 |
PDBsum entry 5dmx

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

 234 a.a.
234 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

 259 a.a.
259 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 276 a.a.
276 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 197 a.a.
197 a.a.
|
 |

|

|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Ligase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of d-alanine-d-alanine ligase from acinetobacter baumannii, space group p212121
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
D-alanine--d-alanine ligase. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f. Synonym: d-ala-d-ala ligase,d-alanylalanine synthetase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Acinetobacter baumannii acicu. Organism_taxid: 405416. Strain: acicu. Gene: ddl, acicu_03532. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.81Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.250
|
R-free:
|
0.293
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
K.H.Huynh,M.K.Hong,L.W.Kang
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
K.H.Huynh
et al.
(2015).
The crystal structure of the D-alanine-D-alanine ligase from Acinetobacter baumannii suggests a flexible conformational change in the central domain before nucleotide binding.
J Microbiol,
53,
776-782.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
09-Sep-15
|
Release date:
|
17-Aug-16
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
B2I1J3
(DDL_ACIBC) -
D-alanine--D-alanine ligase from Acinetobacter baumannii (strain ACICU)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
308 a.a.
234 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|

|

|
|
B2I1J3
(DDL_ACIBC) -
D-alanine--D-alanine ligase from Acinetobacter baumannii (strain ACICU)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
308 a.a.
259 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B, C, D, E, F:
E.C.6.3.2.4
- D-alanine--D-alanine ligase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Peptidoglycan Biosynthesis (Part 1)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
2 D-alanine + ATP = D-alanyl-D-alanine + ADP + phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
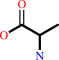 2
×
D-alanine
2
×
D-alanine
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
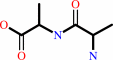 D-alanyl-D-alanine
D-alanyl-D-alanine
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Microbiol
53:776-782
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The crystal structure of the D-alanine-D-alanine ligase from Acinetobacter baumannii suggests a flexible conformational change in the central domain before nucleotide binding.
|
|
K.H.Huynh,
M.K.Hong,
C.Lee,
H.T.Tran,
S.H.Lee,
Y.J.Ahn,
S.S.Cha,
L.W.Kang.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Acinetobacter baumannii, which is emerging as a multidrug-resistant nosocomial
pathogen, causes a number of diseases, including pneumonia, bacteremia,
meningitis, and skin infections. With ATP hydrolysis, the D-alanine-D-alanine
ligase (DDL) catalyzes the synthesis of D-alanyl-D-alanine, which is an
essential component of bacterial peptidoglycan. In this study, we determined the
crystal structure of DDL from A. baumannii (AbDDL) at a resolution of 2.2 Å.
The asymmetric unit contained six protomers of AbDDL. Five protomers had a
closed conformation in the central domain, while one protomer had an open
conformation in the central domain. The central domain with an open conformation
did not interact with crystallographic symmetry-related protomers and the
conformational change of the central domain was not due to crystal packing. The
central domain of AbDDL can have an ensemble of the open and closed
conformations before the binding of substrate ATP. The conformational change of
the central domain is important for the catalytic activity and the detail
information will be useful for the development of inhibitors against AbDDL and
putative antibacterial agents against A. baumannii. The AbDDL structure was
compared with that of other DDLs that were in complex with potent inhibitors and
the catalytic activity of AbDDL was confirmed using enzyme kinetics assays.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

| | |

