 |
PDBsum entry 1nq5

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1nq5
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase mutant with cys 149 replaced by ser complexed with NAD+
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Chain: o, q, a, c. Synonym: gapdh. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Geobacillus stearothermophilus. Organism_taxid: 1422. Gene: gap. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
Tetramer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.11Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.198
|
R-free:
|
0.249
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
C.Didierjean,C.Corbier,M.Fatih,F.Favier,S.Boschi-Muller,G.Branlant, A.Aubry
|
Key ref:

|
 |
C.Didierjean
et al.
(2003).
Crystal structure of two ternary complexes of phosphorylating glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase from Bacillus stearothermophilus with NAD and D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.
J Biol Chem,
278,
12968-12976.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
21-Jan-03
|
Release date:
|
22-Apr-03
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P00362
(G3P_GEOSE) -
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase from Geobacillus stearothermophilus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
335 a.a.
334 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.2.1.12
- glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (phosphorylating).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase (phosphorylating)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + phosphate + NAD+ = (2R)-3-phospho- glyceroyl phosphate + NADH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
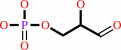 D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
|
+
|
phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
=
|
(2R)-3-phospho- glyceroyl phosphate
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
278:12968-12976
(2003)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of two ternary complexes of phosphorylating glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase from Bacillus stearothermophilus with NAD and D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.
|
|
C.Didierjean,
C.Corbier,
M.Fatih,
F.Favier,
S.Boschi-Muller,
G.Branlant,
A.Aubry.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The crystal structure of the phosphorylating glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
dehydrogenase (GAPDH) from Bacillus stearothermophilus was solved in complex
with its cofactor, NAD, and its physiological substrate, D-glyceraldehyde
3-phosphate (D-G3P). To isolate a stable ternary complex, the nucleophilic
residue of the active site, Cys(149), was substituted with alanine or serine.
The C149A and C149S GAPDH ternary complexes were obtained by soaking the
crystals of the corresponding binary complexes (enzyme.NAD) in a solution
containing G3P. The structures of the two binary and the two ternary complexes
are presented. The D-G3P adopts the same conformation in the two ternary
complexes. It is bound in a non-covalent way, in the free aldehyde form, its C-3
phosphate group being positioned in the P(s) site and not in the P(i) site. Its
C-1 carbonyl oxygen points toward the essential His(176), which supports the
role proposed for this residue along the two steps of the catalytic pathway.
Arguments are provided that the structures reported here are representative of a
productive enzyme.NAD.D-G3P complex in the ground state (Michaelis complex).

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Fig. 1. Schematic representation of the postulated
catalytic mechanism of phosphorylating GAPDHs. The catalytic
mechanism can be divided into two steps. In the acylation step,
Cys149 and His176 form an ion pair in holo-GAPDH (a). This
decreases the pK[app] of Cys149, thus facilitating the thiolate
attack toward the C-1 of D-G3P. The role of His 176 is also to
stabilize the binding of the substrate in the Michaelis complex
GAPDH·NAD·D-G3P (b), the thiohemiacetal
intermediate (c), and the thioacylenzyme intermediate (d).
His176 also plays a role as a base catalyst facilitating the
hydride transfer from the thiohemiacetal toward the
nicotinamidium of NAD (c). In the phosphorylating step, the
binding of inorganic phosphate to the thioacylenzyme is followed
by its nucleophilic attack toward the thioacyl intermediate (d),
which leads via a sp3-phosphorylated intermediate (e) to the
formation and release of 1,3-dPG (f). His176 is postulated to
stabilize the tetrahedral intermediate (e) and to facilitate, as
an acid (d) or base (e) catalyst, the 1,3-dPG formation. The
exchange cofactor step, which consists of NADH release prior to
NAD and inorganic phosphate binding, remains controversial
(32-40). R' represents the
adenine-ribose-phosphate-phosphate-ribose part of the cofactor,
NAD. R represents the CH(OH)COPO[3] part of the substrate, D-G3P.
|
 |
Figure 5.
Fig. 5. Stereoview of the active site in monomer O of the
ternary complexes. A, ternary complex I (C149A mutant GAPDH); B,
ternary complex II (C149A mutant GAPDH). The residues that
interact with the D-G3P molecule are labeled.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2003,
278,
12968-12976)
copyright 2003.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
W.J.Cook,
O.Senkovich,
and
D.Chattopadhyay
(2009).
An unexpected phosphate binding site in glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase: crystal structures of apo, holo and ternary complex of Cryptosporidium parvum enzyme.
|
| |
BMC Struct Biol,
9,
9.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Alvarez-Dominguez,
F.Madrazo-Toca,
L.Fernandez-Prieto,
J.Vandekerckhove,
E.Pareja,
R.Tobes,
M.T.Gomez-Lopez,
E.Del Cerro-Vadillo,
M.Fresno,
F.Leyva-Cobián,
and
E.Carrasco-Marín
(2008).
Characterization of a Listeria monocytogenes Protein Interfering with Rab5a.
|
| |
Traffic,
9,
325-337.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Zaffagnini,
L.Michelet,
C.Marchand,
F.Sparla,
P.Decottignies,
P.Le Maréchal,
M.Miginiac-Maslow,
G.Noctor,
P.Trost,
and
S.D.Lemaire
(2007).
The thioredoxin-independent isoform of chloroplastic glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase is selectively regulated by glutathionylation.
|
| |
FEBS J,
274,
212-226.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Fermani,
F.Sparla,
G.Falini,
P.L.Martelli,
R.Casadio,
P.Pupillo,
A.Ripamonti,
and
P.Trost
(2007).
Molecular mechanism of thioredoxin regulation in photosynthetic A2B2-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
104,
11109-11114.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Robien,
J.Bosch,
F.S.Buckner,
W.C.Van Voorhis,
E.A.Worthey,
P.Myler,
C.Mehlin,
E.E.Boni,
O.Kalyuzhniy,
L.Anderson,
A.Lauricella,
S.Gulde,
J.R.Luft,
G.DeTitta,
J.M.Caruthers,
K.O.Hodgson,
M.Soltis,
F.Zucker,
C.L.Verlinde,
E.A.Merritt,
L.W.Schoenfeld,
and
W.G.Hol
(2006).
Crystal structure of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase from Plasmodium falciparum at 2.25 A resolution reveals intriguing extra electron density in the active site.
|
| |
Proteins,
62,
570-577.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Vido,
H.Diemer,
A.Van Dorsselaer,
E.Leize,
V.Juillard,
A.Gruss,
and
P.Gaudu
(2005).
Roles of thioredoxin reductase during the aerobic life of Lactococcus lactis.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
187,
601-610.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.A.Ismail,
and
H.W.Park
(2005).
Structural analysis of human liver glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
61,
1508-1513.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Warizaya,
T.Kinoshita,
A.Kato,
H.Nakajima,
and
T.Fujii
(2004).
Cloning, expression, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of human liver glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
60,
567-568.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

