 |
PDBsum entry 5c5h
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Ligase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
R195k e. Coli mene with bound osb-ams
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
2-succinylbenzoate--coa ligase. Chain: a, b. Synonym: o-succinylbenzoyl-coa synthetase,osb-coa synthetase. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli (strain k12). Organism_taxid: 83333. Strain: k12. Gene: mene, b2260, jw2255. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.40Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.203
|
R-free:
|
0.247
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.S.Matarlo,R.Shek,K.R.Rajashankar,P.J.Tonge,J.B.French
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
J.S.Matarlo
et al.
(2015).
Mechanism of MenE inhibition by acyl-adenylate analogues and discovery of novel antibacterial agents.
Biochemistry,
54,
6514-6524.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
19-Jun-15
|
Release date:
|
07-Oct-15
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P37353
(MENE_ECOLI) -
2-succinylbenzoate--CoA ligase from Escherichia coli (strain K12)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
451 a.a.
443 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.6.2.1.26
- o-succinylbenzoate--CoA ligase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Vitamin K Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
2-succinylbenzoate + ATP + CoA = 2-succinylbenzoyl-CoA + AMP + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 2-succinylbenzoate
2-succinylbenzoate
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
+
|
 CoA
CoA
|
=
|
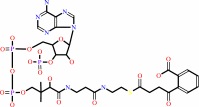 2-succinylbenzoyl-CoA
2-succinylbenzoyl-CoA
|
+
|
AMP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 45.24% similarity
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
54:6514-6524
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Mechanism of MenE inhibition by acyl-adenylate analogues and discovery of novel antibacterial agents.
|
|
J.S.Matarlo,
C.E.Evans,
I.Sharma,
L.J.Lavaud,
S.C.Ngo,
R.Shek,
K.R.Rajashankar,
J.B.French,
D.S.Tan,
P.J.Tonge.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
MenE is an o-succinylbenzoyl-CoA (OSB-CoA) synthetase in the bacterial
menaquinone biosynthesis pathway and is a promising target for the development
of novel antibacterial agents. The enzyme catalyzes CoA ligation via an
acyl-adenylate intermediate, and we have previously reported tight-binding
inhibitors of MenE based on stable acyl-sulfonyladenosine analogues of this
intermediate, including OSB-AMS (1), which has an IC50 value of ≤25 nM for
Escherichia coli MenE. Herein, we show that OSB-AMS reduces menaquinone levels
in Staphylococcus aureus, consistent with its proposed mechanism of action,
despite the observation that the antibacterial activity of OSB-AMS is
∼1000-fold lower than the IC50 for enzyme inhibition. To inform the synthesis
of MenE inhibitors with improved antibacterial activity, we have undertaken a
structure-activity relationship (SAR) study stimulated by the knowledge that
OSB-AMS can adopt two isomeric forms in which the OSB side chain exists either
as an open-chain keto acid or a cyclic lactol. These studies revealed that
negatively charged analogues of the keto acid form bind, while neutral analogues
do not, consistent with the hypothesis that the negatively charged keto acid
form of OSB-AMS is the active isomer. X-ray crystallography and site-directed
mutagenesis confirm the importance of a conserved arginine for binding the OSB
carboxylate. Although most lactol isomers tested were inactive, a novel
difluoroindanediol inhibitor (11) with improved antibacterial activity was
discovered, providing a pathway toward the development of optimized MenE
inhibitors in the future.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

