 |
PDBsum entry 6f67
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.5.1.18
- glutathione transferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
RX + glutathione = an S-substituted glutathione + a halide anion + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
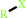 RX
RX
|
+
|
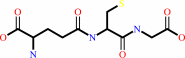 glutathione
glutathione
|
=
|
S-substituted glutathione
|
+
|
halide anion
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Sci Rep
8:8472
(2018)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Molecular recognition of wood polyphenols by phase II detoxification enzymes of the white rot Trametes versicolor.
|
|
M.Schwartz,
T.Perrot,
E.Aubert,
S.Dumarçay,
F.Favier,
P.Gérardin,
M.Morel-Rouhier,
G.Mulliert,
F.Saiag,
C.Didierjean,
E.Gelhaye.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Wood decay fungi have complex detoxification systems that enable them to cope
with secondary metabolites produced by plants. Although the number of genes
encoding for glutathione transferases is especially expanded in lignolytic
fungi, little is known about their target molecules. In this study, by combining
biochemical, enzymatic and structural approaches, interactions between
polyphenols and six glutathione transferases from the white-rot fungus Trametes
versicolor have been demonstrated. Two isoforms, named TvGSTO3S and TvGSTO6S
have been deeply studied at the structural level. Each isoform shows two
distinct ligand-binding sites, a narrow L-site at the dimer interface and a
peculiar deep hydrophobic H-site. In TvGSTO3S, the latter appears optimized for
aromatic ligand binding such as hydroxybenzophenones. Affinity crystallography
revealed that this H-site retains the flavonoid dihydrowogonin from a partially
purified wild-cherry extract. Besides, TvGSTO6S binds two molecules of the
flavonoid naringenin in the L-site. These data suggest that TvGSTO isoforms
could interact with plant polyphenols released during wood degradation.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

