 |
PDBsum entry 6f05

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|





 (+ 3 more)
204 a.a.
(+ 3 more)
204 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 193 a.a.
193 a.a.
|
 |

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Arabidopsis thaliana gstf9, gso3 bound
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Glutathione s-transferase f9. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j. Synonym: atgstf9,atgstf7,gst class-phi member 9. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Arabidopsis thaliana. Mouse-ear cress. Organism_taxid: 3702. Gene: gstf9, gluttr, gstf7, at2g30860, f7f1.7. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.20Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.164
|
R-free:
|
0.209
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
M.A.Tossounian,K.Wahni,I.Vanmolle,D.Vertommen,L.Rosado,J.Messens
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
M.A.Tossounian
et al.
(2019).
Redox-regulated methionine oxidation of Arabidopsis thaliana glutathione transferase Phi9 induces H-site flexibility.
Protein Sci,
28,
56-67.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
17-Nov-17
|
Release date:
|
15-Aug-18
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J:
E.C.2.5.1.18
- glutathione transferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
RX + glutathione = an S-substituted glutathione + a halide anion + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
RX
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 86.96% similarity
|
+
|
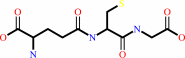 glutathione
glutathione
|
=
|
S-substituted glutathione
|
+
|
halide anion
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Protein Sci
28:56-67
(2019)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Redox-regulated methionine oxidation of Arabidopsis thaliana glutathione transferase Phi9 induces H-site flexibility.
|
|
M.A.Tossounian,
K.Wahni,
I.Van Molle,
D.Vertommen,
L.Astolfi Rosado,
J.Messens.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Glutathione transferase enzymes help plants to cope with biotic and abiotic
stress. They mainly catalyze the conjugation of glutathione (GSH) onto
xenobiotics, and some act as glutathione peroxidase. With X-ray crystallography,
kinetics, and thermodynamics, we studied the impact of oxidation on Arabidopsis
thaliana glutathione transferase Phi 9 (GSTF9). GSTF9 has no cysteine in its
sequence, and it adopts a universal GST structural fold characterized by a
typical conserved GSH-binding site (G-site) and a hydrophobic
co-substrate-binding site (H-site). At elevated H2 O2
concentrations, methionine sulfur oxidation decreases its transferase activity.
This oxidation increases the flexibility of the H-site loop, which is reflected
in lower activities for hydrophobic substrates. Determination of the transition
state thermodynamic parameters shows that upon oxidation an increased enthalpic
penalty is counterbalanced by a more favorable entropic contribution. All in
all, to guarantee functionality under oxidative stress conditions, GSTF9 employs
a thermodynamic and structural compensatory mechanism and becomes substrate of
methionine sulfoxide reductases, making it a redox-regulated enzyme.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

