 |
PDBsum entry 1v9y

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Signaling protein
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1v9y
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.4.52
- cyclic-guanylate-specific phosphodiesterase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
3',3'-c-di-GMP + H2O = 5'-phosphoguanylyl(3'->5')guanosine + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
3',3'-c-di-GMP
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
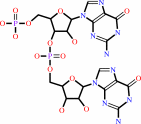 5'-phosphoguanylyl(3'->5')guanosine
5'-phosphoguanylyl(3'->5')guanosine
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Heme; Mg(2+); Mn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Heme
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
HEM)
matches with 95.45% similarity
|
Mg(2+)
|
Mn(2+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
279:20186-20193
(2004)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
A redox-controlled molecular switch revealed by the crystal structure of a bacterial heme PAS sensor.
|
|
H.Kurokawa,
D.S.Lee,
M.Watanabe,
I.Sagami,
B.Mikami,
C.S.Raman,
T.Shimizu.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
PAS domains, which have been identified in over 1100 proteins from all three
kingdoms of life, convert various input stimuli into signals that propagate to
downstream components by modifying protein-protein interactions. One such
protein is the Escherichia coli redox sensor, Ec DOS, a phosphodiesterase that
degrades cyclic adenosine monophosphate in a redox-dependent manner. Here we
report the crystal structures of the heme PAS domain of Ec DOS in both inactive
Fe(3+) and active Fe(2+) forms at 1.32 and 1.9 A resolution, respectively. The
protein folds into a characteristic PAS domain structure and forms a homodimer.
In the Fe(3+) form, the heme iron is ligated to a His-77 side chain and a water
molecule. Heme iron reduction is accompanied by heme-ligand switching from the
water molecule to a side chain of Met-95 from the FG loop. Concomitantly, the
flexible FG loop is significantly rigidified, along with a change in the
hydrogen bonding pattern and rotation of subunits relative to each other. The
present data led us to propose a novel redox-regulated molecular switch in which
local heme-ligand switching may trigger a global "scissor-type"
subunit movement that facilitates catalytic control.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
FIG. 2. Dimer of Ec DOSH and redox-induced changes at the
heme distal site. a, left, Fe^3+ form of the Ec DOSH dimer. The
2-fold axis of subunits is specified as a blue stick. Right, the
view after 90° rotation of the left figure. Heme and
proximal histidine 77 are shown as a ball-and-stick model.
Disordered FG loop regions are indicated by blue broken lines.
Water molecules are represented by spheres (cyan). N, N
terminus; C, C terminus. b, close-up view of the heme site of
the Fe^3+ form of Ec DOSH (left); the same region of the Fe^2+
form (right). FG loop regions are rigidified in the Fe^2+ form
(cyan). The distal axial ligand is replaced by Met-95, as
indicated in the sphere model.
|
 |
Figure 4.
FIG. 4. Reorganization of the hydrogen bond network at the
heme distal site near the dimer interface. a, comparison of heme
distal sites between Fe^3+ (cyan) and Fe^2+ (yellow) forms of Ec
DOSH. Residues 31-85 and 97-132 of subunit I in each form were
superimposed. Residues in subunit II are colored in blue for the
Fe^3+ form and orange for the Fe^2+ form. Hydrogen bonds are
presented as dotted lines. Met-95 coordination to the heme iron
upon reduction induces reorganization of the hydrogen bond
network at the heme distal site. Side chains of Phe-113 and
Leu-115 move slightly to adjust to heme-ligand switching. These
changes induce hydrogen bond formation between Phe-113 and
Arg-131. No effects were observed on the hydrogen bond between
Ser-116 and Met-30. The buried dimer surface areas of the Fe^3+
form (b) and Fe^2+ form (c) of subunit I are shown. Distances
between the surfaces of each subunit were calculated with MOLMOL
and ranged from <2 Å (red) to >7 Å (blue). Met-30
and Arg-131 of subunit II are presented as a stick model.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2004,
279,
20186-20193)
copyright 2004.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by the author.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
K.J.Watts,
B.L.Taylor,
and
M.S.Johnson
(2011).
PAS/poly-HAMP signalling in Aer-2, a soluble haem-based sensor.
|
| |
Mol Microbiol,
79,
686-699.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.J.Austin,
B.M.Mailu,
G.J.Maghzal,
A.Sanchez-Perez,
S.Rahlfs,
K.Zocher,
H.J.Yuasa,
J.W.Arthur,
K.Becker,
R.Stocker,
N.H.Hunt,
and
H.J.Ball
(2010).
Biochemical characteristics and inhibitor selectivity of mouse indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-2.
|
| |
Amino Acids,
39,
565-578.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Kobayashi,
A.Tanaka,
H.Takahashi,
J.Igarashi,
Y.Ishitsuka,
N.Yokota,
and
T.Shimizu
(2010).
Catalysis and oxygen binding of Ec DOS: a haem-based oxygen-sensor enzyme from Escherichia coli.
|
| |
J Biochem,
148,
693-703.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Slavny,
R.Little,
P.Salinas,
T.A.Clarke,
and
R.Dixon
(2010).
Quaternary structure changes in a second Per-Arnt-Sim domain mediate intramolecular redox signal relay in the NifL regulatory protein.
|
| |
Mol Microbiol,
75,
61-75.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Möglich,
R.A.Ayers,
and
K.Moffat
(2009).
Structure and signaling mechanism of Per-ARNT-Sim domains.
|
| |
Structure,
17,
1282-1294.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Lechauve,
L.Bouzhir-Sima,
T.Yamashita,
M.C.Marden,
M.H.Vos,
U.Liebl,
and
L.Kiger
(2009).
Heme ligand binding properties and intradimer interactions in the full-length sensor protein dos from Escherichia coli and its isolated heme domain.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
36146-36159.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.W.Outten,
and
E.C.Theil
(2009).
Iron-based redox switches in biology.
|
| |
Antioxid Redox Signal,
11,
1029-1046.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.S.Brody,
V.Stewart,
and
C.W.Price
(2009).
Bypass suppression analysis maps the signalling pathway within a multidomain protein: the RsbP energy stress phosphatase 2C from Bacillus subtilis.
|
| |
Mol Microbiol,
72,
1221-1234.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.K.Small,
S.Puri,
and
M.R.O'Brian
(2009).
Heme-dependent metalloregulation by the iron response regulator (Irr) protein in Rhizobium and other Alpha-proteobacteria.
|
| |
Biometals,
22,
89-97.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Yamada,
H.Sugimoto,
M.Kobayashi,
A.Ohno,
H.Nakamura,
and
Y.Shiro
(2009).
Structure of PAS-linked histidine kinase and the response regulator complex.
|
| |
Structure,
17,
1333-1344.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.H.Scheuermann,
D.R.Tomchick,
M.Machius,
Y.Guo,
R.K.Bruick,
and
K.H.Gardner
(2009).
Artificial ligand binding within the HIF2alpha PAS-B domain of the HIF2 transcription factor.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
106,
450-455.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.K.Bidwai,
E.Y.Ok,
and
J.E.Erman
(2008).
pH dependence of cyanide binding to the ferric heme domain of the direct oxygen sensor from Escherichia coli and the effect of alkaline denaturation.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
10458-10470.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.D.Zoltowski,
and
B.R.Crane
(2008).
Light activation of the LOV protein vivid generates a rapidly exchanging dimer.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
7012-7019.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.A.Marvin,
R.L.Kerby,
H.Youn,
G.P.Roberts,
and
J.N.Burstyn
(2008).
The transcription regulator RcoM-2 from Burkholderia xenovorans is a cysteine-ligated hemoprotein that undergoes a redox-mediated ligand switch.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
9016-9028.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.J.Watts,
M.S.Johnson,
and
B.L.Taylor
(2008).
Structure-function relationships in the HAMP and proximal signaling domains of the aerotaxis receptor Aer.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
190,
2118-2127.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.M.Podust,
A.Ioanoviciu,
and
P.R.Ortiz de Montellano
(2008).
2.3 A X-ray structure of the heme-bound GAF domain of sensory histidine kinase DosT of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
12523-12531.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.A.Ayers,
and
K.Moffat
(2008).
Changes in quaternary structure in the signaling mechanisms of PAS domains.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
12078-12086.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.L.Kerby,
H.Youn,
and
G.P.Roberts
(2008).
RcoM: a new single-component transcriptional regulator of CO metabolism in bacteria.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
190,
3336-3343.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
X.Ma,
N.Sayed,
P.Baskaran,
A.Beuve,
and
F.van den Akker
(2008).
PAS-mediated dimerization of soluble guanylyl cyclase revealed by signal transduction histidine kinase domain crystal structure.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
1167-1178.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Möglich,
and
K.Moffat
(2007).
Structural basis for light-dependent signaling in the dimeric LOV domain of the photosensor YtvA.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
373,
112-126.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Schneider,
J.Marles-Wright,
K.H.Sharp,
and
M.Paoli
(2007).
Diversity and conservation of interactions for binding heme in b-type heme proteins.
|
| |
Nat Prod Rep,
24,
621-630.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Singh,
P.Madzelan,
and
R.Banerjee
(2007).
Properties of an unusual heme cofactor in PLP-dependent cystathionine beta-synthase.
|
| |
Nat Prod Rep,
24,
631-639.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Khorchid,
and
M.Ikura
(2006).
Bacterial histidine kinase as signal sensor and transducer.
|
| |
Int J Biochem Cell Biol,
38,
307-312.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.J.Watts,
K.Sommer,
S.L.Fry,
M.S.Johnson,
and
B.L.Taylor
(2006).
Function of the N-terminal cap of the PAS domain in signaling by the aerotaxis receptor Aer.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
188,
2154-2162.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Yokota,
Y.Araki,
H.Kurokawa,
O.Ito,
J.Igarashi,
and
T.Shimizu
(2006).
Critical roles of Leu99 and Leu115 at the heme distal side in auto-oxidation and the redox potential of a heme-regulated phosphodiesterase from Escherichia coli.
|
| |
FEBS J,
273,
1210-1223.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Mukaiyama,
T.Uchida,
E.Sato,
A.Sasaki,
Y.Sato,
J.Igarashi,
H.Kurokawa,
I.Sagami,
T.Kitagawa,
and
T.Shimizu
(2006).
Spectroscopic and DNA-binding characterization of the isolated heme-bound basic helix-loop-helix-PAS-A domain of neuronal PAS protein 2 (NPAS2), a transcription activator protein associated with circadian rhythms.
|
| |
FEBS J,
273,
2528-2539.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Reinking,
M.M.Lam,
K.Pardee,
H.M.Sampson,
S.Liu,
P.Yang,
S.Williams,
W.White,
G.Lajoie,
A.Edwards,
and
H.M.Krause
(2005).
The Drosophila nuclear receptor e75 contains heme and is gas responsive.
|
| |
Cell,
122,
195-207.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Koudo,
H.Kurokawa,
E.Sato,
J.Igarashi,
T.Uchida,
I.Sagami,
T.Kitagawa,
and
T.Shimizu
(2005).
Spectroscopic characterization of the isolated heme-bound PAS-B domain of neuronal PAS domain protein 2 associated with circadian rhythms.
|
| |
FEBS J,
272,
4153-4162.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Yoshimura-Suzuki,
I.Sagami,
N.Yokota,
H.Kurokawa,
and
T.Shimizu
(2005).
DOS(Ec), a heme-regulated phosphodiesterase, plays an important role in the regulation of the cyclic AMP level in Escherichia coli.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
187,
6678-6682.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Green,
and
M.S.Paget
(2004).
Bacterial redox sensors.
|
| |
Nat Rev Microbiol,
2,
954-966.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Watanabe,
H.Kurokawa,
T.Yoshimura-Suzuki,
I.Sagami,
and
T.Shimizu
(2004).
Critical roles of Asp40 at the haem proximal side of haem-regulated phosphodiesterase from Escherichia coli in redox potential, auto-oxidation and catalytic control.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
271,
3937-3942.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

