181/0710-mr-287. PMID:18375835.
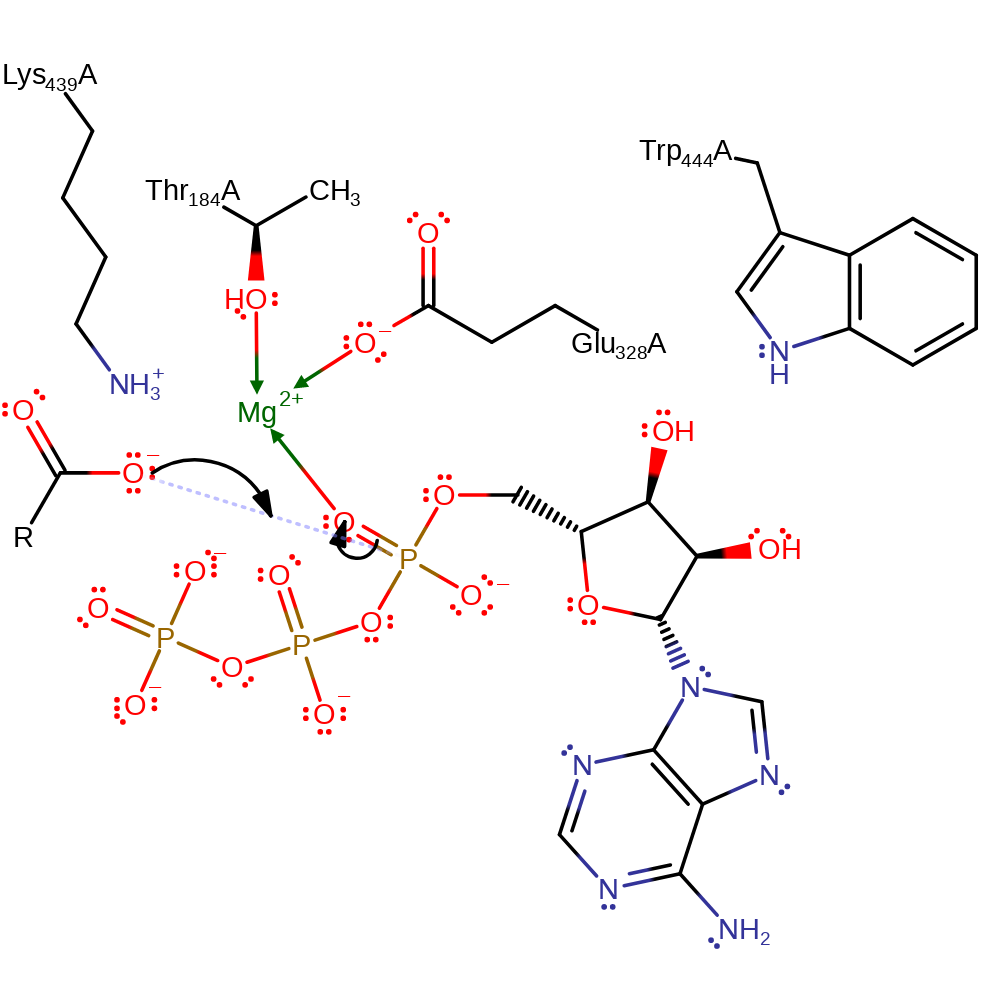
Step 1. The carboxylate of the long chain carboxylate acts as a nucleophile and attacks the alpha-phosphate of ATP in an addition reaction to form a pentavalent phosphate intermediate. Mg(II), Trp444 and Lys439 stabilise the intermediates formed.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys439A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp444A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu328A | metal ligand |
| Thr184A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition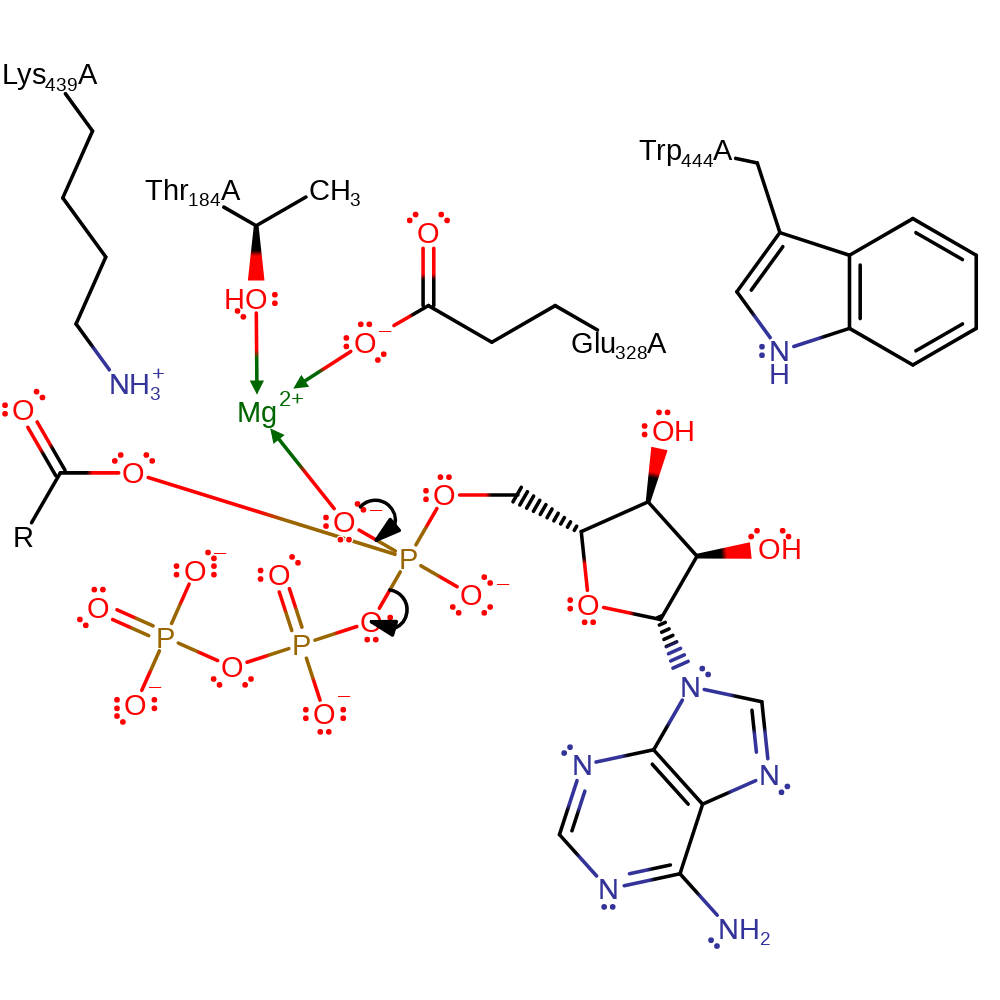
Step 2. The pentavalent phosphate intermediate breaks down in a conjugate base elimination, liberating pyrophosphate. Mg(II), Trp444 and Lys439 stabilise the intermediates formed.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys439A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp444A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu328A | metal ligand |
| Thr184A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base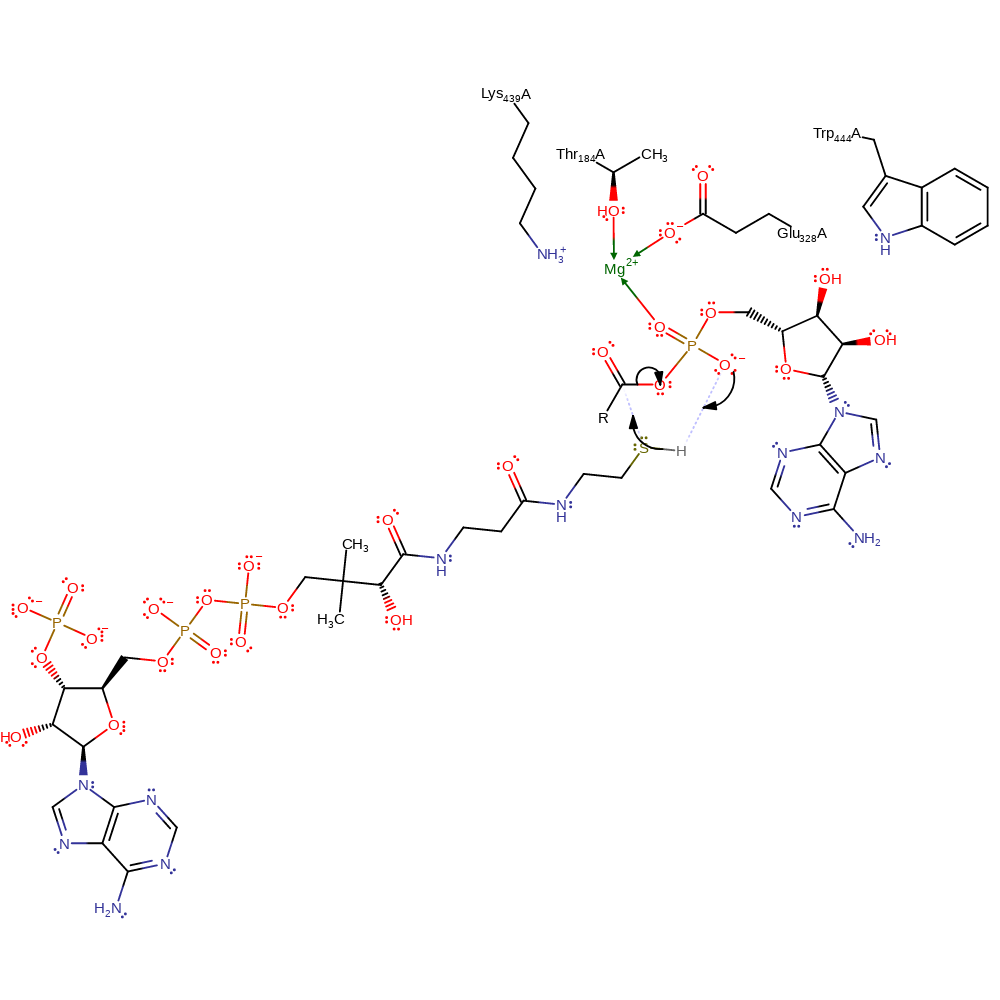
Step 3. CoA (probably activated by the phosphate group) acts as a nucleophile which attacks the carbonyl group of the intermediate complex in a substitution reaction, liberating AMP. Mg(II), Trp444 and Lys439 stabilise the intermediates formed.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys439A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp444A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu328A | metal ligand |
| Thr184A | metal ligand |






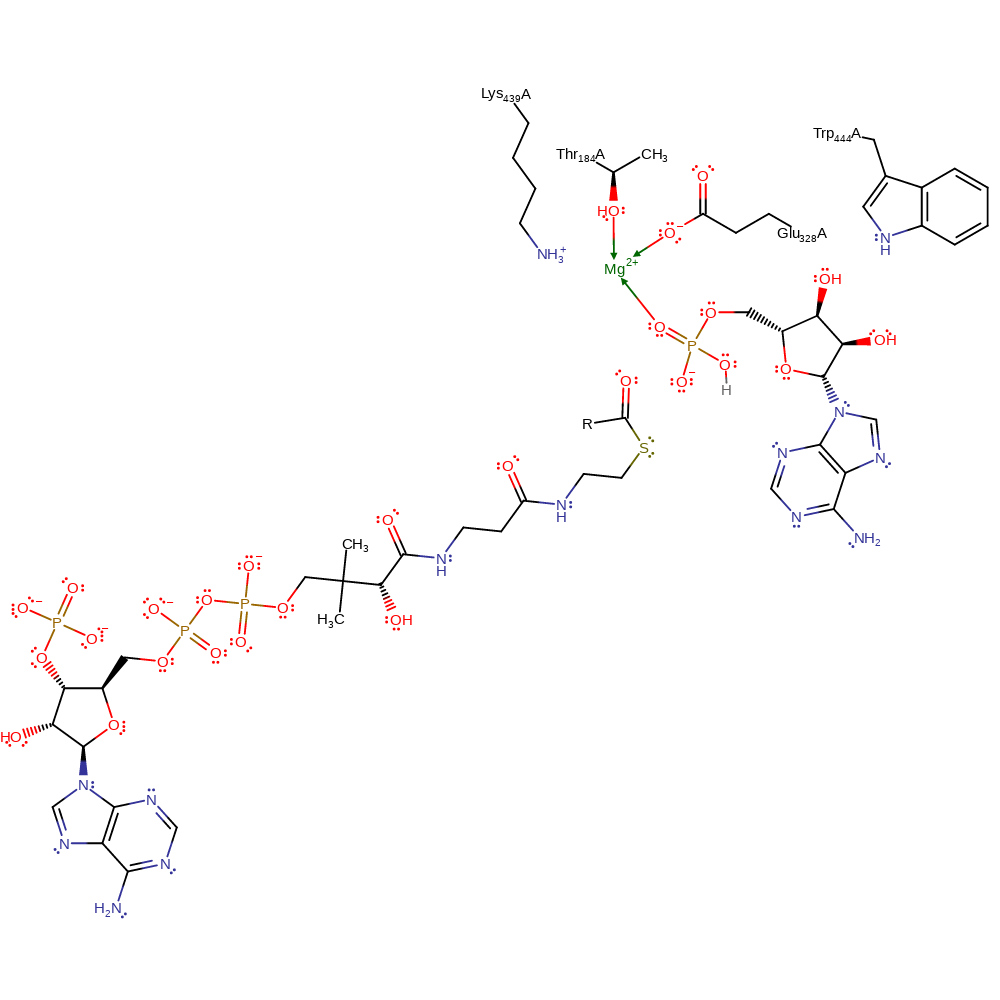 Download:
Download: