Sulfite oxidase
Sulfite oxidase (SO) catalyses the terminal reaction in the oxidative degradation of the sulfur-containing amino acids cysteine and methionine specifically the oxidation of sulfite to sulfate by the transfer of an oxygen to the lone pair of electrons on the substrate. It is a member of the molybdopterin oxidoreductase family of proteins that contain a single pterin cofactor ligated to Mo(VI) and two oxo ligands. SO also contains a heme b molecule which is part of the electron transfer pathway from the molybdenum centre to the final electron acceptor (in this case ferrocytochrome c).
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P07850
 (1.8.3.1)
(1.8.3.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Gallus gallus (Chicken)

- PDB
-
1sox
- SULFITE OXIDASE FROM CHICKEN LIVER
(1.9 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.90.420.10
 3.10.120.10
3.10.120.10  (see all for 1sox)
(see all for 1sox)
- Cofactors
- Heme b (1), Moo2-molybdopterin cofactor(2−) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
This protein requires both Heme and a molybdenum (VI) centre to be catalytically active. The sulfite substrate initiates a nucleophilic attack on one of the oxo ligands of the Mo(VI) centre, reducing the Mo to +4. This forms the sulfate product, which is displaced from the active site by water. Deprotonation of the new water ligand initiates the transfer of a single electron from the Mo centre to heme and then to an external electron acceptor. This occurs twice to regenerate the oxo ligand and Mo(VI) centre.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1sox) | ||
| Cys185 | Cys185A | Forms part of the Molybdenum binding site. | metal ligand |
| His40, His65 | His40A, His65A | Forms part of the heme binding site as the axial ligands to the iron ion. Not shown in the reaction diagrams for clarity. | metal ligand |
| Arg138 | Arg138A | Prevents formation of a blocked non-catalytic form of the enzyme. | steric role |
| Tyr322 | Tyr322A | Acts as a general acid/base as part of a proton relay chain from bulk solvent to the active site. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, cofactor used, intermediate formation, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, coordination to a metal ion, decoordination from a metal ion, overall product formed, electron transfer, proton transfer, proton relay, electron relay, native state of cofactor regenerated, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Feng C et al. (2003), J Biol Chem, 278, 2913-2920. Role of Conserved Tyrosine 343 in Intramolecular Electron Transfer in Human Sulfite Oxidase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m210374200. PMID:12424234.
- Caldararu O et al. (2018), Sci Rep, 8, 4684-. QM/MM study of the reaction mechanism of sulfite oxidase. DOI:10.1038/s41598-018-22751-6. PMID:29549261.
- Davis AC et al. (2014), Metallomics, 6, 1664-1670. Kinetic results for mutations of conserved residues H304 and R309 of human sulfite oxidase point to mechanistic complexities. DOI:10.1039/c4mt00099d. PMID:24968320.
- van Severen MC et al. (2014), J Biol Inorg Chem, 19, 1165-1179. A quantum-mechanical study of the reaction mechanism of sulfite oxidase. DOI:10.1007/s00775-014-1172-z. PMID:24957901.
- Davis AC et al. (2013), Dalton Trans, 42, 3043-3049. Effects of mutating aromatic surface residues of the heme domain of human sulfite oxidase on its heme midpoint potential, intramolecular electron transfer, and steady-state kinetics. DOI:10.1039/c2dt31508d. PMID:22975842.
- Klein EL et al. (2012), Inorg Chem, 51, 1408-1418. Identity of the exchangeable sulfur-containing ligand at the Mo(V) center of R160Q human sulfite oxidase. DOI:10.1021/ic201643t. PMID:22225516.
- Astashkin AV et al. (2012), J Phys Chem B, 116, 1942-1950. Determination of the distance between the Mo(V) and Fe(III) heme centers of wild type human sulfite oxidase by pulsed EPR spectroscopy. DOI:10.1021/jp210578f. PMID:22229742.
- Enemark JH et al. (2011), Faraday Discuss, 148, 249-67; discussion 299. Implications for the mechanism of sulfite oxidizing enzymes from pulsed EPR spectroscopy and DFT calculations for "difficult" nuclei. PMID:21322488.
- Johnson-Winters K et al. (2010), Biochemistry, 49, 7242-7254. Elucidating the catalytic mechanism of sulfite oxidizing enzymes using structural, spectroscopic, and kinetic analyses. DOI:10.1021/bi1008485. PMID:20666399.
- Qiu JA et al. (2010), Biochemistry, 49, 3989-4000. The structures of the C185S and C185A mutants of sulfite oxidase reveal rearrangement of the active site. DOI:10.1021/bi1001954. PMID:20356030.
- Emesh S et al. (2009), Biochemistry, 48, 2156-2163. Intramolecular electron transfer in sulfite-oxidizing enzymes: elucidating the role of a conserved active site arginine. DOI:10.1021/bi801553q. PMID:19226119.
- Astashkin AV et al. (2008), J Am Chem Soc, 130, 8471-8480. Structural Studies of the Molybdenum Center of the Pathogenic R160Q Mutant of Human Sulfite Oxidase by Pulsed EPR Spectroscopy and17O and33S Labeling. DOI:10.1021/ja801406f. PMID:18529001.
- Raitsimring AM et al. (2008), Inorganica Chim Acta, 361, 941-946. Studies of the Mo(V) center of the Y343F mutant of human sulfite oxidase by variable frequency pulsed EPR spectroscopy. DOI:10.1016/j.ica.2007.05.023. PMID:18496596.
- Neumann M et al. (2008), FEBS J, 275, 5678-5689. Heavy metal ions inhibit molybdoenzyme activity by binding to the dithiolene moiety of molybdopterin in Escherichia coli. DOI:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06694.x. PMID:18959753.
- Karakas E et al. (2005), J Biol Chem, 280, 33506-33515. Structural insights into sulfite oxidase deficiency. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M505035200. PMID:16048997.
- Wilson HL et al. (2004), J Biol Chem, 279, 15105-15113. The Role of Tyrosine 343 in Substrate Binding and Catalysis by Human Sulfite Oxidase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m314288200. PMID:14729666.
- Feng C et al. (2003), Biochemistry, 42, 12235-12242. Essential Role of Conserved Arginine 160 in Intramolecular Electron Transfer in Human Sulfite Oxidase†. DOI:10.1021/bi0350194. PMID:14567685.
- Rudolph MJ et al. (2003), Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, 59, 1183-1191. The 1.2 Å structure of the human sulfite oxidase cytochromeb5domain. DOI:10.1107/s0907444903009934. PMID:12832761.
- Kisker C et al. (1997), Annu Rev Biochem, 66, 233-267. MOLYBDENUM-COFACTOR–CONTAINING ENZYMES:Structure and Mechanism. DOI:10.1146/annurev.biochem.66.1.233. PMID:9242907.
- Kisker C et al. (1997), Cell, 91, 973-983. Molecular Basis of Sulfite Oxidase Deficiency from the Structure of Sulfite Oxidase. DOI:10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80488-2. PMID:9428520.
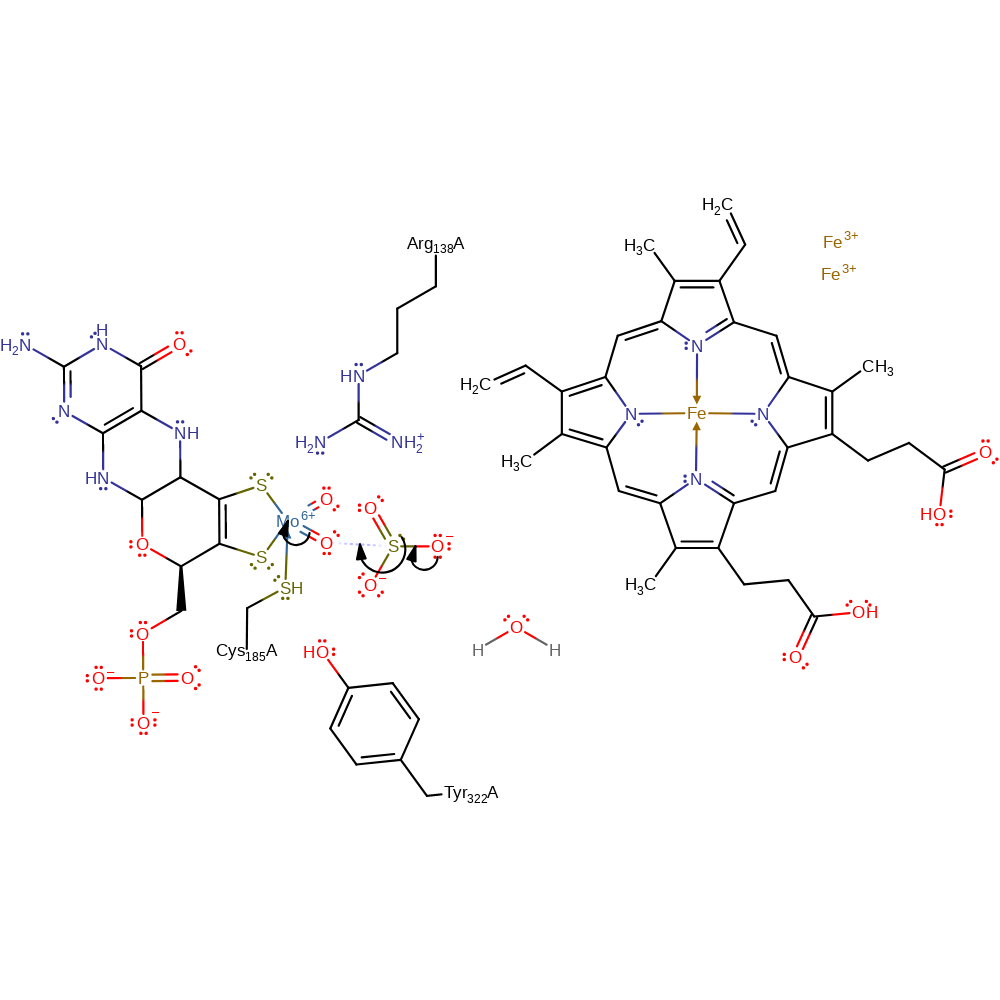
Step 1. Sulfite initiates a nucleophilic attack upon one of the oxo groups coordinated to the Mo(VI) centre in an addition reaction, resulting in a two electron reduction of the centre to Mo(IV). It seems very likely that only one of the two oxygen ligands is the catalytically labile oxygen, whereas the other oxygen cannot be attacked owing to steric hindrance in the active site of the enzyme [PMID:9242907].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg138A | steric role |
| Cys185A | metal ligand |
| His40A | metal ligand |
| His65A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, cofactor used, intermediate formationCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys185A | metal ligand |
| His40A | metal ligand |
| His65A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, coordination to a metal ion, decoordination from a metal ion, intermediate formation, overall product formed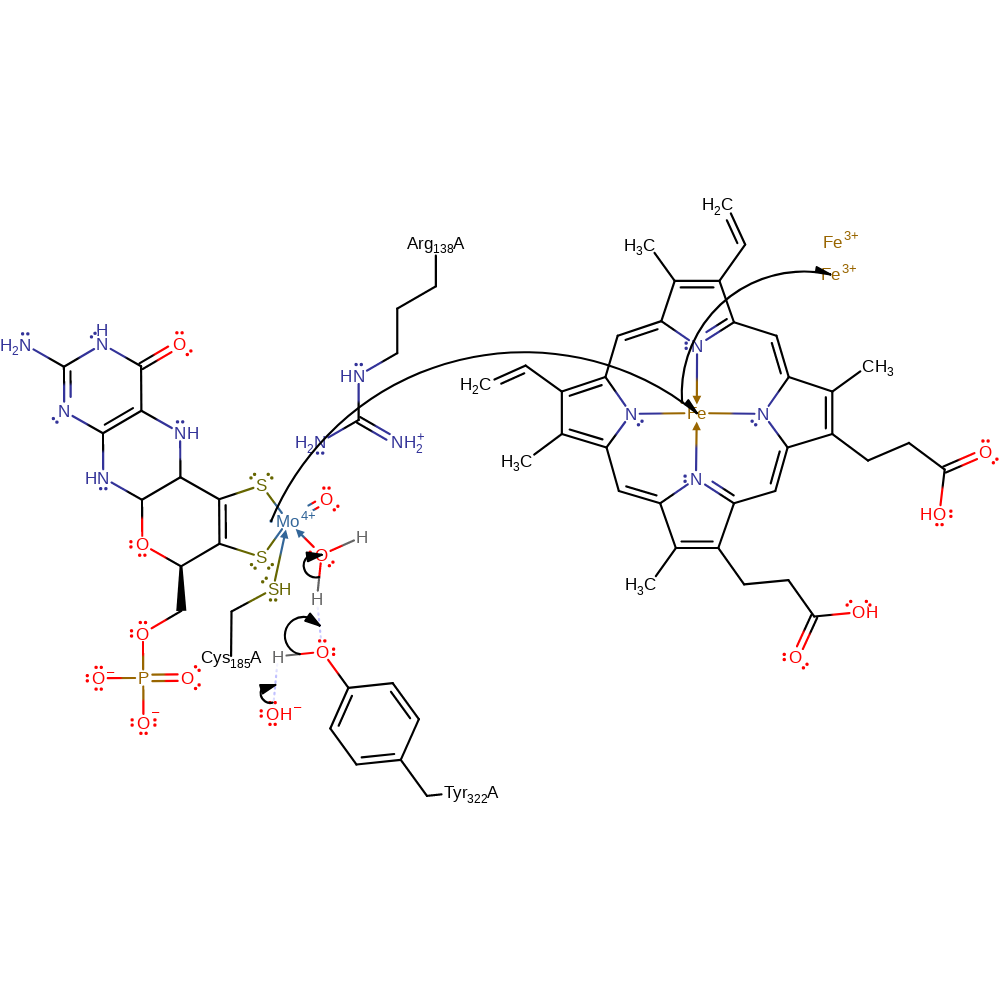
Step 3. Water deprotonates Tyr322, which deprotonates the Mo-bound water causing a single electron to be transferred from the Mo(IV) centre to Haem and thence to ferricyrochrome C.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr322A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Cys185A | metal ligand |
| His40A | metal ligand |
| His65A | metal ligand |
| Tyr322A | proton donor, proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, overall product formed, proton relay, electron relay, cofactor used, native state of cofactor regenerated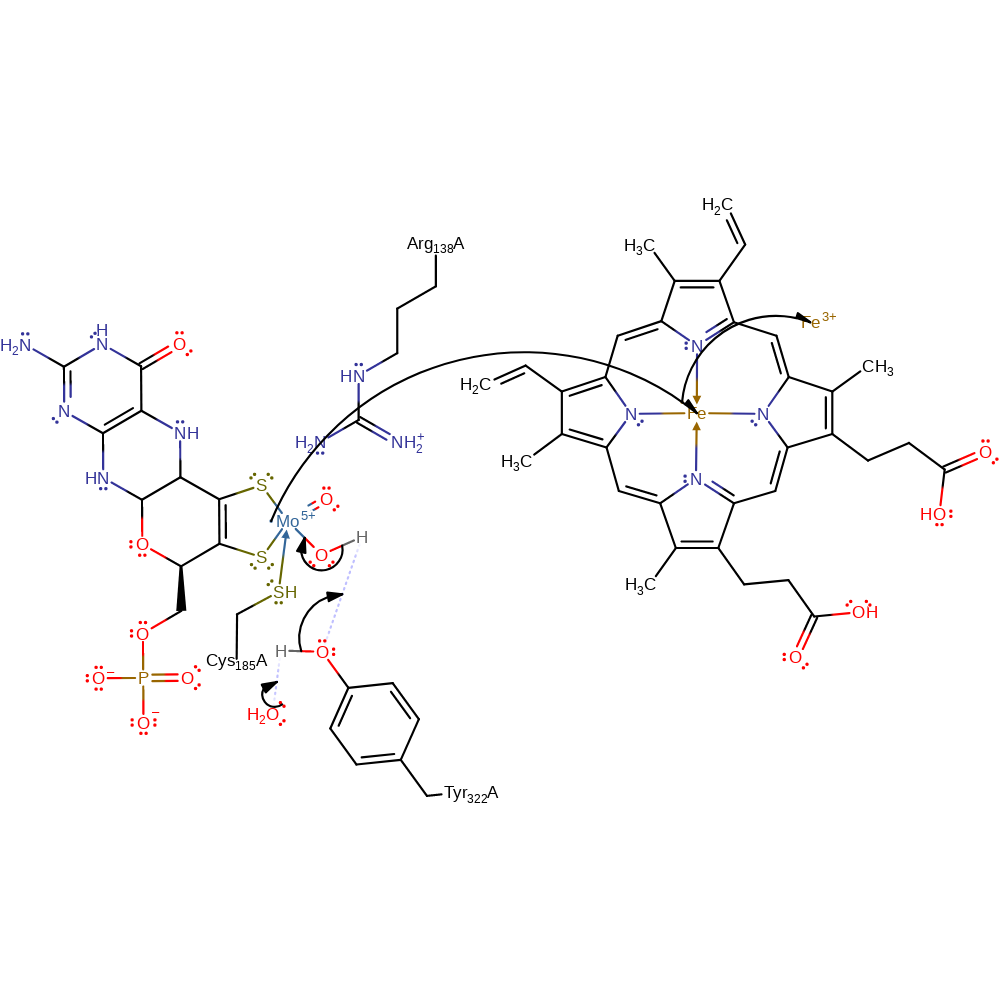
Step 4. Water deprotonates Tyr322, which deprotonates the Mo-bound hydroxide causing a single electron to be transferred from the Mo(V) centre to Haem and thence to ferricyrochrome C and regenerating the cofactor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr322A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Cys185A | metal ligand |
| His40A | metal ligand |
| His65A | metal ligand |
| Tyr322A | proton donor, proton acceptor |







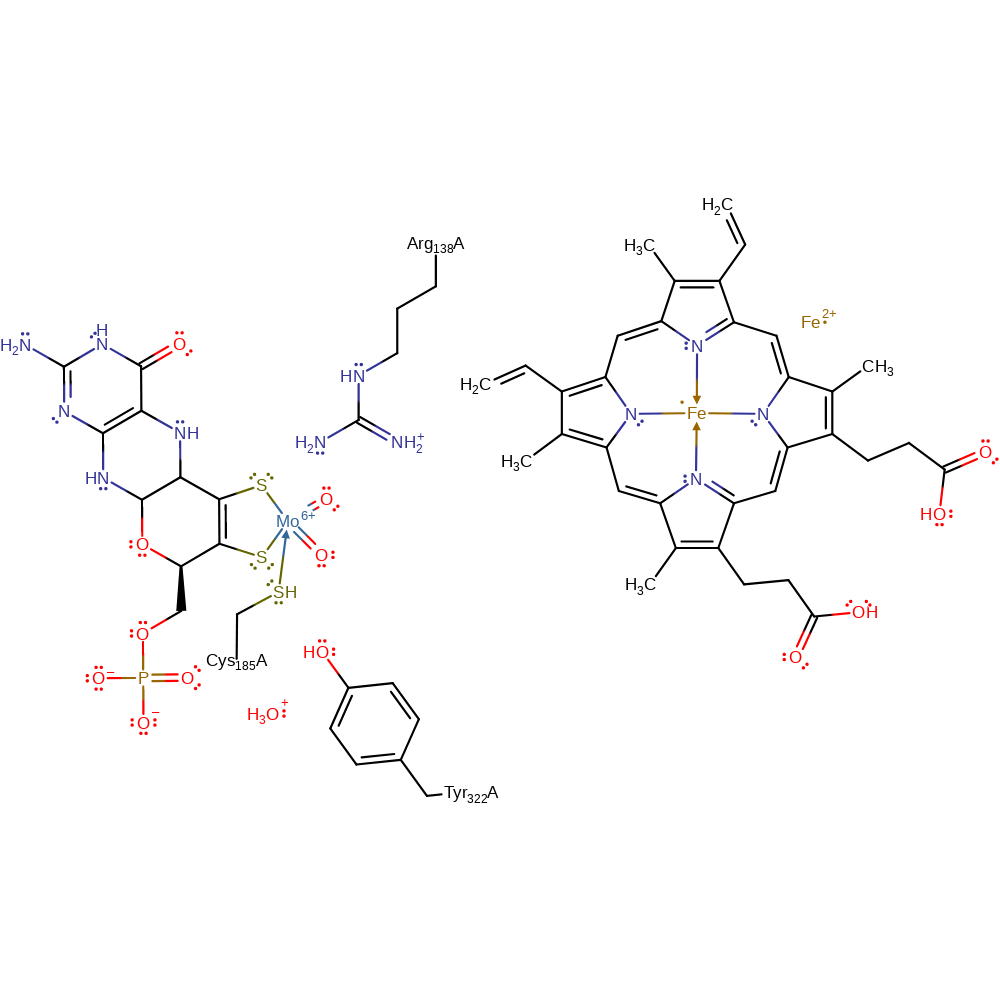 Download:
Download: