 |
PDBsum entry 1vip

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.4
- phospholipase A2.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine + H2O = a 1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine + a fatty acid + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
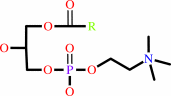 1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine
1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine
|
+
|
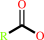 fatty acid
fatty acid
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Ca(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Toxicon
36:75-92
(1998)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The three-dimensional structures of two toxins from snake venom throw light on the anticoagulant and neurotoxic sites of phospholipase A2.
|
|
E.Carredano,
B.Westerlund,
B.Persson,
M.Saarinen,
S.Ramaswamy,
D.Eaker,
H.Eklund.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The three-dimensional structures of the class II anticoagulant phospholipase A2
(PLA2) toxin RVV-VD from the venom of Russell's viper, Vipera russelli russelli,
and the class I neurotoxic PLA2 Notechis II-5 from the, Australian tiger snake,
Notechis scutatus scutatus, were determined to 2.2 A and 3.0 A resolution,
respectively. Both enzymes are monomeric and consist of 121 and 119 residues,
respectively. A comparison of ten class I/II PLA2 structures showed, among other
differences, that the beta-sheet of these enzymes (residues 76-83) is about 90
degrees less twisted in class I than in class II PLA2s. This, along with the
insertion of some residues in the region 57-59 in class I enzymes (the elapid
loop), could be the main reason for the significant difference in the
anticoagulant and (presynaptic) neurotoxic properties between the two classes of
PLA2. It seems apparent from sequence and structural comparisons that the toxic
site of PLA2 responsible for the strong anticoagulancy of these toxins consists
of a negatively charged part, Glu53, together with a positively charged ridge of
lysine residues free for intermolecular interactions. These lysines differ
between the two classes of PLA2.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.Razpotnik,
I.Krizaj,
J.Sribar,
D.Kordis,
P.Macek,
R.Frangez,
W.R.Kem,
and
T.Turk
(2010).
A new phospholipase A2 isolated from the sea anemone Urticina crassicornis - its primary structure and phylogenetic classification.
|
| |
FEBS J,
277,
2641-2653.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.P.Marchi-Salvador,
L.C.Corrêa,
A.J.Magro,
C.Z.Oliveira,
A.M.Soares,
and
M.R.Fontes
(2008).
Insights into the role of oligomeric state on the biological activities of crotoxin: crystal structure of a tetrameric phospholipase A2 formed by two isoforms of crotoxin B from Crotalus durissus terrificus venom.
|
| |
Proteins,
72,
883-891.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.L.Gibbs,
and
W.Rossiter
(2008).
Rapid evolution by positive selection and gene gain and loss: PLA(2) venom genes in closely related Sistrurus rattlesnakes with divergent diets.
|
| |
J Mol Evol,
66,
151-166.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Faure,
V.T.Gowda,
and
R.C.Maroun
(2007).
Characterization of human coagulation factor Xa-binding site on Viperidae snake venom phospholipases A2 by affinity binding studies and molecular bioinformatics.
|
| |
BMC Struct Biol,
7,
82.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.J.Magro,
A.A.Takeda,
A.M.Soares,
and
M.R.Fontes
(2005).
Structure of BthA-I complexed with p-bromophenacyl bromide: possible correlations with lack of pharmacological activity.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
61,
1670-1677.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.M.Wang,
H.F.Peng,
and
I.H.Tsai
(2005).
Unusual venom phospholipases A2 of two primitive tree vipers Trimeresurus puniceus and Trimeresurus borneensis.
|
| |
FEBS J,
272,
3015-3025.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.J.Rigden,
L.W.Hwa,
S.Marangoni,
M.H.Toyama,
and
I.Polikarpov
(2003).
The structure of the D49 phospholipase A2 piratoxin III from Bothrops pirajai reveals unprecedented structural displacement of the calcium-binding loop: possiblerelationship to cooperative substrate binding.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
59,
255-262.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Perbandt,
I.H.Tsai,
A.Fuchs,
S.Banumathi,
K.R.Rajashankar,
D.Georgieva,
N.Kalkura,
T.P.Singh,
N.Genov,
and
C.Betzel
(2003).
Structure of the heterodimeric neurotoxic complex viperotoxin F (RV-4/RV-7) from the venom of Vipera russelli formosensis at 1.9 A resolution.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
59,
1679-1687.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
W.H.Lee,
M.T.da Silva Giotto,
S.Marangoni,
M.H.Toyama,
I.Polikarpov,
and
R.C.Garratt
(2001).
Structural basis for low catalytic activity in Lys49 phospholipases A2--a hypothesis: the crystal structure of piratoxin II complexed to fatty acid.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
40,
28-36.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Montecucco,
and
O.Rossetto
(2000).
How do presynaptic PLA2 neurotoxins block nerve terminals?
|
| |
Trends Biochem Sci,
25,
266-270.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Reichsman,
H.M.Moore,
and
S.Cumberledge
(1999).
Sequence homology between Wingless/Wnt-1 and a lipid-binding domain in secreted phospholipase A2.
|
| |
Curr Biol,
9,
R353-R355.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

