 |
PDBsum entry 1vlr

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
RNA binding protein
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1vlr
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.6.1.59
- 5'-(N(7)-methyl 5'-triphosphoguanosine)-[mRNA] diphosphatase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 5'-end (N7-methyl 5'-triphosphoguanosine)-ribonucleoside in mRNA + H2O = N(7)-methyl-GMP + a 5'-end diphospho-ribonucleoside in mRNA + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
M(7)G5'ppp5'N(3'ppp5'N)(n)
|
+
|
H(2)O
|
=
|
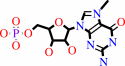 7-methylguanosine 5'-phosphate
7-methylguanosine 5'-phosphate
|
+
|
pp5'N(3'ppp5'N)(n)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
7-methylguanosine 5'-diphosphate
|
+
|
H(2)O
|
=
|
 7-methylguanosine 5'-phosphate
7-methylguanosine 5'-phosphate
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proteins
60:797-802
(2005)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of an Apo mRNA decapping enzyme (DcpS) from Mouse at 1.83 A resolution.
|
|
G.W.Han,
R.Schwarzenbacher,
D.McMullan,
P.Abdubek,
E.Ambing,
H.Axelrod,
T.Biorac,
J.M.Canaves,
H.J.Chiu,
X.Dai,
A.M.Deacon,
M.DiDonato,
M.A.Elsliger,
A.Godzik,
C.Grittini,
S.K.Grzechnik,
J.Hale,
E.Hampton,
J.Haugen,
M.Hornsby,
L.Jaroszewski,
H.E.Klock,
E.Koesema,
A.Kreusch,
P.Kuhn,
S.A.Lesley,
T.M.McPhillips,
M.D.Miller,
K.Moy,
E.Nigoghossian,
J.Paulsen,
K.Quijano,
R.Reyes,
G.Spraggon,
R.C.Stevens,
H.van den Bedem,
J.Velasquez,
J.Vincent,
A.White,
G.Wolf,
Q.Xu,
K.O.Hodgson,
J.Wooley,
I.A.Wilson.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. Crystal structure of mRNA decapping enzyme (DcpS)
from Mouse. (A) Stereo ribbon diagram of Mouse DcpS color-coded
from N-terminus (blue) to C-terminus (red) showing the domain
organization with helices H1-H13 and  -strands -strands
 1- 1-
 14,
as well as 14,
as well as  -sheets
A, B, C, and D. (B) Diagram showing the secondary structure
elements in Mouse DcpS (chain A) superimposed on its primary
sequence. The -sheets
A, B, C, and D. (B) Diagram showing the secondary structure
elements in Mouse DcpS (chain A) superimposed on its primary
sequence. The  -sheet
strands are indicated by a red A, B, C, and D. -sheet
strands are indicated by a red A, B, C, and D.  -bulges
and -bulges
and  -turns
are indicated. -turns
are indicated.  -hairpins
are depicted as red loops. Disordered regions are depicted by a
dashed line with the corresponding sequence in brackets. The HIT
sequence motif is indicated by a black line above the three
histidines. -hairpins
are depicted as red loops. Disordered regions are depicted by a
dashed line with the corresponding sequence in brackets. The HIT
sequence motif is indicated by a black line above the three
histidines.
|
 |
Figure 2.
Figure 2. Comparison of Mouse and human DcpS. (A) Ribbon
diagram of the Mouse DcpS dimer. Chain A is in gray and chain B
is in pink. The dimer is symmetric with a C  -C -C
 distance
between Asp110 and Trp174 of distance
between Asp110 and Trp174 of  28
Å. Residues 131 and 147 flanking the linker region are
labeled. (B) Ribbon diagram of the human DcpS/mGpppG complex.
Chain A is shown in gray and chain B in purple. The dimer has a
symmetric bottom and an asymmetric top and features an open side
and a closed side with a 36 Å and 6 Å C 28
Å. Residues 131 and 147 flanking the linker region are
labeled. (B) Ribbon diagram of the human DcpS/mGpppG complex.
Chain A is shown in gray and chain B in purple. The dimer has a
symmetric bottom and an asymmetric top and features an open side
and a closed side with a 36 Å and 6 Å C  -C -C
 gap
between Asp111 and Trp175, respectively. The mGpppG nucleotides
bound to the active sites are shown in ball-and-stick
configuration, with carbon atoms colored in yellow, phosphorous
in purple, oxygen in red, and nitrogen in blue. The movement of
the N-terminal domain is facilitated by a conformational change
in the linker region around helix gap
between Asp111 and Trp175, respectively. The mGpppG nucleotides
bound to the active sites are shown in ball-and-stick
configuration, with carbon atoms colored in yellow, phosphorous
in purple, oxygen in red, and nitrogen in blue. The movement of
the N-terminal domain is facilitated by a conformational change
in the linker region around helix  3.
Superposition of the DcpS active sites in the relaxed empty
state with the open (C) and closed (D) mGpppG bound state. The
mGpppG-interacting residues from human DcpS (gray, residues
labeled in brackets) and their counterparts in Mouse DcpS (blue)
are shown in ball-and-stick configuration. 3.
Superposition of the DcpS active sites in the relaxed empty
state with the open (C) and closed (D) mGpppG bound state. The
mGpppG-interacting residues from human DcpS (gray, residues
labeled in brackets) and their counterparts in Mouse DcpS (blue)
are shown in ball-and-stick configuration.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from John Wiley & Sons, Inc.:
Proteins
(2005,
60,
797-802)
copyright 2005.
|
|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.Singh,
M.Salcius,
S.W.Liu,
B.L.Staker,
R.Mishra,
J.Thurmond,
G.Michaud,
D.R.Mattoon,
J.Printen,
J.Christensen,
J.M.Bjornsson,
B.A.Pollok,
M.Kiledjian,
L.Stewart,
J.Jarecki,
and
M.E.Gurney
(2008).
DcpS as a therapeutic target for spinal muscular atrophy.
|
| |
ACS Chem Biol,
3,
711-722.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

