 |
PDBsum entry 4pnk

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Transferase/transferase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4pnk
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 625 a.a.
625 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 339 a.a.
339 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 62 a.a.
62 a.a.
|
 |

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase/transferase inhibitor
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 in complex with gsk180736a
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1. Chain: a. Synonym: beta-ark-1,g-protein coupled receptor kinase 2. Engineered: yes. Guanine nucleotide-binding protein g(i)/g(s)/g(t) subunit beta-1. Chain: b. Synonym: transducin beta chain 1. Engineered: yes.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: adrbk1, bark, bark1, grk2. Expressed in: trichoplusia ni. Expression_system_taxid: 7111. Gene: gnb1. Bos taurus. Bovine.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.56Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.194
|
R-free:
|
0.259
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
K.T.Homan,K.M.Larimore,J.Elkins,S.Knapp,J.J.G.Tesmer
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
K.T.Homan
et al.
(2015).
Identification and structure-function analysis of subfamily selective G protein-coupled receptor kinase inhibitors.
Acs Chem Biol,
10,
310-319.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
23-May-14
|
Release date:
|
08-Oct-14
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P25098
(ARBK1_HUMAN) -
Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
689 a.a.
625 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chain A:
E.C.2.7.11.15
- [beta-adrenergic-receptor] kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
[beta-adrenergic receptor] + ATP = [beta-adrenergic receptor]-phosphate + ADP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
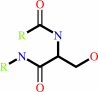 [beta-adrenergic receptor]
[beta-adrenergic receptor]
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
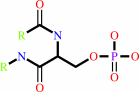 [beta-adrenergic receptor]-phosphate
[beta-adrenergic receptor]-phosphate
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acs Chem Biol
10:310-319
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Identification and structure-function analysis of subfamily selective G protein-coupled receptor kinase inhibitors.
|
|
K.T.Homan,
K.M.Larimore,
J.M.Elkins,
M.Szklarz,
S.Knapp,
J.J.Tesmer.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Selective inhibitors of individual subfamilies of G protein-coupled receptor
kinases (GRKs) would serve as useful chemical probes as well as leads for
therapeutic applications ranging from heart failure to Parkinson's disease. To
identify such inhibitors, differential scanning fluorimetry was used to screen a
collection of known protein kinase inhibitors that could increase the melting
points of the two most ubiquitously expressed GRKs: GRK2 and GRK5. Enzymatic
assays on 14 of the most stabilizing hits revealed that three exhibit nanomolar
potency of inhibition for individual GRKs, some of which exhibiting orders of
magnitude selectivity. Most of the identified compounds can be clustered into
two chemical classes: indazole/dihydropyrimidine-containing compounds that are
selective for GRK2 and pyrrolopyrimidine-containing compounds that potently
inhibit GRK1 and GRK5 but with more modest selectivity. The two most potent
inhibitors representing each class, GSK180736A and GSK2163632A, were
cocrystallized with GRK2 and GRK1, and their atomic structures were determined
to 2.6 and 1.85 Å spacings, respectively. GSK180736A, developed as a
Rho-associated, coiled-coil-containing protein kinase inhibitor, binds to GRK2
in a manner analogous to that of paroxetine, whereas GSK2163632A, developed as
an insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor inhibitor, occupies a novel region of
the GRK active site cleft that could likely be exploited to achieve more
selectivity. However, neither compound inhibits GRKs more potently than their
initial targets. This data provides the foundation for future efforts to
rationally design even more potent and selective GRK inhibitors.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| |

