 |
PDBsum entry 2rjs

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.4.3.1.23
- tyrosine ammonia-lyase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-tyrosine = (E)-4-coumarate + NH4+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-tyrosine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 70.59% similarity
|
=
|
(E)-4-coumarate
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
MIO
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.5.4.3.6
- tyrosine 2,3-aminomutase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-tyrosine = 3-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
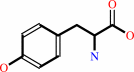 L-tyrosine
L-tyrosine
|
=
|
3-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 81.25% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
MIO
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cobalamin
|
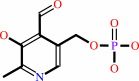 Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Bioorg Med Chem Lett
18:3099-3102
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Design and characterization of mechanism-based inhibitors for the tyrosine aminomutase SgTAM.
|
|
T.J.Montavon,
C.V.Christianson,
G.M.Festin,
B.Shen,
S.D.Bruner.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The synthesis and evaluation of two classes of inhibitors for SgTAM, a
4-methylideneimidazole-5-one (MIO) containing tyrosine aminomutase, are
described. A mechanism-based strategy was used to design analogs that mimic the
substrate or product of the reaction and form covalent interactions with the
enzyme through the MIO prosthetic group. The analogs were characterized by
measuring inhibition constants and X-ray crystallographic structural analysis of
the co-complexes bound to the aminomutase, SgTAM.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
H.A.Cooke,
and
S.D.Bruner
(2010).
Probing the active site of MIO-dependent aminomutases, key catalysts in the biosynthesis of beta-amino acids incorporated in secondary metabolites.
|
| |
Biopolymers,
93,
802-810.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.X.Liang
(2010).
Complexity and simplicity in the biosynthesis of enediyne natural products.
|
| |
Nat Prod Rep,
27,
499-528.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Wu,
W.Szymanski,
P.Wietzes,
S.de Wildeman,
G.J.Poelarends,
B.L.Feringa,
and
D.B.Janssen
(2009).
Enzymatic Synthesis of Enantiopure alpha- and beta-Amino Acids by Phenylalanine Aminomutase-Catalysed Amination of Cinnamic Acid Derivatives.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
10,
338-344.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.A.Cooke,
C.V.Christianson,
and
S.D.Bruner
(2009).
Structure and chemistry of 4-methylideneimidazole-5-one containing enzymes.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
13,
460-468.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.L.Meier,
and
M.D.Burkart
(2009).
The chemical biology of modular biosynthetic enzymes.
|
| |
Chem Soc Rev,
38,
2012-2045.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

