 |
PDBsum entry 2pc6

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of putative acetolactate synthase- small subunit from nitrosomonas europaea
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Probable acetolactate synthase isozyme iii (small subunit). Chain: a, b, c, d. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Nitrosomonas europaea atcc 19718. Organism_taxid: 228410. Strain: ifo 14298. Gene: ilvh, ne1324. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.50Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.208
|
R-free:
|
0.276
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.J.Petkowski,M.Chruszcz,M.D.Zimmerman,H.Zheng,M.T.Cymborowski, T.Skarina,O.Onopriyenko,A.Savchenko,A.Edwards,W.Minor,A.Joachimiak, Midwest Center For Structural Genomics (Mcsg)
|
Key ref:

|
 |
J.J.Petkowski
et al.
(2007).
Crystal structures of TM0549 and NE1324--two orthologs of E. coli AHAS isozyme III small regulatory subunit.
Protein Sci,
16,
1360-1367.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
29-Mar-07
|
Release date:
|
10-Apr-07
|
|
|
Supersedes:
|

|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q82UZ2
(Q82UZ2_NITEU) -
Acetolactate synthase small subunit from Nitrosomonas europaea (strain ATCC 19718 / CIP 103999 / KCTC 2705 / NBRC 14298)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
163 a.a.
164 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.2.1.6
- acetolactate synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Isoleucine and Valine Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
2 pyruvate + H+ = (2S)-2-acetolactate + CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 2
×
pyruvate
2
×
pyruvate
|
+
|
H(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 70.00% similarity
|
=
|
(2S)-2-acetolactate
|
+
|
 CO2
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Thiamine diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
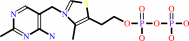 Thiamine diphosphate
Thiamine diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Protein Sci
16:1360-1367
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structures of TM0549 and NE1324--two orthologs of E. coli AHAS isozyme III small regulatory subunit.
|
|
J.J.Petkowski,
M.Chruszcz,
M.D.Zimmerman,
H.Zheng,
T.Skarina,
O.Onopriyenko,
M.T.Cymborowski,
K.D.Koclega,
A.Savchenko,
A.Edwards,
W.Minor.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Crystal structures of two orthologs of the regulatory subunit of
acetohydroxyacid synthase III (AHAS, EC 2.2.1.6) from Thermotoga maritima
(TM0549) and Nitrosomonas europea (NE1324) were determined by single-wavelength
anomalous diffraction methods with the use of selenomethionine derivatives at
2.3 A and 2.5 A, respectively. TM0549 and NE1324 share the same fold, and in
both proteins the polypeptide chain contains two separate domains of a similar
size. Each protein contains a C-terminal domain with ferredoxin-type fold and an
N-terminal ACT domain, of which the latter is characteristic for several
proteins involved in amino acid metabolism. The ferredoxin domain is stabilized
by a calcium ion in the crystal structure of NE1324 and by a Mg(H2O)(6)2+ ion in
TM0549. Both TM0549 and NE1324 form dimeric assemblies in the crystal lattice.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
Figure 2. (A) Sequence alignment of NE1324 (NE), SSU from E. coli (EC), and TM0549 (TM). Conserved amino acids marked by
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figure is
reprinted
by permission from the Protein Society:
Protein Sci
(2007,
16,
1360-1367)
copyright 2007.
|
|
| |
Figure was
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
M.Kyselková,
J.Janata,
M.Ságová-Marecková,
and
J.Kopecký
(2010).
Subunit-subunit interactions are weakened in mutant forms of acetohydroxy acid synthase insensitive to valine inhibition.
|
| |
Arch Microbiol,
192,
195-200.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

