 |
PDBsum entry 6b2c

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Isomerase/isomerase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
6b2c
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Isomerase/isomerase inhibitor
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor in complex with a naphthyridinone inhibitor (4b)
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Chain: a, b, c. Synonym: mif,glycosylation-inhibiting factor,gif,l-dopachrome isomerase,l-dopachrome tautomerase,phenylpyruvate tautomerase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: mif, glif, mmif. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562. Expression_system_cell: bl21.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.00Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.193
|
R-free:
|
0.222
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
S.G.Krimmer,M.J.Robertson,W.L.Jorgensen
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
T.K.Dawson
et al.
(2017).
Adding a Hydrogen Bond May Not Help: Naphthyridinone vs Quinoline Inhibitors of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor.
ACS Med Chem Lett,
8,
1287-1291.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
19-Sep-17
|
Release date:
|
03-Jan-18
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P14174
(MIF_HUMAN) -
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
115 a.a.
114 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.5.3.2.1
- phenylpyruvate tautomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
3-phenylpyruvate = enol-phenylpyruvate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
3-phenylpyruvate
|
=
|
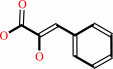 enol-phenylpyruvate
enol-phenylpyruvate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.5.3.3.12
- L-dopachrome isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-dopachrome = 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
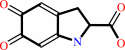 L-dopachrome
L-dopachrome
|
=
|
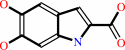 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylate
5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
ACS Med Chem Lett
8:1287-1291
(2017)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Adding a Hydrogen Bond May Not Help: Naphthyridinone vs Quinoline Inhibitors of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor.
|
|
T.K.Dawson,
P.Dziedzic,
M.J.Robertson,
J.A.Cisneros,
S.G.Krimmer,
A.S.Newton,
J.Tirado-Rives,
W.L.Jorgensen.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Coordination of the ammonium group of Lys32 in the active site of human
macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) using a 1,7-naphthyridin-8-one
instead of a quinoline is investigated. Both gas- and aqueous-phase DFT
calculations for model systems indicate potential benefits for the added
hydrogen bond with the lactam carbonyl group, while FEP results are neutral.
Three crystal structures are reported for complexes of MIF
with3a,4a, and4b, which show that the desired hydrogen bond
is formed with O-N distances of 2.8-3.0 Å. Compound4bis the most potent
new MIF inhibitor withKiandKdvalues of 90
and 94 nM; it also has excellent aqueous solubility, 288 μg/mL. Consistent with
the FEP results, the naphthyridinones are found to have similar potency as
related quinolines in spite of the additional protein-ligand hydrogen bond.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

