 |
PDBsum entry 1fv0

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.4
- phospholipase A2.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine + H2O = a 1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine + a fatty acid + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
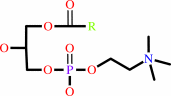 1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine
1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine
|
+
|
fatty acid
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 60.00% similarity
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Ca(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
41:10914-10919
(2002)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural basis of phospholipase A2 inhibition for the synthesis of prostaglandins by the plant alkaloid aristolochic acid from a 1.7 A crystal structure.
|
|
V.Chandra,
J.Jasti,
P.Kaur,
A.Srinivasan,
C.h.Betzel,
T.P.Singh.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
This is the first structural observation of a plant product showing high
affinity for phospholipase A(2) and regulating the synthesis of arachidonic
acid, an intermediate in the production of prostaglandins. The crystal structure
of a complex formed between Vipera russelli phospholipase A(2) and a plant
alkaloid aristolochic acid has been determined and refined to 1.7 A resolution.
The structure contains two crystallographically independent molecules of
phospholipase A(2) in the form of an asymmetric dimer with one molecule of
aristolochic acid bound to one of them specifically. The most significant
differences introduced by asymmetric molecular association in the structures of
two molecules pertain to the conformations of their calcium binding loops,
beta-wings, and the C-terminal regions. These differences are associated with a
unique conformational behavior of Trp(31). Trp(31) is located at the entrance of
the characteristic hydrophobic channel which works as a passage to the active
site residues in the enzyme. In the case of molecule A, Trp(31) is found at the
interface of two molecules and it forms a number of hydrophobic interactions
with the residues of molecule B. Consequently, it is pulled outwardly, leaving
the mouth of the hydrophobic channel wide open. On the other hand, Trp(31) in
molecule B is exposed to the surface and moves inwardly due to the polar
environment on the molecular surface, thus narrowing the opening of the
hydrophobic channel. As a result, the aristolochic acid is bound to molecule A
only while the binding site of molecule B is empty. It is noteworthy that the
most critical interactions in the binding of aristolochic acid are provided by
its OH group which forms two hydrogen bonds, one each with His(48) and Asp(49).

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
S.M.Farrell,
G.Groeger,
L.Bhatt,
S.Finnegan,
C.J.O'Brien,
and
T.G.Cotter
(2011).
bFGF-mediated redox activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway in retinal photoreceptor cells.
|
| |
Eur J Neurosci,
33,
632-641.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Groeger,
A.M.Mackey,
C.A.Pettigrew,
L.Bhatt,
and
T.G.Cotter
(2009).
Stress-induced activation of Nox contributes to cell survival signalling via production of hydrogen peroxide.
|
| |
J Neurochem,
109,
1544-1554.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Paoli,
M.Rigoni,
G.Koster,
O.Rossetto,
C.Montecucco,
and
A.D.Postle
(2009).
Mass spectrometry analysis of the phospholipase A(2) activity of snake pre-synaptic neurotoxins in cultured neurons.
|
| |
J Neurochem,
111,
737-744.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Gardiner,
Z.Andreeva,
D.Barton,
A.Ritchie,
R.Overall,
and
J.Marc
(2008).
The phospholipase A inhibitor, aristolochic acid, disrupts cortical microtubule arrays and root growth in Arabidopsis.
|
| |
Plant Biol (Stuttg),
10,
725-731.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Sekar,
D.Gayathri,
D.Velmurugan,
J.Jeyakanthan,
T.Yamane,
M.J.Poi,
and
M.D.Tsai
(2006).
Third calcium ion found in an inhibitor-bound phospholipase A2.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
62,
392-397.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Singh,
T.Jabeen,
A.Pal,
S.Sharma,
M.Perbandt,
C.Betzel,
and
T.P.Singh
(2006).
Crystal structures of the complexes of a group IIA phospholipase A2 with two natural anti-inflammatory agents, anisic acid, and atropine reveal a similar mode of binding.
|
| |
Proteins,
64,
89.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Singh,
T.Jabeen,
S.Sharma,
R.K.Somvanshi,
S.Dey,
A.Srinivasan,
and
T.P.Singh
(2006).
Specific binding of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to phospholipase A2: structure of the complex formed between phospholipase A2 and diclofenac at 2.7 A resolution.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
62,
410-416.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Singh,
J.Jasti,
K.Saravanan,
S.Sharma,
P.Kaur,
A.Srinivasan,
and
T.P.Singh
(2005).
Crystal structure of the complex formed between a group I phospholipase A2 and a naturally occurring fatty acid at 2.7 A resolution.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
14,
395-400.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Jabeen,
S.Sharma,
N.Singh,
R.K.Singh,
A.K.Verma,
M.Paramasivam,
A.Srinivasan,
and
T.P.Singh
(2005).
Structure of the zinc-induced heterodimer of two calcium-free isoforms of phospholipase A2 from Naja naja sagittifera at 2.7 angstroms resolution.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
61,
302-308.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Penzo,
V.Petronilli,
A.Angelin,
C.Cusan,
R.Colonna,
L.Scorrano,
F.Pagano,
M.Prato,
F.Di Lisa,
and
P.Bernardi
(2004).
Arachidonic acid released by phospholipase A(2) activation triggers Ca(2+)-dependent apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
25219-25225.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.K.Singh,
P.Vikram,
J.Makker,
T.Jabeen,
S.Sharma,
S.Dey,
P.Kaur,
A.Srinivasan,
and
T.P.Singh
(2003).
Design of specific peptide inhibitors for group I phospholipase A2: structure of a complex formed between phospholipase A2 from Naja naja sagittifera (group I) and a designed peptide inhibitor Val-Ala-Phe-Arg-Ser (VAFRS) at 1.9 A resolution reveals unique features.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
42,
11701-11706.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Chandra,
J.Jasti,
P.Kaur,
S.Dey,
M.Perbandt,
A.Srinivasan,
C.h.Betzel,
and
T.P.Singh
(2002).
Crystal structure of a complex formed between a snake venom phospholipase A(2) and a potent peptide inhibitor Phe-Leu-Ser-Tyr-Lys at 1.8 A resolution.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
41079-41085.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

