 |
PDBsum entry 3dss

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of rabggtase(delta lrr; delta ig)
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Geranylgeranyl transferase type-2 subunit alpha. Chain: a. Fragment: pfta domains, unp residues 1-237 and 353-441. Synonym: geranylgeranyl transferase type ii subunit alpha, rab geranylgeranyltransferase subunit alpha, rab geranyl- geranyltransferase subunit alpha, rab gg transferase alpha, rab ggtase alpha. Engineered: yes. Geranylgeranyl transferase type-2 subunit beta.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Rattus norvegicus. Rat. Organism_taxid: 10116. Gene: rabggta, ggta. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562. Other_details: coexpression of engineered alpha-subunit from pgatev and beta-subunit from pet3 0a. Gene: rabggtb, ggtb.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.80Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.151
|
R-free:
|
0.194
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
Z.Guo,S.Yu,R.S.Goody,K.Alexandrov,W.Blankenfeldt
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
Z.Guo
et al.
(2008).
Structures of RabGGTase-substrate/product complexes provide insights into the evolution of protein prenylation.
Embo J,
27,
2444-2456.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
14-Jul-08
|
Release date:
|
09-Sep-08
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.2.5.1.60
- protein geranylgeranyltransferase type Ii.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
geranylgeranyl diphosphate + L-cysteinyl-[protein] = S-geranylgeranyl-L- cysteinyl-[protein] + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
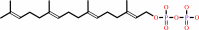 geranylgeranyl diphosphate
geranylgeranyl diphosphate
|
+
|
L-cysteinyl-[protein]
|
=
|
S-geranylgeranyl-L- cysteinyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Embo J
27:2444-2456
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structures of RabGGTase-substrate/product complexes provide insights into the evolution of protein prenylation.
|
|
Z.Guo,
Y.W.Wu,
D.Das,
C.Delon,
J.Cramer,
S.Yu,
S.Thuns,
N.Lupilova,
H.Waldmann,
L.Brunsveld,
R.S.Goody,
K.Alexandrov,
W.Blankenfeldt.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Post-translational isoprenylation of proteins is carried out by three related
enzymes: farnesyltransferase, geranylgeranyl transferase-I, and Rab
geranylgeranyl transferase (RabGGTase). Despite the fact that the last one is
responsible for the largest number of individual protein prenylation events in
the cell, no structural information is available on its interaction with
substrates and products. Here, we present structural and biophysical analyses of
RabGGTase in complex with phosphoisoprenoids as well as with the prenylated
peptides that mimic the C terminus of Rab7 GTPase. The data demonstrate that,
unlike other protein prenyl transferases, both RabGGTase and its substrate
RabGTPases completely 'outsource' their specificity for each other to an
accessory subunit, the Rab escort protein (REP). REP mediates the placement of
the C terminus of RabGTPase into the active site of RabGGTase through a series
protein-protein interactions of decreasing strength and selectivity. This
arrangement enables RabGGTase to prenylate any cysteine-containing sequence. On
the basis of our structural and thermodynamic data, we propose that RabGGTase
has evolved from a GGTase-I-like molecule that 'learned' to interact with a
recycling factor (GDI) that, in turn, eventually gave rise to REP.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.Brighouse,
J.B.Dacks,
and
M.C.Field
(2010).
Rab protein evolution and the history of the eukaryotic endomembrane system.
|
| |
Cell Mol Life Sci,
67,
3449-3465.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.L.Hovlid,
R.L.Edelstein,
O.Henry,
J.Ochocki,
A.DeGraw,
S.Lenevich,
T.Talbot,
V.G.Young,
A.W.Hruza,
F.Lopez-Gallego,
N.P.Labello,
C.L.Strickland,
C.Schmidt-Dannert,
and
M.D.Distefano
(2010).
Synthesis, properties, and applications of diazotrifluropropanoyl-containing photoactive analogs of farnesyl diphosphate containing modified linkages for enhanced stability.
|
| |
Chem Biol Drug Des,
75,
51-67.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
U.T.Nguyen,
R.S.Goody,
and
K.Alexandrov
(2010).
Understanding and exploiting protein prenyltransferases.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
11,
1194-1201.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
U.T.Nguyen,
Z.Guo,
C.Delon,
Y.Wu,
C.Deraeve,
B.Fränzel,
R.S.Bon,
W.Blankenfeldt,
R.S.Goody,
H.Waldmann,
D.Wolters,
and
K.Alexandrov
(2009).
Analysis of the eukaryotic prenylome by isoprenoid affinity tagging.
|
| |
Nat Chem Biol,
5,
227-235.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.W.Wu,
R.S.Goody,
R.Abagyan,
and
K.Alexandrov
(2009).
Structure of the Disordered C Terminus of Rab7 GTPase Induced by Binding to the Rab Geranylgeranyl Transferase Catalytic Complex Reveals the Mechanism of Rab Prenylation.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
13185-13192.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |
|

