 |
PDBsum entry 1r9c

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.2.5.1.1
- dimethylallyltranstransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Terpenoid biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
isopentenyl diphosphate + dimethylallyl diphosphate = (2E)- geranyl diphosphate + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
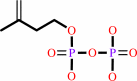 isopentenyl diphosphate
isopentenyl diphosphate
|
+
|
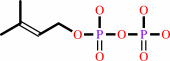 dimethylallyl diphosphate
dimethylallyl diphosphate
|
=
|
(2E)- geranyl diphosphate
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Am Chem Soc
125:15730-15731
(2003)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Mechanistic diversity of fosfomycin resistance in pathogenic microorganisms.
|
|
K.L.Fillgrove,
S.Pakhomova,
M.E.Newcomer,
R.N.Armstrong.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Microbial resistance to the antibiotic fosfomycin [(1R,2S)-epoxypropylphosphonic
acid, 1] is known to be mediated by thiol transferase enzymes FosA and FosB,
which catalyze the addition of glutathione and l-cysteine to C1 of the oxirane,
respectively. A probe of the microbial genome database reveals a related group
of enzymes (FosX). The genes mlr3345 from Mesorhizobium loti and lmo1702 from
Listeria monocytogenes were cloned and the proteins expressed. This heretofore
unrecognized group of enzymes is shown to catalyze the Mn(II)-dependent addition
of water to C1 of the oxirane. The ability of each enzyme to confer resistance
in Escherichia coli is correlated with their catalytic efficiency, such that the
M. loti protein confers low resistance while the Listeria enzyme confers very
robust resistance. The crystal structure of the FosX from M. loti was solved at
a resolution of 1.83 A. The structure reveals an active-site carboxylate (E44)
located about 5 A from the expected position of the substrate that appears to be
poised to participate in catalysis. Single turnover experiments in H218O and
kinetic analysis of the E44G mutant of the FosX enzymes indicate that the
carboxylate of E44 acts as a general base in the direct addition of water to 1.
The FosX from M. loti also catalyzes the addition of glutathione to the
antibiotic. The catalytic promiscuity and low efficiency of the M. loti protein
suggest that it may be an intermediate in the evolution of clinically relevant
fosfomycin resistance proteins such as the FosX from Listeria monocytogenese.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
V.N.De Groote,
M.Fauvart,
C.I.Kint,
N.Verstraeten,
A.Jans,
P.Cornelis,
and
J.Michiels
(2011).
Pseudomonas aeruginosa fosfomycin resistance mechanisms affect non-inherited fluoroquinolone tolerance.
|
| |
J Med Microbiol,
60,
329-336.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Morar,
and
G.D.Wright
(2010).
The genomic enzymology of antibiotic resistance.
|
| |
Annu Rev Genet,
44,
25-51.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.W.Brown,
M.R.Schaab,
W.R.Birmingham,
and
R.N.Armstrong
(2009).
Evolution of the antibiotic resistance protein, FosA, is linked to a catalytically promiscuous progenitor.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
1847-1849.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Decker,
M.Arand,
and
A.Cronin
(2009).
Mammalian epoxide hydrolases in xenobiotic metabolism and signalling.
|
| |
Arch Toxicol,
83,
297-318.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Allocati,
L.Federici,
M.Masulli,
and
C.Di Ilio
(2009).
Glutathione transferases in bacteria.
|
| |
FEBS J,
276,
58-75.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Kumar,
A.Parvathi,
R.L.Hernandez,
K.M.Cadle,
and
M.F.Varela
(2009).
Identification of a novel UDP-N-acetylglucosamine enolpyruvyl transferase (MurA) from Vibrio fischeri that confers high fosfomycin resistance in Escherichia coli.
|
| |
Arch Microbiol,
191,
425-429.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.R.Partridge,
and
R.M.Hall
(2005).
Gene cassettes potentially encoding fosfomycin resistance determinants.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
49,
860-861.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Beharry,
and
T.Palzkill
(2005).
Functional analysis of active site residues of the fosfomycin resistance enzyme FosA from Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
17786-17791.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |
|

