 |
PDBsum entry 1vfl

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.4.4
- adenosine deaminase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
adenosine + H2O + H+ = inosine + NH4+
|
|
2.
|
2'-deoxyadenosine + H2O + H+ = 2'-deoxyinosine + NH4+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
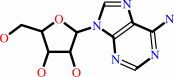 adenosine
adenosine
|
+
|
H2O
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
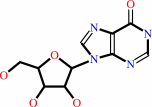 inosine
inosine
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 2'-deoxyadenosine
2'-deoxyadenosine
|
+
|
H2O
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
2'-deoxyinosine
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
44:10562-10569
(2005)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural basis of compound recognition by adenosine deaminase.
|
|
T.Kinoshita,
I.Nakanishi,
T.Terasaka,
M.Kuno,
N.Seki,
M.Warizaya,
H.Matsumura,
T.Inoue,
K.Takano,
H.Adachi,
Y.Mori,
T.Fujii.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Structural snapshots corresponding to various states enable elucidation of the
molecular recognition mechanism of enzymes. Adenosine deaminase has two distinct
conformations, an open form and a closed form, although it has so far been
unclear what factors influence adaptation of the alternative conformations.
Herein, we have determined the first nonligated structure as an initial state,
which was the open form, and have thereby rationally deduced the molecular
recognition mechanism. Inspection of the active site in the nonligated and
ligated states indicated that occupancy at one of the water-binding positions in
the nonligated state was highly significant in determining alternate
conformations. When this position is empty, subsequent movement of Phe65 toward
the space induces the closed form. On the other hand, while occupied, the
overall conformation remains in the open form. This structural understanding
should greatly assist structure-oriented drug design and enable control of the
enzymatic activity.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
E.T.Larson,
W.Deng,
B.E.Krumm,
A.Napuli,
N.Mueller,
W.C.Van Voorhis,
F.S.Buckner,
E.Fan,
A.Lauricella,
G.DeTitta,
J.Luft,
F.Zucker,
W.G.Hol,
C.L.Verlinde,
and
E.A.Merritt
(2008).
Structures of substrate- and inhibitor-bound adenosine deaminase from a human malaria parasite show a dramatic conformational change and shed light on drug selectivity.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
381,
975-988.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Kinoshita
(2007).
[Application and development of structure-based drug design using X-ray analysis]
|
| |
Nippon Yakurigaku Zasshi,
129,
186-190.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

