 |
PDBsum entry 1ceh

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Hydrolase (carboxylic ester)
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1ceh
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.4
- phospholipase A2.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine + H2O = a 1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine + a fatty acid + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
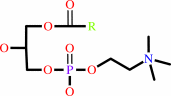 1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine
1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine
|
+
|
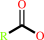 fatty acid
fatty acid
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Ca(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Protein Sci
3:2082-2088
(1994)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure and function of the catalytic site mutant Asp 99 Asn of phospholipase A2: absence of the conserved structural water.
|
|
A.Kumar,
C.Sekharudu,
B.Ramakrishnan,
C.M.Dupureur,
H.Zhu,
M.D.Tsai,
M.Sundaralingam.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
To probe the role of the Asp-99 ... His-48 pair in phospholipase A2 (PLA2)
catalysis, the X-ray structure and kinetic characterization of the mutant
Asp-99-->Asn-99 (D99N) of bovine pancreatic PLA2 was undertaken. Crystals of
D99N belong to the trigonal space group P3(1)21 and were isomorphous to the wild
type (WT) (Noel JP et al., 1991, Biochemistry 30:11801-11811). The 1.9-A X-ray
structure of the mutant showed that the carbonyl group of Asn-99 side chain is
hydrogen bonded to His-48 in the same way as that of Asp-99 in the WT, thus
retaining the tautomeric form of His-48 and the function of the enzyme. The NH2
group of Asn-99 points away from His-48. In contrast, in the D102N mutant of the
protease enzyme trypsin, the NH2 group of Asn-102 is hydrogen bonded to His-57
resulting in the inactive tautomeric form and hence the loss of enzymatic
activity. Although the geometry of the catalytic triad in the PLA2 mutant
remains the same as in the WT, we were surprised that the conserved structural
water, linking the catalytic site with the ammonium group of Ala-1 of the
interfacial site, was ejected by the proximity of the NH2 group of Asn-99. The
NH2 group now forms a direct hydrogen bond with the carbonyl group of Ala-1.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 3.
Fig. 3. A: Hypothtical hydrogen bonding scheme for the D99N
mutant with theNH2 group of Asn-99 hydrogen bonding to His-
48 and Tyr-52. B The alternateconformationofthe Asn-99 side
chain with the NH group pointing away from the His-48 nd hy-
drogen bonding to Tyr-73 and the structural water-3 molecule. The
hydroxyl groups of Tyr-52 nd Tyr-73 have switched orientation
from A to B to accommodatethe hydrogen bonding. Notice hat
the hydrogen bonding pattern of thestructural water molecule in
A and B is different from each other and the WT lthough the
structural water is 4-coordinated in all3 cases. C: The hydrogen
bonding scheme in the X-ray structure of themutant D99N. The
structural water is missing andthe mino roup Asn-99 is
directly hydrogen bonded to thecarbonl group of Ala-1.
|
 |
Figure 4.
Fig. 4. Van der Waals surface diagram ofthe residues aroundthe
structural water in the WT (A) an the D99N mutant (B). Notice
that the new position and conformation of la-1 in B fiis the void
created by the missing structural water. C: Overlay fthe skele-
tal drawings ofthe WT (red) and hemtant D99N (green) show-
ing the hydrogen bonding scheme. Residues around Ala-I that are
hydrogen bonded to theammoniumgroup are also Notice
the large change in theorientationofthe NH3+and p
groups of Ala-1. Despite this change, theammonium group in the
mutant still forms 3 hydrogen bonds, 2 f which areto thesame
acceptorsas in he WT.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
from an Open Access publication published by the Protein Society:
Protein Sci
(1994,
3,
2082-2088)
copyright 1994.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
Y.L.Boersma,
M.J.Dröge,
A.M.van der Sloot,
T.Pijning,
R.H.Cool,
B.W.Dijkstra,
and
W.J.Quax
(2008).
A novel genetic selection system for improved enantioselectivity of Bacillus subtilis lipase A.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
9,
1110-1115.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.A.Bottoms,
T.A.White,
and
J.J.Tanner
(2006).
Exploring structurally conserved solvent sites in protein families.
|
| |
Proteins,
64,
404-421.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Oubrie,
and
B.W.Dijkstra
(2000).
Structural requirements of pyrroloquinoline quinone dependent enzymatic reactions.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
9,
1265-1273.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.L.Kingma,
M.Fragiathaki,
H.J.Snijder,
B.W.Dijkstra,
H.M.Verheij,
N.Dekker,
and
M.R.Egmond
(2000).
Unusual catalytic triad of Escherichia coli outer membrane phospholipase A.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
10017-10022.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Z.Yu,
J.Rogers,
M.D.Tsai,
C.Pidgeon,
and
M.K.Jain
(1999).
Contributions of residues of pancreatic phospholipase A2 to interfacial binding, catalysis, and activation.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
4875-4884.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Yuan,
I.J.Byeon,
Y.Li,
and
M.D.Tsai
(1999).
Structural analysis of phospholipase A2 from functional perspective. 1. Functionally relevant solution structure and roles of the hydrogen-bonding network.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
2909-2918.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Yuan,
and
M.Tsai
(1999).
Pancreatic phospholipase A(2): new views on old issues.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1441,
215-222.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Sekar,
R.Biswas,
Y.Li,
M.Tsai,
and
M.Sundaralingam
(1999).
Structures of the catalytic site mutants D99A and H48Q and the calcium-loop mutant D49E of phospholipase A2.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
55,
443-447.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.H.Krooshof,
E.M.Kwant,
J.Damborský,
J.Koca,
and
D.B.Janssen
(1997).
Repositioning the catalytic triad aspartic acid of haloalkane dehalogenase: effects on stability, kinetics, and structure.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
36,
9571-9580.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Sekar,
B.Z.Yu,
J.Rogers,
J.Lutton,
X.Liu,
X.Chen,
M.D.Tsai,
M.K.Jain,
and
M.Sundaralingam
(1997).
Phospholipase A2 engineering. Structural and functional roles of the highly conserved active site residue aspartate-99.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
36,
3104-3114.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.R.Annand,
M.Kontoyianni,
J.E.Penzotti,
T.Dudler,
T.P.Lybrand,
and
M.H.Gelb
(1996).
Active site of bee venom phospholipase A2: the role of histidine-34, aspartate-64 and tyrosine-87.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
35,
4591-4601.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

