 |
PDBsum entry 2iq7

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of the polygalacturonase from colletotrichum lupini and its implications for the interaction with polygalacturonase- inhibiting proteins
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Endopolygalacturonase. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f, g. Ec: 3.2.1.15
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Colletotrichum lupini. Organism_taxid: 145971
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.94Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.154
|
R-free:
|
0.196
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
D.Bonivento,L.Federici,A.D.Matteo
|
Key ref:

|
 |
D.Bonivento
et al.
(2008).
Crystal structure of the endopolygalacturonase from the phytopathogenic fungus Colletotrichum lupini and its interaction with polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins.
Proteins,
70,
294-299.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
13-Oct-06
|
Release date:
|
23-Oct-07
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
A1E266
(A1E266_9PEZI) -
endo-polygalacturonase from Colletotrichum lupini var. setosum
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
362 a.a.
339 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.2.1.15
- endo-polygalacturonase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(1,4-alpha-D-galacturonosyl)n+m + H2O = (1,4-alpha-D-galacturonosyl)n + (1,4-alpha-D-galacturonosyl)m
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(1,4-alpha-D-galacturonosyl)n+m
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
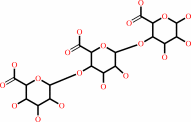 (1,4-alpha-D-galacturonosyl)n
(1,4-alpha-D-galacturonosyl)n
|
+
|
(1,4-alpha-D-galacturonosyl)m
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proteins
70:294-299
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of the endopolygalacturonase from the phytopathogenic fungus Colletotrichum lupini and its interaction with polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins.
|
|
D.Bonivento,
D.Pontiggia,
A.D.Matteo,
J.Fernandez-Recio,
G.Salvi,
D.Tsernoglou,
F.Cervone,
G.D.Lorenzo,
L.Federici.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. (A) Ribbon representation of CluPG1. A cross section
of the  -helix
is shown on the right panel; the color code indicates the
secondary structure elements in a representative coil. (B)
Structural superposition of CluPG1 with AnPGII and FmPG. The red
circle indicates an eight residues insertion in the structure of
FmPG that likely plays a role in the interaction of this enzyme
with PGIPs. -helix
is shown on the right panel; the color code indicates the
secondary structure elements in a representative coil. (B)
Structural superposition of CluPG1 with AnPGII and FmPG. The red
circle indicates an eight residues insertion in the structure of
FmPG that likely plays a role in the interaction of this enzyme
with PGIPs.
|
 |
Figure 2.
Figure 2. (A) CluPG1 enzyme kinetics and inhibition played by
PvPGIP2. The uninhibited enzyme is represented in squares;
triangles and circles represent the data obtained in the
presence of 4 and 8 nM PvPGIP2, respectively. Curves represent
the fits of experimental data with non-linear regression
analysis using the Michaelis-Menten equation. K[m] and V[max]
values are reported in the inset. A decrease in V[max] while
K[m] remains constant is indicative of noncompetitive
inhibition. (B) Optimal docking areas of CluPG1, AnPGII, and
FmPG. Surface residues with an ODA value lower than -2 kcal/mol
are colored in red, otherwise in blue. Black arrows mark the
position of the active sites. The putative interaction areas of
CluPG1 and AnPGII, located below the binding cleft, are almost
superimposable. Differently, FmPG shows two distinct patches on
opposite sides of the active site. A different PG-PGIP
interaction area for the latter enzyme with respect to CluPG1
and AnPGII is suggested, which accounts for the different modes
of inhibition observed. The view is  90°
anticlockwise rotated over the z-axis with respect to Figure 1. 90°
anticlockwise rotated over the z-axis with respect to Figure 1.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from John Wiley & Sons, Inc.:
Proteins
(2008,
70,
294-299)
copyright 2008.
|
|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
C.Di,
M.Li,
F.Long,
M.Bai,
Y.Liu,
X.Zheng,
S.Xu,
Y.Xiang,
Z.Sun,
and
L.An
(2009).
Molecular cloning, functional analysis and localization of a novel gene encoding polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein in Chorispora bungeana.
|
| |
Planta,
231,
169-178.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Casasoli,
L.Federici,
F.Spinelli,
A.Di Matteo,
N.Vella,
F.Scaloni,
J.Fernandez-Recio,
F.Cervone,
and
G.De Lorenzo
(2009).
Integration of evolutionary and desolvation energy analysis identifies functional sites in a plant immunity protein.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
106,
7666-7671.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Lagaert,
T.Beliën,
and
G.Volckaert
(2009).
Plant cell walls: Protecting the barrier from degradation by microbial enzymes.
|
| |
Semin Cell Dev Biol,
20,
1064-1073.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Xiao,
S.Wang,
H.Bergeron,
J.Zhang,
and
P.C.Lau
(2008).
A flax-retting endopolygalacturonase-encoding gene from Rhizopus oryzae.
|
| |
Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek,
94,
563-571.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

