 |
PDBsum entry 1tpf

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Isomerase(intramolecular oxidoreductase)
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1tpf
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.5.3.1.1
- triose-phosphate isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate = dihydroxyacetone phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
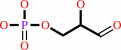 D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
|
=
|
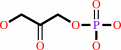 dihydroxyacetone phosphate
dihydroxyacetone phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Protein Sci
3:779-787
(1994)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Comparison of the structures and the crystal contacts of trypanosomal triosephosphate isomerase in four different crystal forms.
|
|
K.V.Kishan,
J.P.Zeelen,
M.E.Noble,
T.V.Borchert,
R.K.Wierenga.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Triosephosphate isomerase (TIM) is a dimeric enzyme consisting of 2 identical
subunits. Trypanosomal TIM can be crystallized in 4 different spacegroups:
P2(1)2(1)2(1), C2(big cell), C2(small cell), and P1. The P1 crystal form only
grows in the presence of 1.4 M DMSO; there are 2 DMSO binding sites per subunit.
The structures have been refined at a resolution of 1.83 A, 2.10 A, 2.13 A, and
1.80 A, respectively. In the 4 different spacegroups the TIM subunit can be
observed in the context of 7 different crystallographic environments. In the C2
cells, the dimer 2-fold axis coincides with a crystallographic 2-fold axis. The
similarities and differences of the 7 subunits are discussed. In 6 subunits the
flexible loop (loop 6) is open, whereas in the P2(1)2(1)2(1) cell, the flexible
loop of subunit 2 is in an almost closed conformation. The crystal contacts in
the 4 different crystal forms are predominantly generated by polar residues in
loops. A statistical analysis of the residues involved in crystal contacts shows
that, in particular, serines are frequently involved in these interactions; 19%
of the exposed serines are involved in crystal contacts.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
Fig. 2. Superposition of the7different
loop 6structures.Thedeviating loop 6
structureisthe closed structure as ob-
servedinsubunit of theP212121form.
Glu 167is one of theactivesiteresdues.
Residues172-175 move asarigid ody
(Wierengaet al., 1991a).
|
 |
Figure 3.
Fig. 3. Residuesinvolvedin crystal con-
tacts in the 4 different crysta! forms. The
cut-off value usedwas 3.5 A, therefore
only tight crystal contact interactions have
been considered. The labeled secondary
structure elements identify the@-strands
and a-helics of the 8 (&)-units. At the
bottom f he figure: Ntot(residues)
counts the total number ofresiduesin the
4 different secondary structure elements.
Ntot(contacts)countsthe accumulated
number of crystal contact residues per
type of secondary structure. The loops be-
forethe @-strands are located at he back
side of thesubunit,far frm the active
site; theloopsafterthe@-strandsare at
thefront side of thesubunit, near the ac-
tivesite (loop 1-loop 8) and near the di-
mer interface (loop 1-loop 4).
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
from an Open Access publication published by the Protein Society:
Protein Sci
(1994,
3,
779-787)
copyright 1994.
|
|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
K.V.Kishan,
M.E.Newcomer,
T.H.Rhodes,
and
S.D.Guilliot
(2001).
Effect of pH and salt bridges on structural assembly: molecular structures of the monomer and intertwined dimer of the Eps8 SH3 domain.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
10,
1046-1055.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.R.Gunner,
M.A.Saleh,
E.Cross,
A.ud-Doula,
and
M.Wise
(2000).
Backbone dipoles generate positive potentials in all proteins: origins and implications of the effect.
|
| |
Biophys J,
78,
1126-1144.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Dasgupta,
G.H.Iyer,
S.H.Bryant,
C.E.Lawrence,
and
J.A.Bell
(1997).
Extent and nature of contacts between protein molecules in crystal lattices and between subunits of protein oligomers.
|
| |
Proteins,
28,
494-514.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.V.Kurinov,
and
R.W.Harrison
(1996).
Two crystal structures of the leupeptin-trypsin complex.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
5,
752-758.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.D.Durbin,
and
G.Feher
(1996).
Protein crystallization.
|
| |
Annu Rev Phys Chem,
47,
171-204.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

