 |
PDBsum entry 1a5c

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase from plasmodium falciparum
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase. Chain: a, b. Synonym: pfaldo. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Plasmodium falciparum. Malaria parasite p. Falciparum. Organism_taxid: 5833. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Tetramer (from PDB file)
Tetramer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
3.00Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.239
|
R-free:
|
0.329
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
H.Kim,U.Certa,H.Dobeli,P.Jakob,W.G.J.Hol
|
Key ref:

|
 |
H.Kim
et al.
(1998).
Crystal structure of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase from the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum.
Biochemistry,
37,
4388-4396.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
13-Feb-98
|
Release date:
|
10-Jun-98
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P14223
(ALF_PLAFA) -
Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase from Plasmodium falciparum
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
369 a.a.
342 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.1.2.13
- fructose-bisphosphate aldolase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
beta-D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate = D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + dihydroxyacetone phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
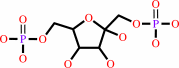 beta-D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
beta-D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
|
=
|
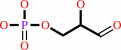 D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
|
+
|
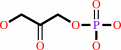 dihydroxyacetone phosphate
dihydroxyacetone phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
37:4388-4396
(1998)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase from the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum.
|
|
H.Kim,
U.Certa,
H.Döbeli,
P.Jakob,
W.G.Hol.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The structure of the glycolytic enzyme class I fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate
aldolase from the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum has been
determined by X-ray crystallography. Homotetrameric P. falciparum aldolase
(PfALDO) crystallizes in space group P3221 with one 80 kDa dimer per asymmetric
unit. The final refined PfALDO model has an R-factor of 0.239 and an R-free of
0.329 with respect to data from 8 to 3.0 A resolution. PfALDO is potentially a
target for antimalarial drug design as the intraerythrocytic merozoite lifestage
of P. falciparum is completely dependent upon glycolysis for its ATP production.
Thus, inhibitors directed against the glycolytic enzymes in P. falciparum may be
effective in killing the parasite. The structure of PfALDO is compared with the
previously determined structure of human aldolase in order to determine possible
targets for the structure-based design of selective PfALDO ligands. The salient
structural differences include a hydrophobic pocket on the surface of PfALDO,
which results from some amino acid changes and a single residue deletion
compared with human aldolase, and the overall quaternary structure of the PfALDO
tetramer, which buries less surface area than human aldolase.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
D.W.Song,
J.G.Lee,
H.S.Youn,
S.H.Eom,
and
d.o. .H.Kim
(2011).
Ryanodine receptor assembly: A novel systems biology approach to 3D mapping.
|
| |
Prog Biophys Mol Biol,
105,
145-161.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Kuehn,
N.Simon,
and
G.Pradel
(2010).
Family members stick together: multi-protein complexes of malaria parasites.
|
| |
Med Microbiol Immunol,
199,
209-226.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.A.Buscaglia,
W.G.Hol,
V.Nussenzweig,
and
T.Cardozo
(2007).
Modeling the interaction between aldolase and the thrombospondin-related anonymous protein, a key connection of the malaria parasite invasion machinery.
|
| |
Proteins,
66,
528-537.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Bosch,
C.A.Buscaglia,
B.Krumm,
B.P.Ingason,
R.Lucas,
C.Roach,
T.Cardozo,
V.Nussenzweig,
and
W.G.Hol
(2007).
Aldolase provides an unusual binding site for thrombospondin-related anonymous protein in the invasion machinery of the malaria parasite.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
104,
7015-7020.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Y.Forlemu,
V.F.Waingeh,
I.V.Ouporov,
S.L.Lowe,
and
K.A.Thomasson
(2007).
Theoretical study of interactions between muscle aldolase and F-actin: insight into different species.
|
| |
Biopolymers,
85,
60-71.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Jana,
and
J.Paliwal
(2007).
Novel molecular targets for antimalarial chemotherapy.
|
| |
Int J Antimicrob Agents,
30,
4.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.A.Buscaglia,
D.Penesetti,
M.Tao,
and
V.Nussenzweig
(2006).
Characterization of an aldolase-binding site in the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
1324-1331.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.K.Yu,
and
S.F.Altschul
(2005).
The construction of amino acid substitution matrices for the comparison of proteins with non-standard compositions.
|
| |
Bioinformatics,
21,
902-911.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Liotard,
and
J.Sygusch
(2004).
Purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of native and selenomethionine class I tagatose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase from Streptococcus pyogenes.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
60,
528-530.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Lundmark,
and
S.R.Carlsson
(2004).
Regulated membrane recruitment of dynamin-2 mediated by sorting nexin 9.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
42694-42702.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Izard,
and
J.Sygusch
(2004).
Induced fit movements and metal cofactor selectivity of class II aldolases: structure of Thermus aquaticus fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
11825-11833.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.A.Buscaglia,
I.Coppens,
W.G.Hol,
and
V.Nussenzweig
(2003).
Sites of interaction between aldolase and thrombospondin-related anonymous protein in plasmodium.
|
| |
Mol Biol Cell,
14,
4947-4957.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Joët,
C.Morin,
J.Fischbarg,
A.I.Louw,
U.Eckstein-Ludwig,
C.Woodrow,
and
S.Krishna
(2003).
Why is the Plasmodium falciparum hexose transporter a promising new drug target?
|
| |
Expert Opin Ther Targets,
7,
593-602.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Maurady,
A.Zdanov,
D.de Moissac,
D.Beaudry,
and
J.Sygusch
(2002).
A conserved glutamate residue exhibits multifunctional catalytic roles in D-fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolases.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
9474-9483.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Kroemer,
and
G.E.Schulz
(2002).
The structure of L-rhamnulose-1-phosphate aldolase (class II) solved by low-resolution SIR phasing and 20-fold NCS averaging.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
58,
824-832.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Heine,
G.DeSantis,
J.G.Luz,
M.Mitchell,
C.H.Wong,
and
I.A.Wilson
(2001).
Observation of covalent intermediates in an enzyme mechanism at atomic resolution.
|
| |
Science,
294,
369-374.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

