 |
PDBsum entry 4zky

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4zky
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.4.3.5
- pyridoxal 5'-phosphate synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate + O2 + H2O = pyridoxal 5'-phosphate + H2O2 + NH4+
|
|
2.
|
pyridoxine 5'-phosphate + O2 = pyridoxal 5'-phosphate + H2O2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate
pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
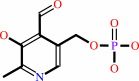 pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
+
|
 H2O2
H2O2
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 pyridoxine 5'-phosphate
pyridoxine 5'-phosphate
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
=
|
 pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
+
|
 H2O2
H2O2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FMN
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
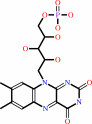 FMN
FMN
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
427:3554-3571
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Sequence-Structure-Function Classification of a Catalytically Diverse Oxidoreductase Superfamily in Mycobacteria.
|
|
F.H.Ahmed,
P.D.Carr,
B.M.Lee,
L.Afriat-Jurnou,
A.E.Mohamed,
N.S.Hong,
J.Flanagan,
M.C.Taylor,
C.Greening,
C.J.Jackson.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The deazaflavin cofactor F420 enhances the persistence of mycobacteria during
hypoxia, oxidative stress, and antibiotic treatment. However, the identities and
functions of the mycobacterial enzymes that utilize F420 under these conditions
have yet to be resolved. In this work, we used sequence similarity networks to
analyze the distribution of the largest F420-dependent protein family in
mycobacteria. We show that these enzymes are part of a larger split β-barrel
enzyme superfamily (flavin/deazaflavin oxidoreductases, FDORs) that include
previously characterized pyridoxamine/pyridoxine-5'-phosphate oxidases and heme
oxygenases. We show that these proteins variously utilize F420, flavin
mononucleotide, flavin adenine dinucleotide, and heme cofactors. Functional
annotation using phylogenetic, structural, and spectroscopic methods revealed
their involvement in heme degradation, biliverdin reduction, fatty acid
modification, and quinone reduction. Four novel crystal structures show that
plasticity in substrate binding pockets and modifications to cofactor binding
motifs enabled FDORs to carry out a variety of functions. This systematic
classification and analysis provides a framework for further functional analysis
of the roles of FDORs in mycobacterial pathogenesis and persistence.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

