 |
PDBsum entry 4mk0

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Signaling protein/inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4mk0
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 631 a.a.
631 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 339 a.a.
339 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 59 a.a.
59 a.a.
|
 |

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Signaling protein/inhibitor
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of g protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 in complex with a a rationally designed paroxetine derivative
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1. Chain: a. Fragment: unp residues 30-668. Synonym: beta-ark-1, g-protein coupled receptor kinase 2. Engineered: yes. Guanine nucleotide-binding protein g(i)/g(s)/g(t) subunit beta-1. Chain: b. Synonym: transducin beta chain 1.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: adrbk1, bark, bark1, grk2. Expressed in: trichoplusia ni. Expression_system_taxid: 7111. Bos taurus. Cow. Organism_taxid: 9913.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.40Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.179
|
R-free:
|
0.238
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
K.T.Homan,J.J.G.Tesmer
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
K.T.Homan
et al.
(2014).
Structural and functional analysis of g protein-coupled receptor kinase inhibition by paroxetine and a rationally designed analog.
Mol Pharmacol,
85,
237-248.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
04-Sep-13
|
Release date:
|
22-Jan-14
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P25098
(ARBK1_HUMAN) -
Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
689 a.a.
631 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chain A:
E.C.2.7.11.15
- [beta-adrenergic-receptor] kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
[beta-adrenergic receptor] + ATP = [beta-adrenergic receptor]-phosphate + ADP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
[beta-adrenergic receptor]
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 41.67% similarity
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
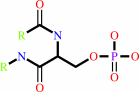 [beta-adrenergic receptor]-phosphate
[beta-adrenergic receptor]-phosphate
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Mol Pharmacol
85:237-248
(2014)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural and functional analysis of g protein-coupled receptor kinase inhibition by paroxetine and a rationally designed analog.
|
|
K.T.Homan,
E.Wu,
M.W.Wilson,
P.Singh,
S.D.Larsen,
J.J.Tesmer.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Recently we identified the serotonin reuptake inhibitor paroxetine as an
inhibitor of G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2) that improves cardiac
performance in live animals. Paroxetine exhibits up to 50-fold selectivity for
GRK2 versus other GRKs. A better understanding of the molecular basis of this
selectivity is important for the development of even more selective and potent
small molecule therapeutics and chemical genetic probes. We first sought to
understand the molecular mechanisms underlying paroxetine selectivity among
GRKs. We directly measured the KD for paroxetine and assessed its mechanism of
inhibition for each of the GRK subfamilies and then determined the atomic
structure of its complex with GRK1, the most weakly inhibited GRK tested. Our
results suggest that the selectivity of paroxetine for GRK2 largely reflects its
lower affinity for adenine nucleotides. Thus, stabilization of off-pathway
conformational states unique to GRK2 will likely be key for the development of
even more selective inhibitors. Next, we designed a benzolactam derivative of
paroxetine that has optimized interactions with the hinge of the GRK2 kinase
domain. The crystal structure of this compound in complex with GRK2 confirmed
the predicted interactions. Although the benzolactam derivative did not
significantly alter potency of inhibition among GRKs, it exhibited 20-fold lower
inhibition of serotonin reuptake. However, there was an associated increase in
the potency for inhibition of other AGC kinases, suggesting that the
unconventional hydrogen bond formed by the benzodioxole ring of paroxetine is
better accommodated by GRKs.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| |

