 |
PDBsum entry 1kv8

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.1.1.85
- 3-dehydro-L-gulonate-6-phosphate decarboxylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
3-dehydro-L-gulonate 6-phosphate + H+ = L-xylulose 5-phosphate + CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 3-dehydro-L-gulonate 6-phosphate
3-dehydro-L-gulonate 6-phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
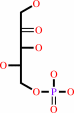 L-xylulose 5-phosphate
L-xylulose 5-phosphate
|
+
|
 CO2
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Mg(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
41:3861-3869
(2002)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Homologous (beta/alpha)8-barrel enzymes that catalyze unrelated reactions: orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase and 3-keto-L-gulonate 6-phosphate decarboxylase.
|
|
E.Wise,
W.S.Yew,
P.C.Babbitt,
J.A.Gerlt,
I.Rayment.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The 3-keto-L-gulonate 6-phosphate decarboxylase (KGPDC) encoded by the ulaD gene
in the Escherichia coli genome [Yew, W. S., and Gerlt, J. A. (2002) J.
Bacteriol. 184, 302-306] and orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase (OMPDC)
are homologous (derived from a common ancestor) but catalyze different
reactions. The metal-independent decarboxylation reaction catalyzed by OMPDC
avoids the formation of a vinyl anion intermediate; the Mg2+-dependent
decarboxylation reaction catalyzed by KGPDC involves the formation of an
enediolate anion intermediate. Based on the available structures of OMPDC, a
sequence alignment allows the predictions that (1) KGPDC is a dimer of
(beta/alpha)8-barrels, with the active sites located at the dimer interface; (2)
KGPDC and OMPDC share an aspartate residue at the end of the first beta-strand
and an Asp-x-Lys-x-x-Asp motif at the end of the third beta-strand with OMPDC;
but (3) KGPDC has a Glu instead of a Lys at the end of the second beta-strand.
The structure of KGPDC has been determined in the presence of Mg2+ and the
substrate analogue L-gulonate 6-phosphate and confirms these predictions. The
carboxylate functional groups at the ends of the first, second, and third
beta-strands in KGPDC are ligands of the Mg2+; in OMPDC, the homologues of these
residues participate in a hydrogen-bonded network that facilitates the
decarboxylation reaction. The 3-OH group of the substrate analogue is
coordinated to the Mg2+, supporting the hypothesis that the mechanism of the
decarboxylation catalyzed by KGPDC involves stabilization of an enediolate anion
intermediate. These structural studies establish the existence of the OMPDC
"suprafamily," in which members catalyze reactions that occur in different
metabolic pathways and share no mechanistic relationship. The existence of this
suprafamily demonstrates that divergent evolution can be opportunistic,
conscripting active site features of a progenitor to catalyze unrelated
functions. Accordingly, sequence or structure homology alone cannot be used to
infer the functions of new proteins discovered in genome projects.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
I.Orita,
A.Kita,
H.Yurimoto,
N.Kato,
Y.Sakai,
and
K.Miki
(2010).
Crystal structure of 3-hexulose-6-phosphate synthase, a member of the orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase suprafamily.
|
| |
Proteins,
78,
3488-3492.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Yurimoto,
N.Kato,
and
Y.Sakai
(2009).
Genomic organization and biochemistry of the ribulose monophosphate pathway and its application in biotechnology.
|
| |
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,
84,
407-416.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Gerlt,
and
P.C.Babbitt
(2009).
Enzyme (re)design: lessons from natural evolution and computation.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
13,
10-18.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.J.Drake,
and
A.M.Gulick
(2008).
Three-dimensional structures of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PvcA and PvcB, two proteins involved in the synthesis of 2-isocyano-6,7-dihydroxycoumarin.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
384,
193-205.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
O.A.Barski,
S.M.Tipparaju,
and
A.Bhatnagar
(2008).
The aldo-keto reductase superfamily and its role in drug metabolism and detoxification.
|
| |
Drug Metab Rev,
40,
553-624.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.R.Tabita,
T.E.Hanson,
H.Li,
S.Satagopan,
J.Singh,
and
S.Chan
(2007).
Function, structure, and evolution of the RubisCO-like proteins and their RubisCO homologs.
|
| |
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev,
71,
576-599.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.L.Amyes,
and
J.P.Richard
(2007).
Enzymatic catalysis of proton transfer at carbon: activation of triosephosphate isomerase by phosphite dianion.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
46,
5841-5854.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.E.Nichols,
C.Johnson,
M.Lockyer,
I.G.Charles,
H.K.Lamb,
A.R.Hawkins,
and
D.K.Stammers
(2006).
Structural characterization of Salmonella typhimurium YeaZ, an M22 O-sialoglycoprotein endopeptidase homolog.
|
| |
Proteins,
64,
111-123.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Saghatelian,
and
B.F.Cravatt
(2005).
Assignment of protein function in the postgenomic era.
|
| |
Nat Chem Biol,
1,
130-142.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Pal,
and
D.Eisenberg
(2005).
Inference of protein function from protein structure.
|
| |
Structure,
13,
121-130.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Pirun,
G.Babnigg,
and
F.J.Stevens
(2005).
Template-based recognition of protein fold within the midnight and twilight zones of protein sequence similarity.
|
| |
J Mol Recognit,
18,
203-212.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.R.Hall,
R.Zheng,
L.Antony,
M.Pusztai-Carey,
P.R.Carey,
and
V.C.Yee
(2004).
Transcarboxylase 5S structures: assembly and catalytic mechanism of a multienzyme complex subunit.
|
| |
EMBO J,
23,
3621-3631.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.E.Shakhnovich,
J.M.Harvey,
S.Comeau,
D.Lorenz,
C.DeLisi,
and
E.Shakhnovich
(2003).
ELISA: structure-function inferences based on statistically significant and evolutionarily inspired observations.
|
| |
BMC Bioinformatics,
4,
34.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.L.Wise,
W.S.Yew,
J.A.Gerlt,
and
I.Rayment
(2003).
Structural evidence for a 1,2-enediolate intermediate in the reaction catalyzed by 3-keto-L-gulonate 6-phosphate decarboxylase, a member of the orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase suprafamily.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
42,
12133-12142.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.H.Dawe,
C.T.Porter,
J.M.Thornton,
and
A.B.Tabor
(2003).
A template search reveals mechanistic similarities and differences in beta-ketoacyl synthases (KAS) and related enzymes.
|
| |
Proteins,
52,
427-435.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Zhang,
M.Aboulwafa,
M.H.Smith,
and
M.H.Saier
(2003).
The ascorbate transporter of Escherichia coli.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
185,
2243-2250.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

