 |
PDBsum entry 4ywz
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.13.3
- histidine kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 ATP
ATP
|
+
|
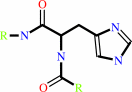 protein L-histidine
protein L-histidine
|
=
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
protein N-phospho-L-histidine
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Nat Commun
7:11000
(2016)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure and mechanism of the essential two-component signal-transduction system WalKR in Staphylococcus aureus.
|
|
Q.Ji,
P.J.Chen,
G.Qin,
X.Deng,
Z.Hao,
Z.Wawrzak,
W.S.Yeo,
J.W.Quang,
H.Cho,
G.Z.Luo,
X.Weng,
Q.You,
C.H.Luan,
X.Yang,
T.Bae,
K.Yu,
H.Jiang,
C.He.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Most low GC Gram-positive bacteria possess an essential walKR two-component
system (TCS) for signal transduction involved in regulating cell wall
homoeostasis. Despite the well-established intracellular regulatory mechanism,
the role of this TCS in extracellular signal recognition and factors that
modulate the activity of this TCS remain largely unknown. Here we identify the
extracellular receptor of the kinase 'WalK' (erWalK) as a key hub for bridging
extracellular signal input and intracellular kinase activity modulation in
Staphylococcus aureus. Characterization of the crystal structure of erWalK
revealed a canonical Per-Arnt-Sim (PAS) domain for signal sensing. Single
amino-acid mutation of potential signal-transduction residues resulted in
severely impaired function of WalKR. A small molecule derived from
structure-based virtual screening against erWalK is capable of selectively
activating the walKR TCS. The molecular level characterization of erWalK will
not only facilitate exploration of natural signal(s) but also provide a template
for rational design of erWalK inhibitors.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

