 |
PDBsum entry 5fol
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of the cryptosporidium muris cytosolic leucyl-tRNA synthetase editing domain complex with a post-transfer editing analogue of isoeucine (ile2aa)
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Leucyl-tRNA synthetase. Chain: a. Fragment: editing domain, unp residues 254-541. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Cryptosporidium muris. Organism_taxid: 441375. Strain: rn66. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008. Expression_system_variant: ril.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.77Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.198
|
R-free:
|
0.232
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
A.Palencia,R.J.Liu,M.Lukarska,J.Gut,A.Bougdour,B.Touquet,E.D.Wang, M.R.K.Alley,P.J.Rosenthal,M.A.Hakimi,S.Cusack
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
A.Palencia
et al.
(2016).
Cryptosporidium and Toxoplasma Parasites Are Inhibited by a Benzoxaborole Targeting Leucyl-tRNA Synthetase.
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
60,
5817-5827.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
24-Nov-15
|
Release date:
|
03-Aug-16
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
B6AA20
(B6AA20_CRYMR) -
leucine--tRNA ligase from Cryptosporidium muris (strain RN66)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
1128 a.a.
274 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.6.1.1.4
- leucine--tRNA ligase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
tRNA(Leu) + L-leucine + ATP = L-leucyl-tRNA(Leu) + AMP + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 tRNA(Leu)
tRNA(Leu)
|
+
|
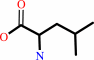 L-leucine
L-leucine
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
L-leucyl-tRNA(Leu)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 56.25% similarity
|
+
|
AMP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 55.56% similarity
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Antimicrob Agents Chemother
60:5817-5827
(2016)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Cryptosporidium and Toxoplasma Parasites Are Inhibited by a Benzoxaborole Targeting Leucyl-tRNA Synthetase.
|
|
A.Palencia,
R.J.Liu,
M.Lukarska,
J.Gut,
A.Bougdour,
B.Touquet,
E.D.Wang,
X.Li,
M.R.Alley,
Y.R.Freund,
P.J.Rosenthal,
M.A.Hakimi,
S.Cusack.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The apicomplexan parasites Cryptosporidium and Toxoplasma are serious threats to
human health. Cryptosporidiosis is a severe diarrheal disease in malnourished
children and immunocompromised individuals, with the only FDA-approved drug
treatment currently being nitazoxanide. The existing therapies for
toxoplasmosis, an important pathology in immunocompromised individuals and
pregnant women, also have serious limitations. With the aim of developing
alternative therapeutic options to address these health problems, we tested a
number of benzoxaboroles, boron-containing compounds shown to be active against
various infectious agents, for inhibition of the growth of Cryptosporidium
parasites in mammalian cells. A 3-aminomethyl benzoxaborole, AN6426, with
activity in the micromolar range and with activity comparable to that of
nitazoxanide, was identified and further characterized using biophysical
measurements of affinity and crystal structures of complexes with the editing
domain of Cryptosporidium leucyl-tRNA synthetase (LeuRS). The same compound was
shown to be active against Toxoplasma parasites, with the activity being
enhanced in the presence of norvaline, an amino acid that can be mischarged by
LeuRS. Our observations are consistent with AN6426 inhibiting protein synthesis
in both Cryptosporidium and Toxoplasma by forming a covalent adduct with
tRNA(Leu) in the LeuRS editing active site and suggest that further exploitation
of the benzoxaborole scaffold is a valid strategy to develop novel, much needed
antiparasitic agents.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

