 |
PDBsum entry 4m2r

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Lyase/lyase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4m2r
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase/lyase inhibitor
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Human carbonic anhydrase ii in complex with brinzolamide
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Carbonic anhydrase 2. Chain: a. Synonym: carbonate dehydratase ii, carbonic anhydrasE C, cac, carbonic anhydrase ii, ca-ii. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: ca2. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.99Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.174
|
R-free:
|
0.216
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
M.P.Pinard,C.D.Boone,B.D.Rife,C.T.Supuran,R.Mckenna
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
M.A.Pinard
et al.
(2013).
Structural study of interaction between brinzolamide and dorzolamide inhibition of human carbonic anhydrases.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett,
21,
7210-7215.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
05-Aug-13
|
Release date:
|
06-Nov-13
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P00918
(CAH2_HUMAN) -
Carbonic anhydrase 2 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
260 a.a.
257 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.1
- carbonic anhydrase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
hydrogencarbonate + H+ = CO2 + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 hydrogencarbonate
hydrogencarbonate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
 CO2
CO2
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.69
- cyanamide hydratase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
urea = cyanamide + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
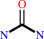 urea
urea
|
=
|
 cyanamide
cyanamide
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Bioorg Med Chem Lett
21:7210-7215
(2013)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural study of interaction between brinzolamide and dorzolamide inhibition of human carbonic anhydrases.
|
|
M.A.Pinard,
C.D.Boone,
B.D.Rife,
C.T.Supuran,
R.McKenna.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Carbonic anhydrases (CAs, EC 4.2.1.1) are metalloenzymes that catalyze the
reversible hydration of carbon dioxide and bicarbonate. Their pivotal role in
metabolism, ubiquitous nature, and multiple isoforms (CA I-XIV) has made CAs an
attractive drug target in clinical applications. The usefulness of CA inhibitors
(CAIs) in the treatment of glaucoma and epilepsy are well documented. In
addition several isoforms of CAs (namely, CA IX) also serve as biological
markers for certain tumors, and therefore they have the potential for useful
applications in the treatment of cancer. This is a structural study on the
binding interactions of the widely used CA inhibitory drugs brinzolamide
(marketed as Azopt®) and dorzolamide (marketed as Trusopt®) with CA II and a
CA IX-mimic, which was created via site-directed mutagenesis of CA II cDNA such
that the active site resembles that of CA IX. Also the inhibition of CA II and
CA IX and molecular docking reveal brinzolamide to be a more potent inhibitor
among the other catalytically active CA isoforms compared to dorzolamide. The
structures show that the tail end of the sulfonamide inhibitor is critical in
forming stabilizing interactions that influence tight binding; therefore, for
future drug design it is the tail moiety that will ultimately determine isoform
specificity.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

