Tyrosine-tRNA ligase
Tyrosine-tRNA ligases (TyrRS; also known as Tyrosyl-tRNA synthetases, EC:6.1.1.1) are widely distributed, being found in archaea, bacteria and eukaryotes. TyrRS is a homodimer which attaches Tyr to the appropriate tRNA. TyrRS is a class I tRNA synthetases, so it aminoacylates the 2'-OH of the nucleotide at the 3' end of the tRNA.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P00952
 (6.1.1.1)
(6.1.1.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Geobacillus stearothermophilus (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
2ts1
- STRUCTURE OF TYROSYL-T/RNA SYNTHETASE REFINED AT 2.3 ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION. INTERACTION OF THE ENZYME WITH THE TYROSYL ADENYLATE INTERMEDIATE
(2.3 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.240.10
 3.40.50.620
3.40.50.620  (see all for 2ts1)
(see all for 2ts1)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:6.1.1.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Substrate binding induces a conformational change that brings the residues Lys82 and Arg86 into catalytic range [PMID:3284584]. The carboxylate group of the substrate L-tyrosine acts as a nucleophile and attacks the alpha-phosphate of the ATP in a substitution reaction that liberates pyrophosphate. The phosphate of the tyrosine-AMP complex deprotonates the OH of the ribose ring, which acts as a nucleophile to attack the carbonyl group of the tyrosine in the tyrosine-AMP complex in a substitution reaction, liberating AMP.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (2ts1) | ||
| Thr234 | Thr234A | Helps to stabilise the negatively charged intermediates and transition states formed during the course of the reaction. Also affects the steric outcome of the reaction. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His48, Asp194, Lys230, Lys233, Gln173, Thr40, His45, Lys82, Arg86 | His48A, Asp194A, Lys230A, Lys233A, Gln173A, Thr40A, His45A, Lys82A, Arg86A | Act to stabilise the negatively charged intermediates and transition states formed during the course of the reaction. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, overall product formed, proton transfer, intermediate terminatedReferences
- Fersht AR et al. (1988), Biochemistry, 27, 1581-1587. Reconstruction by site-directed mutagenesis of the transition state for the activation of tyrosine by the tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase: a mobile loop envelopes the transition state in an induced-fit mechanism. DOI:10.1021/bi00405a028. PMID:3284584.
- Caprara MG et al. (2001), J Mol Biol, 308, 165-190. Interaction of the Neurospora crassa mitochondrial tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase (CYT-18 protein) with the group I intron P4-P6 domain. thermodynamic analysis and the role of metal ions1 1Edited by D. E. Draper. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2001.4581. PMID:11327760.
- Xin Y et al. (2000), J Mol Biol, 303, 299-310. Stabilization of the transition state for the transfer of tyrosine to tRNATyr by tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2000.4126. PMID:11023794.
- Xin Y et al. (2000), J Mol Biol, 303, 287-298. Correlating amino acid conservation with function in tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2000.4125. PMID:11023793.
- First EA et al. (1993), Biochemistry, 32, 13644-13650. Involvement of threonine 234 in catalysis of tyrosyl adenylate formation by tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase. DOI:10.1021/bi00212a032. PMID:8257697.

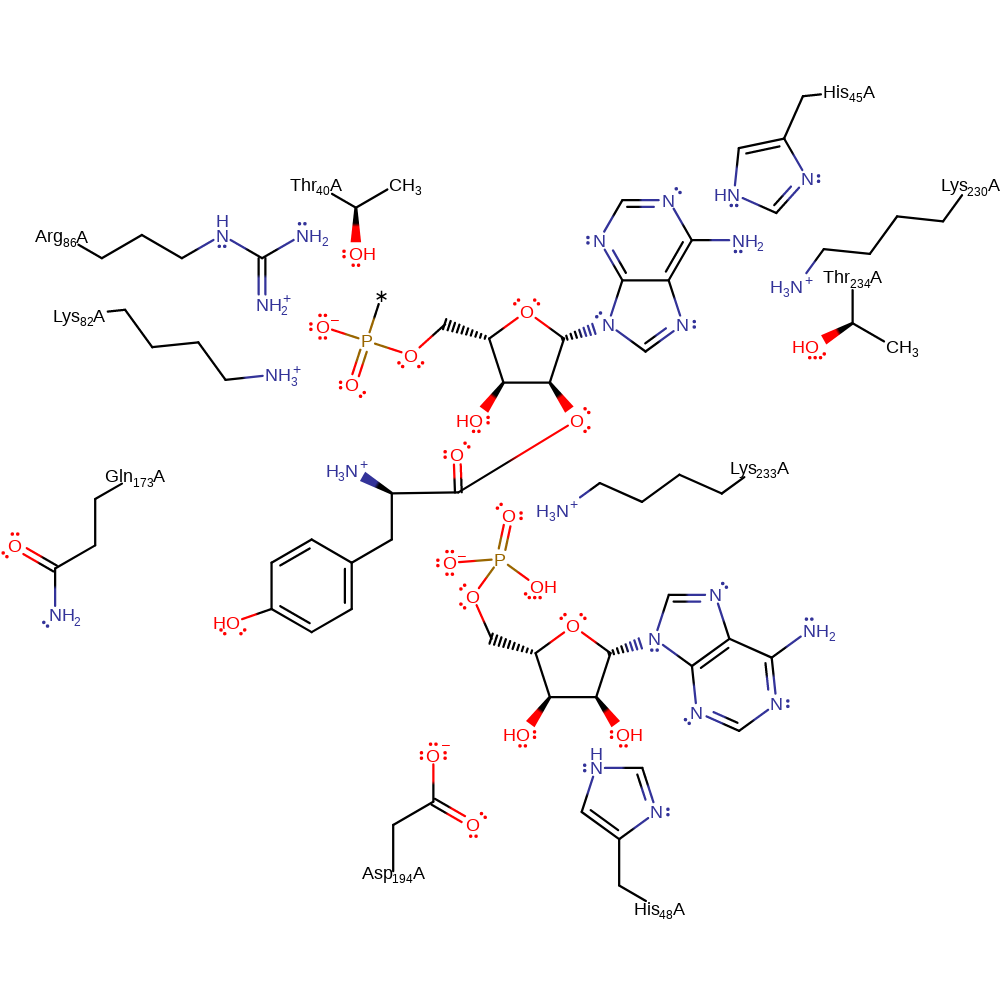
Step 1. The carboxylate group of the substrate L-tyrosine acts as a nucleophile and attacks the alpha-phosphate of the ATP in a substitution reaction that liberates pyrophosphate. Mg(II) and all catalytic residues stabilise the intermediates formed. Thr234 also affects the steric outcome of the reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr40A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His45A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His48A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys82A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg86A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln173A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys230A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys233A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr234A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, metal ligand, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp194A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, overall product formed
Step 2. The phosphate of the tyrosine-AMP complex deprotonates the OH of the ribose ring, which acts as a nucleophile to attack the carbonyl group of the tyrosine in the tyrosine-AMP complex in a substitution reaction, liberating AMP. Mg(II), Thr40, His48, Lys82, Arg86 and Gln173 all stabilise the intermediates formed.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr40A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His48A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys82A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg86A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln173A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp194A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |







 Download:
Download: