 |
PDBsum entry 3bji

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Signaling protein
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
3bji
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

 372 a.a.
372 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 177 a.a.
177 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 164 a.a.
164 a.a.
|
 |

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Signaling protein
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Structural basis of promiscuous guanine nucleotide exchange by the t- cell essential vav1
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Proto-oncogene vav. Chain: a, b. Fragment: vav1 dh/ph/crd. Engineered: yes. Ras-related c3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 precursor. Chain: c, d. Fragment: rac1. Synonym: p21-rac1, ras- like protein tc25, cell migration-inducing gene 5 protein.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: vav1, vav. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562. Gene: rac1.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.60Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.225
|
R-free:
|
0.293
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.E.Chrencik,A.Brooun,P.Kuhn,Accelerated Technologies Center For Gene To 3d Structure (Atcg3d)
|
Key ref:

|
 |
J.E.Chrencik
et al.
(2008).
Structural basis of guanine nucleotide exchange mediated by the T-cell essential Vav1.
J Mol Biol,
380,
828-843.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
04-Dec-07
|
Release date:
|
15-Jul-08
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P15498
(VAV_HUMAN) -
Proto-oncogene vav from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
845 a.a.
372 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains C, D:
E.C.3.6.5.2
- small monomeric GTPase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
GTP + H2O = GDP + phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 GTP
GTP
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
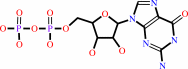 GDP
GDP
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
380:828-843
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural basis of guanine nucleotide exchange mediated by the T-cell essential Vav1.
|
|
J.E.Chrencik,
A.Brooun,
H.Zhang,
I.I.Mathews,
G.L.Hura,
S.A.Foster,
J.J.Perry,
M.Streiff,
P.Ramage,
H.Widmer,
G.M.Bokoch,
J.A.Tainer,
G.Weckbecker,
P.Kuhn.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) Vav1 plays an important role in
T-cell activation and tumorigenesis. In the GEF superfamily, Vav1 has the
ability to interact with multiple families of Rho GTPases. The structure of the
Vav1 DH-PH-CRD/Rac1 complex to 2.6 A resolution reveals a unique intramolecular
network of contacts between the Vav1 cysteine-rich domain (CRD) and the
C-terminal helix of the Vav1 Dbl homology (DH) domain. These unique interactions
stabilize the Vav1 DH domain for its intimate association with the Switch II
region of Rac1 that is critical for the displacement of the guanine nucleotide.
Small angle x-ray scattering (SAXS) studies support this domain arrangement for
the complex in solution. Further, mutational analyses confirms that the atypical
CRD is critical for maintaining both optimal guanine nucleotide exchange
activity and broader specificity of Vav family GEFs. Taken together, the data
outline the detailed nature of Vav1's ability to contact a range of Rho GTPases
using a novel protein-protein interaction network.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
Fig. 2. (a) Complete interlock network between the Vav1 DH
domain, PH domain, and CRD. The DH domain is depicted in blue,
the PH domain in cyan, and the CRD in magenta. Critical
interactions between the domains are shown with dotted black
lines. (b) Superposition of the Vav1 CRD (magenta) on the Raf1
CRD (grey) previously described.^22 The overall structures are
similar, with both similarly coordinating two zinc ions depicted
as spheres.
|
 |
Figure 8.
Fig. 8. Disruption of the β2/β3 region interface in the
Vav1/Rac1 structure. Comparison of the Tiam1/Rac β2/β3 region
(left) and the Vav/Rac β2/β3 region (right). Tiam1 (cyan)
forms an integrated network with the B2/B3 region of Rac1 (grey)
in addition to a hydrogen bond between Trp56 of Rac1 and His1178
of Tiam1. Vav1 (blue) forms only one hydrogen bond in this
region, between Ser41 of the B2/B3 of Rac1 (green) and Arg319 of
the DH domain of Vav1. In addition, Trp56 of Rac1 does not form
any interaction with the DH domain of Vav1, polar or hydrophobic.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
from an Open Access publication published by Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2008,
380,
828-843)
copyright 2008.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
B.Yu,
I.R.Martins,
P.Li,
G.K.Amarasinghe,
J.Umetani,
M.E.Fernandez-Zapico,
D.D.Billadeau,
M.Machius,
D.R.Tomchick,
and
M.K.Rosen
(2010).
Structural and energetic mechanisms of cooperative autoinhibition and activation of Vav1.
|
| |
Cell,
140,
246-256.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.P.Rambo,
and
J.A.Tainer
(2010).
Bridging the solution divide: comprehensive structural analyses of dynamic RNA, DNA, and protein assemblies by small-angle X-ray scattering.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
20,
128-137.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Cierpicki,
J.Bielnicki,
M.Zheng,
J.Gruszczyk,
M.Kasterka,
M.Petoukhov,
A.Zhang,
E.J.Fernandez,
D.I.Svergun,
U.Derewenda,
J.H.Bushweller,
and
Z.S.Derewenda
(2009).
The solution structure and dynamics of the DH-PH module of PDZRhoGEF in isolation and in complex with nucleotide-free RhoA.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
18,
2067-2079.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |
| |

