 |
PDBsum entry 5cyg
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.4.2.3
- uridine phosphorylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
uridine + phosphate = alpha-D-ribose 1-phosphate + uracil
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 uridine
uridine
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
=
|
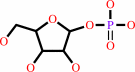 alpha-D-ribose 1-phosphate
alpha-D-ribose 1-phosphate
|
+
|
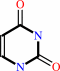 uracil
uracil
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochimie
125:12-22
(2016)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Analysis of two Schistosoma mansoni uridine phosphorylases isoforms suggests the emergence of a protein with a non-canonical function.
|
|
A.M.da Silva Neto,
J.R.Torini de Souza,
L.Romanello,
A.Cassago,
V.H.Serrão,
R.DeMarco,
J.Brandão-Neto,
R.C.Garratt,
H.D.Pereira.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Reports of Schistosoma mansoni strains resistant to praziquantel, the only
therapeutic strategy available for the treatment of schistosomiasis, have
motivated the scientific community towards the search for new possible
therapies. Biochemical characterization of the parasite's metabolism is an
essential component for the rational development of new therapeutic
alternatives. One of the so far uncharacterized enzymes is uridine phosphorylase
(UP) (EC 2.4.2.3), for which the parasite genome presents two isoforms (SmUPa
and SmUPb) that share 92% sequence identity. In this paper, we present crystal
structures for SmUPa and SmUPb in their free states as well as bound to
different ligands. This we have complemented by enzyme kinetic characterization
and phylogenetic analyses. Both enzymes present an overall fold and active site
structure similar to other known UPs. The kinetic analyses showed conclusively
that SmUPa is a regular uridine phosphorylase but by contrast SmUPb presented no
detectable activity. This is particularly noteworthy given the high level of
sequence identity between the two isoforms and is probably the result of the
significant differences observed for SmUPb in the vicinity of the active site
itself, suggesting that it is not a UP at all. On the other hand, it was not
possible to identify an alternative function for SmUPb, although our
phylogenetic analyses and expression data suggest that SmUPb is still functional
and plays a role in parasite metabolism. The unusual UPb isoform may open up new
opportunities for understanding unique features of S. mansoni metabolism.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

