 |
PDBsum entry 1ezd

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Phosphotransferase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1ezd
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.3.9
- phosphoenolpyruvate--protein phosphotransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-histidyl-[protein] + phosphoenolpyruvate = N(pros)-phospho-L-histidyl- [protein] + pyruvate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-histidyl-[protein]
|
+
|
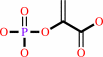 phosphoenolpyruvate
phosphoenolpyruvate
|
=
|
N(pros)-phospho-L-histidyl- [protein]
|
+
|
 pyruvate
pyruvate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
36:2517-2530
(1997)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Solution structure of the 30 kDa N-terminal domain of enzyme I of the Escherichia coli phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system by multidimensional NMR.
|
|
D.S.Garrett,
Y.J.Seok,
D.I.Liao,
A.Peterkofsky,
A.M.Gronenborn,
G.M.Clore.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The three-dimensional solution structure of the 259-residue 30 kDa N-terminal
domain of enzyme I (EIN) of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase
system of Escherichia coli has been determined by multidimensional nuclear
magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Enzyme I, which is autophosphorylated by
phosphoenolpyruvate, reversibly phosphorylates the phosphocarrier protein HPr,
which in turn phosphorylates a group of membrane-associated proteins, known as
enzymes II. To facilitate and confirm NH, 15N, and 13C assignments, extensive
use was made of perdeuterated 15N- and 15N/13C-labeled protein to narrow line
widths. Ninety-eight percent of the 1H, 15N, and 13C assignments for the
backbone and first side chain atoms of protonated EIN were obtained using a
combination of double and triple resonance correlation experiments. The
structure determination was based on a total of 4251 experimental NMR
restraints, and the precision of the coordinates for the final 50 simulated
annealing structures is 0.79 +/- 0.18 A for the backbone atoms and 1.06 +/- 0.15
A for all atoms. The structure is ellipsoidal in shape, approximately 78 A long
and 32 A wide, and comprises two domains: an alpha/beta domain (residues 1-20
and 148-230) consisting of six strands and three helices and an alpha-domain
(residues 33-143) consisting of four helices. The two domains are connected by
two linkers (residues 21-32 and 144-147), and in addition, at the C-terminus
there is another helix which serves as a linker between the N- and C-terminal
domains of intact enzyme I. A comparison with the recently solved X-ray
structure of EIN [Liao, D.-I., Silverton, E., Seok, Y.-J., Lee, B. R.,
Peterkofsky, A., & Davies, D. R. (1996) Structure 4, 861-872] indicates that
there are no significant differences between the solution and crystal structures
within the errors of the coordinates. The active site His189 is located in a
cleft at the junction of the alpha and alpha/beta domains and has a pKa of
approximately 6.3. His189 has a trans conformation about chi1, a g+ conformation
about chi2, and its Nepsilon2 atom accepts a hydrogen bond from the hydroxyl
proton of Thr168. Since His189 is thought to be phosphorylated at the N epsilon2
position, its side chain conformation would have to change upon phosphorylation.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
D.Stratmann,
E.Guittet,
and
C.van Heijenoort
(2010).
Robust structure-based resonance assignment for functional protein studies by NMR.
|
| |
J Biomol NMR,
46,
157-173.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.L.Barneto,
M.Avalos,
R.Babiano,
P.Cintas,
J.L.Jiménez,
and
J.C.Palacios
(2010).
A new model for mapping the peptide backbone: predicting proton chemical shifts in proteins.
|
| |
Org Biomol Chem,
8,
857-863.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Romero-Beviar,
S.Martínez-Rodríguez,
J.Prieto,
E.Goormaghtigh,
U.Ariz,
M.d.e. .L.Martínez-Chantar,
J.Gómez,
and
J.L.Neira
(2010).
The N-terminal domain of the enzyme I is a monomeric well-folded protein with a low conformational stability and residual structure in the unfolded state.
|
| |
Protein Eng Des Sel,
23,
729-742.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Turano,
D.Lalli,
I.C.Felli,
E.C.Theil,
and
I.Bertini
(2010).
NMR reveals pathway for ferric mineral precursors to the central cavity of ferritin.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
545-550.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.S.Jung,
M.Cai,
and
G.M.Clore
(2010).
Solution structure of the IIAChitobiose-IIBChitobiose complex of the N,N'-diacetylchitobiose branch of the Escherichia coli phosphotransferase system.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
285,
4173-4184.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Stratmann,
C.van Heijenoort,
and
E.Guittet
(2009).
NOEnet--use of NOE networks for NMR resonance assignment of proteins with known 3D structure.
|
| |
Bioinformatics,
25,
474-481.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.M.Clore,
and
J.Iwahara
(2009).
Theory, practice, and applications of paramagnetic relaxation enhancement for the characterization of transient low-population states of biological macromolecules and their complexes.
|
| |
Chem Rev,
109,
4108-4139.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Ryabov,
J.Y.Suh,
A.Grishaev,
G.M.Clore,
and
C.D.Schwieters
(2009).
Using the experimentally determined components of the overall rotational diffusion tensor to restrain molecular shape and size in NMR structure determination of globular proteins and protein-protein complexes.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
131,
9522-9531.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.M.Clore
(2008).
Visualizing lowly-populated regions of the free energy landscape of macromolecular complexes by paramagnetic relaxation enhancement.
|
| |
Mol Biosyst,
4,
1058-1069.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.J.Kuszewski,
R.A.Thottungal,
G.M.Clore,
and
C.D.Schwieters
(2008).
Automated error-tolerant macromolecular structure determination from multidimensional nuclear Overhauser enhancement spectra and chemical shift assignments: improved robustness and performance of the PASD algorithm.
|
| |
J Biomol NMR,
41,
221-239.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Y.Suh,
M.Cai,
and
G.M.Clore
(2008).
Impact of phosphorylation on structure and thermodynamics of the interaction between the N-terminal domain of enzyme I and the histidine phosphocarrier protein of the bacterial phosphotransferase system.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
18980-18989.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.C.Kim,
C.Tang,
G.M.Clore,
and
G.Hummer
(2008).
Replica exchange simulations of transient encounter complexes in protein-protein association.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
105,
12855-12860.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Lee,
J.D.Walsh,
M.Migliorini,
P.Yu,
T.Cai,
C.D.Schwieters,
S.Krueger,
D.K.Strickland,
and
Y.X.Wang
(2007).
The structure of receptor-associated protein (RAP).
|
| |
Protein Sci,
16,
1628-1640.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Lee,
J.D.Walsh,
P.Yu,
M.A.Markus,
T.Choli-Papadopoulou,
C.D.Schwieters,
S.Krueger,
D.E.Draper,
and
Y.X.Wang
(2007).
The structure of free L11 and functional dynamics of L11 in free, L11-rRNA(58 nt) binary and L11-rRNA(58 nt)-thiostrepton ternary complexes.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
367,
1007-1022.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Müller,
and
H.Sticht
(2007).
A protein-specifically adapted scoring function for the reranking of docking solutions.
|
| |
Proteins,
67,
98.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Teplyakov,
K.Lim,
P.P.Zhu,
G.Kapadia,
C.C.Chen,
J.Schwartz,
A.Howard,
P.T.Reddy,
A.Peterkofsky,
and
O.Herzberg
(2006).
Structure of phosphorylated enzyme I, the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system sugar translocation signal protein.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
103,
16218-16223.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Hurtado-Gómez,
G.Fernández-Ballester,
H.Nothaft,
J.Gómez,
F.Titgemeyer,
and
J.L.Neira
(2006).
Biophysical characterization of the enzyme I of the Streptomyces coelicolor phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system.
|
| |
Biophys J,
90,
4592-4604.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Deutscher,
C.Francke,
and
P.W.Postma
(2006).
How phosphotransferase system-related protein phosphorylation regulates carbohydrate metabolism in bacteria.
|
| |
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev,
70,
939.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Márquez,
S.Reinelt,
B.Koch,
R.Engelmann,
W.Hengstenberg,
and
K.Scheffzek
(2006).
Structure of the full-length enzyme I of the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sugar phosphotransferase system.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
32508-32515.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Lin,
Y.Xu,
S.Yang,
and
D.Yang
(2006).
Sequence-specific assignment of aromatic resonances of uniformly 13C,15N-labeled proteins by using 13C- and 15N-edited NOESY spectra.
|
| |
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl,
45,
1960-1963.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Tang,
D.C.Williams,
R.Ghirlando,
and
G.M.Clore
(2005).
Solution structure of enzyme IIA(Chitobiose) from the N,N'-diacetylchitobiose branch of the Escherichia coli phosphotransferase system.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
11770-11780.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
H.S.Atreya,
and
T.Szyperski
(2004).
G-matrix Fourier transform NMR spectroscopy for complete protein resonance assignment.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
101,
9642-9647.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.S.Won,
Y.H.Lee,
J.H.Kim,
I.S.Shin,
M.H.Lee,
and
B.J.Lee
(2004).
Structural characterization of the nickel-binding properties of Bacillus pasteurii urease accessory protein (Ure)E in solution.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
17466-17472.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.M.Legler,
M.Cai,
A.Peterkofsky,
and
G.M.Clore
(2004).
Three-dimensional solution structure of the cytoplasmic B domain of the mannitol transporter IImannitol of the Escherichia coli phosphotransferase system.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
279,
39115-39121.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Dobrodumov,
and
A.M.Gronenborn
(2003).
Filtering and selection of structural models: combining docking and NMR.
|
| |
Proteins,
53,
18-32.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Banci,
I.Bertini,
and
R.Del Conte
(2003).
Solution structure of apo CopZ from Bacillus subtilis: further analysis of the changes associated with the presence of copper.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
42,
13422-13428.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Banci,
I.Bertini,
S.Ciofi-Baffoni,
R.Del Conte,
and
L.Gonnelli
(2003).
Understanding copper trafficking in bacteria: interaction between the copper transport protein CopZ and the N-terminal domain of the copper ATPase CopA from Bacillus subtilis.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
42,
1939-1949.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Márquez,
S.Hasenbein,
B.Koch,
S.Fieulaine,
S.Nessler,
R.B.Russell,
W.Hengstenberg,
and
K.Scheffzek
(2002).
Structure of the full-length HPr kinase/phosphatase from Staphylococcus xylosus at 1.95 A resolution: Mimicking the product/substrate of the phospho transfer reactions.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
99,
3458-3463.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.F.Garcia-Alles,
K.Flükiger,
J.Hewel,
R.Gutknecht,
C.Siebold,
S.Schürch,
and
B.Erni
(2002).
Mechanism-based inhibition of enzyme I of the Escherichia coli phosphotransferase system. Cysteine 502 is an essential residue.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
6934-6942.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Ginsburg,
R.H.Szczepanowski,
S.B.Ruvinov,
N.J.Nosworthy,
M.Sondej,
T.C.Umland,
and
A.Peterkofsky
(2000).
Conformational stability changes of the amino terminal domain of enzyme I of the Escherichia coli phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system produced by substituting alanine or glutamate for the active-site histidine 189: implications for phosphorylation effects.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
9,
1085-1094.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Wang,
J.M.Louis,
M.Sondej,
Y.J.Seok,
A.Peterkofsky,
and
G.M.Clore
(2000).
Solution structure of the phosphoryl transfer complex between the signal transducing proteins HPr and IIA(glucose) of the Escherichia coli phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system.
|
| |
EMBO J,
19,
5635-5649.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
N.K.Goto,
and
L.E.Kay
(2000).
New developments in isotope labeling strategies for protein solution NMR spectroscopy.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
10,
585-592.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.J.Brokx,
J.Talbot,
F.Georges,
and
E.B.Waygood
(2000).
Enzyme I of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system. In vitro intragenic complementation: the roles of Arg126 in phosphoryl transfer and the C-terminal domain in dimerization.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
3624-3635.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.P.Zhu,
R.H.Szczepanowski,
N.J.Nosworthy,
A.Ginsburg,
and
A.Peterkofsky
(1999).
Reconstitution studies using the helical and carboxy-terminal domains of enzyme I of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
15470-15479.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.J.Brokx,
S.Napper,
G.Wong,
A.Mirza,
F.Georges,
L.T.Delbaere,
and
E.B.Waygood
(1999).
Identification of the Escherichia coli enzyme I binding site in histidine-containing protein, HPr, by the effects of mutagenesis.
|
| |
Biochem Cell Biol,
77,
507-513.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.L.Chang,
B.J.Wallar,
J.D.Lipscomb,
and
K.H.Mayo
(1999).
Solution structure of component B from methane monooxygenase derived through heteronuclear NMR and molecular modeling.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
5799-5812.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.X.Wang,
N.Neamati,
J.Jacob,
I.Palmer,
S.J.Stahl,
J.D.Kaufman,
P.L.Huang,
P.L.Huang,
H.E.Winslow,
Y.Pommier,
P.T.Wingfield,
S.Lee-Huang,
A.Bax,
and
D.A.Torchia
(1999).
Solution structure of anti-HIV-1 and anti-tumor protein MAP30: structural insights into its multiple functions.
|
| |
Cell,
99,
433-442.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Fomenkov,
A.Valiakhmetov,
L.Brand,
and
S.Roseman
(1998).
In vivo and in vitro complementation of the N-terminal domain of enzyme I of the Escherichia coli phosphotransferase system by the cloned C-terminal domain.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
95,
8491-8495.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.S.Garrett,
Y.J.Seok,
A.Peterkofsky,
G.M.Clore,
and
A.M.Gronenborn
(1998).
Tautomeric state and pKa of the phosphorylated active site histidine in the N-terminal domain of enzyme I of the Escherichia coli phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
7,
789-793.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.M.Clore,
and
A.M.Gronenborn
(1998).
New methods of structure refinement for macromolecular structure determination by NMR.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
95,
5891-5898.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.M.Clore,
and
A.M.Gronenborn
(1998).
NMR structure determination of proteins and protein complexes larger than 20 kDa.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
2,
564-570.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.H.Gardner,
and
L.E.Kay
(1998).
The use of 2H, 13C, 15N multidimensional NMR to study the structure and dynamics of proteins.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct,
27,
357-406.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.J.Nosworthy,
A.Peterkofsky,
S.König,
Y.J.Seok,
R.H.Szczepanowski,
and
A.Ginsburg
(1998).
Phosphorylation destabilizes the amino-terminal domain of enzyme I of the Escherichia coli phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
37,
6718-6726.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.L.van Montfort,
T.Pijning,
K.H.Kalk,
I.Hangyi,
M.L.Kouwijzer,
G.T.Robillard,
and
B.W.Dijkstra
(1998).
The structure of the Escherichia coli phosphotransferase IIAmannitol reveals a novel fold with two conformations of the active site.
|
| |
Structure,
6,
377-388.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Yang,
S.Nanduri,
S.Sen,
and
J.Qin
(1998).
The structural basis of ankyrin-like repeat function as revealed by the solution structure of myotrophin.
|
| |
Structure,
6,
619-626.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.S.Garrett,
Y.J.Seok,
A.Peterkofsky,
G.M.Clore,
and
A.M.Gronenborn
(1997).
Identification by NMR of the binding surface for the histidine-containing phosphocarrier protein HPr on the N-terminal domain of enzyme I of the Escherichia coli phosphotransferase system.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
36,
4393-4398.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.E.Kay,
and
K.H.Gardner
(1997).
Solution NMR spectroscopy beyond 25 kDa.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
7,
722-731.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.M.McEvoy,
and
F.W.Dahlquist
(1997).
Phosphohistidines in bacterial signaling.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
7,
793-797.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Tjandra,
D.S.Garrett,
A.M.Gronenborn,
A.Bax,
and
G.M.Clore
(1997).
Defining long range order in NMR structure determination from the dependence of heteronuclear relaxation times on rotational diffusion anisotropy.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
4,
443-449.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Bhattacharya,
S.F.Sukits,
K.L.MacLaughlin,
and
J.T.Lecomte
(1997).
The tautomeric state of histidines in myoglobin.
|
| |
Biophys J,
73,
3230-3240.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

