 |
PDBsum entry 1m6h

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1m6h
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.-
- ?????
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.1
- alcohol dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
a primary alcohol + NAD+ = an aldehyde + NADH + H+
|
|
2.
|
a secondary alcohol + NAD+ = a ketone + NADH + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
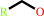 primary alcohol
primary alcohol
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
=
|
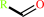 aldehyde
aldehyde
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
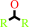 secondary alcohol
secondary alcohol
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
=
|
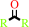 ketone
ketone
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+) or Fe cation
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.284
- S-(hydroxymethyl)glutathione dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
S-(hydroxymethyl)glutathione + NADP+ = S-formylglutathione + NADPH + H+
|
|
2.
|
S-(hydroxymethyl)glutathione + NAD+ = S-formylglutathione + NADH + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
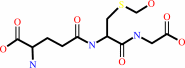 S-(hydroxymethyl)glutathione
S-(hydroxymethyl)glutathione
|
+
|
 NADP(+)
NADP(+)
|
=
|
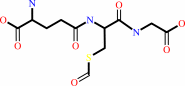 S-formylglutathione
S-formylglutathione
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 S-(hydroxymethyl)glutathione
S-(hydroxymethyl)glutathione
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
=
|
 S-formylglutathione
S-formylglutathione
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
41:10778-10786
(2002)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Human glutathione-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase. Structures of apo, binary, and inhibitory ternary complexes.
|
|
P.C.Sanghani,
H.Robinson,
W.F.Bosron,
T.D.Hurley.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The human glutathione-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase is unique among the
structurally studied members of the alcohol dehydrogenase family in that it
follows a random bi bi kinetic mechanism. The structures of an apo form of the
enzyme, a binary complex with substrate 12-hydroxydodecanoic acid, and a ternary
complex with NAD+ and the inhibitor dodecanoic acid were determined at 2.0, 2.3,
and 2.3 A resolution by X-ray crystallography using the anomalous diffraction
signal of zinc. The structures of the enzyme and its binary complex with the
primary alcohol substrate, 12-hydroxydodecanoic acid, and the previously
reported binary complex with the coenzyme show that the binding of the first
substrate (alcohol or coenzyme) causes only minor changes to the overall
structure of the enzyme. This is consistent with the random mechanism of the
enzyme where either of the substrates binds to the free enzyme. The
catalytic-domain position in these structures is intermediate to the "closed"
and "open" conformations observed in class I alcohol dehydrogenases. More
importantly, two different tetrahedral coordination environments of the active
site zinc are observed in these structures. In the apoenzyme, the active site
zinc is coordinated to Cys44, His66 and Cys173, and a water molecule. In the
inhibitor complex, the coordination environment involves Glu67 instead of the
solvent water molecule. The coordination environment involving Glu67 as the
fourth ligand likely represents an intermediate step during ligand exchange at
the active site zinc. These observations provide new insight into metal-assisted
catalysis and substrate binding in glutathione-dependent formaldehyde
dehydrogenase.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
P.C.Sanghani,
W.I.Davis,
S.L.Fears,
S.L.Green,
L.Zhai,
Y.Tang,
E.Martin,
N.S.Bryan,
and
S.P.Sanghani
(2009).
Kinetic and cellular characterization of novel inhibitors of S-nitrosoglutathione reductase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
24354-24362.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Gao,
Q.Song,
and
D.Wei
(2006).
Coupling of enantioselective biooxidation of DL-1,2-propanediol and bioreduction of pinacolone via regeneration cycle of coenzyme.
|
| |
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,
71,
819-823.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.J.Marx,
J.A.Miller,
L.Chistoserdova,
and
M.E.Lidstrom
(2004).
Multiple formaldehyde oxidation/detoxification pathways in Burkholderia fungorum LB400.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
186,
2173-2178.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Esposito,
I.Bruno,
F.Sica,
C.A.Raia,
A.Giordano,
M.Rossi,
L.Mazzarella,
and
A.Zagari
(2003).
Crystal structure of a ternary complex of the alcohol dehydrogenase from Sulfolobus solfataricus.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
42,
14397-14407.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
O.Kleifeld,
S.P.Shi,
R.Zarivach,
M.Eisenstein,
and
I.Sagi
(2003).
The conserved Glu-60 residue in Thermoanaerobacter brockii alcohol dehydrogenase is not essential for catalysis.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
12,
468-479.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

