 |
PDBsum entry 2dqb

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Hydrolase, DNA binding protein
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2dqb
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase, DNA binding protein
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of dntp triphosphohydrolase from thermus thermophilus hb8, which is homologous to dgtp triphosphohydrolase
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Deoxyguanosinetriphosphate triphosphohydrolase, putative. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f. Synonym: dntp triphosphohydrolase. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Thermus thermophilus. Organism_taxid: 300852. Strain: hb8. Gene: ttha0412. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.20Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.223
|
R-free:
|
0.286
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
N.Kondo,N.Nakagawa,A.Ebihara,L.Chen,Z.-J.Liu,B.-C.Wang,S.Yokoyama, S.Kuramitsu,R.Masui,Riken Structural Genomics/proteomics Initiative (Rsgi)
|
Key ref:

|
 |
N.Kondo
et al.
(2007).
Structure of dNTP-inducible dNTP triphosphohydrolase: insight into broad specificity for dNTPs and triphosphohydrolase-type hydrolysis.
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
63,
230-239.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
25-May-06
|
Release date:
|
23-Jan-07
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q5SL81
(Q5SL81_THET8) -
Deoxyguanosinetriphosphate triphosphohydrolase-like protein from Thermus thermophilus (strain ATCC 27634 / DSM 579 / HB8)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
376 a.a.
363 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.5.1
- dGTPase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
dGTP + H2O = 2'-deoxyguanosine + triphosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
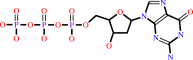 dGTP
dGTP
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
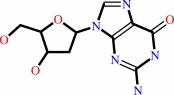 2'-deoxyguanosine
2'-deoxyguanosine
|
+
|
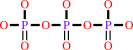 triphosphate
triphosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
63:230-239
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure of dNTP-inducible dNTP triphosphohydrolase: insight into broad specificity for dNTPs and triphosphohydrolase-type hydrolysis.
|
|
N.Kondo,
N.Nakagawa,
A.Ebihara,
L.Chen,
Z.J.Liu,
B.C.Wang,
S.Yokoyama,
S.Kuramitsu,
R.Masui.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate triphosphohydrolase from Thermus thermophilus
(Tt-dNTPase) has a unique regulatory mechanism for the degradation of
deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs). Whereas the Escherichia coli
homologue specifically hydrolyzes dGTP alone, dNTPs act as both substrate and
activator for Tt-dNTPase. Here, the crystal structure of Tt-dNTPase has been
determined at 2.2 A resolution, representing the first report of the tertiary
structure of a dNTPase homologue belonging to the HD superfamily, a diverse
group of metal-dependent phosphohydrolases that includes a variety of
uncharacterized proteins. This enzyme forms a homohexamer as a double ring of
trimers. The subunit is composed of 19 alpha-helices; the inner six helices
include the region annotated as the catalytic domain of the HD superfamily.
Structural comparison with other HD-superfamily proteins indicates that a pocket
at the centre of the inner six helices, formed from highly conserved charged
residues clustered around a bound magnesium ion, constitutes the catalytic site.
Tt-dNTPase also hydrolyzed noncanonical dNTPs, but hardly hydrolyzed dNDP and
dNMP. The broad substrate specificity for different dNTPs might be rationalized
by the involvement of a flexible loop during molecular recognition of the base
moiety. Recognition of the triphosphate moiety crucial for the activity might be
attained by highly conserved positively charged residues. The possible mode of
dNTP binding is discussed in light of the structure.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
Figure 2 Architecture of the hexameric organization. (a) Top
view. (b) Side view. Chain A is represented in the same colours
as in Fig. 1-. The subunits coloured purple, brown, orange, grey
and green indicate chains B, C, D, E and F, respectively. The
view shown in (b) represents a 90° rotation from that in
(a), so that chains F and B are hidden.
|
 |
Figure 7.
Figure 7 Putative dNTP-binding site. Chains C and F are
coloured orange and green, respectively. The residues comprising
the putative binding site predicted by WHAT IF (Vriend,
1990[Vriend, G. (1990). J. Mol. Graph. 8, 52-56.]) are
represented in deep colours. The cavity detected by VOIDOO
(Kleywegt & Jones, 1994[Kleywegt, G. J. & Jones, T. A. (1994).
Acta Cryst. D50, 178-185.]) is represented as a yellow mesh.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the IUCr:
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
(2007,
63,
230-239)
copyright 2007.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
D.C.Goldstone,
V.Ennis-Adeniran,
J.J.Hedden,
H.C.Groom,
G.I.Rice,
E.Christodoulou,
P.A.Walker,
G.Kelly,
L.F.Haire,
M.W.Yap,
L.P.de Carvalho,
J.P.Stoye,
Y.J.Crow,
I.A.Taylor,
and
M.Webb
(2011).
HIV-1 restriction factor SAMHD1 is a deoxynucleoside triphosphate triphosphohydrolase.
|
| |
Nature,
480,
379-382.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Zhang,
E.L.Pohlmann,
J.Serate,
M.C.Conrad,
and
G.P.Roberts
(2010).
Mutagenesis and functional characterization of the four domains of GlnD, a bifunctional nitrogen sensor protein.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
192,
2711-2721.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Mega,
N.Kondo,
N.Nakagawa,
S.Kuramitsu,
and
R.Masui
(2009).
Two dNTP triphosphohydrolases from Pseudomonas aeruginosa possess diverse substrate specificities.
|
| |
FEBS J,
276,
3211-3221.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.D.Zimmerman,
M.Proudfoot,
A.Yakunin,
and
W.Minor
(2008).
Structural insight into the mechanism of substrate specificity and catalytic activity of an HD-domain phosphohydrolase: the 5'-deoxyribonucleotidase YfbR from Escherichia coli.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
378,
215-226.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Kondo,
T.Nishikubo,
T.Wakamatsu,
H.Ishikawa,
N.Nakagawa,
S.Kuramitsu,
and
R.Masui
(2008).
Insights into different dependence of dNTP triphosphohydrolase on metal ion species from intracellular ion concentrations in Thermus thermophilus.
|
| |
Extremophiles,
12,
217-223.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

