 |
PDBsum entry 1bbc

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Structure of recombinant human rheumatoid arthritic synovial fluid phospholipase a2 at 2.2 angstroms resolution
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Phospholipase a2. Chain: a. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.-P.Wery,R.W.Schevitz,D.K.Clawson,J.L.Bobbitt,E.R.Dow,G.Gamboa, T.Goodsonjunior,R.B.Hermann,R.M.Kramer,D.B.Mcclure,E.D.Mihelich, J.E.Putnam,J.D.Sharp,D.H.Stark,C.Teater,M.W.Warrick,N.D.Jones
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
J.P.Wery
et al.
(1991).
Structure of recombinant human rheumatoid arthritic synovial fluid phospholipase A2 at 2.2 A resolution.
Nature,
352,
79-82.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
04-May-92
|
Release date:
|
31-Oct-93
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P14555
(PA2GA_HUMAN) -
Phospholipase A2, membrane associated from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
144 a.a.
124 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.4
- phospholipase A2.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine + H2O = a 1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine + a fatty acid + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
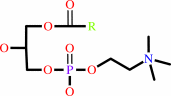 1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine
1-acyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine
|
+
|
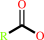 fatty acid
fatty acid
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Ca(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Nature
352:79-82
(1991)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure of recombinant human rheumatoid arthritic synovial fluid phospholipase A2 at 2.2 A resolution.
|
|
J.P.Wery,
R.W.Schevitz,
D.K.Clawson,
J.L.Bobbitt,
E.R.Dow,
G.Gamboa,
T.Goodson,
R.B.Hermann,
R.M.Kramer,
D.B.McClure.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Phospholipases A2 (PLA2s) may be grouped into distinct families of proteins that
catalyse the hydrolysis of the 2-acyl bond of phospholipids and perform a
variety of biological functions. The best characterized are the small (relative
molecular mass approximately 14,000) calcium-dependent, secretory enzymes of
diverse origin, such as pancreatic and venom PLA2s. The structures and functions
of several PLA2s are known. Recently, high-resolution crystal structures of
complexes of secretory PLA2s with phosphonate phospholipid analogues have
provided information about the detailed stereochemistry of transition-state
binding, confirming the proposed catalytic mechanism of esterolysis. By
contrast, studies on mammalian nonpancreatic secretory PLA2s (s-PLA2s) have only
recently begun; s-PLA2s are scarce in normal cells and tissues but large amounts
are found in association with local and systemic inflammatory processes and
tissue injury in animals and man. Such s-PLAs have been purified from rabbit and
rat inflammatory exudate, from synovial fluid from patients with rheumatoid
arthritis and from human platelets. Cloning and sequencing shows that the
primary structure of the human s-PLA2 has about 37% homology with that of bovine
pancreatic PLA2 and 44% homology with that of Crotalus atrox PLA2. The human
s-PLA2 is an unusually basic protein, yet contains most of the highly conserved
amino-acid residues and sequences characteristic of the PLA2s sequenced so far.
Here we report the refined, three-dimensional crystal structure at 2.2 A
resolution of recombinant human rheumatoid arthritic synovial fluid PLA2. This
may aid the development of potent and specific inhibitors of this enzyme using
structure-based design.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
C.E.Cassidy,
and
W.N.Setzer
(2010).
Cancer-relevant biochemical targets of cytotoxic Lonchocarpus flavonoids: a molecular docking analysis.
|
| |
J Mol Model,
16,
311-326.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.N.Birts,
C.H.Barton,
and
D.C.Wilton
(2010).
Catalytic and non-catalytic functions of human IIA phospholipase A2.
|
| |
Trends Biochem Sci,
35,
28-35.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.D.Mouchlis,
T.M.Mavromoustakos,
and
G.Kokotos
(2010).
Design of new secreted phospholipase A2 inhibitors based on docking calculations by modifying the pharmacophore segments of the FPL67047XX inhibitor.
|
| |
J Comput Aided Mol Des,
24,
107-115.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.E.Guy,
U.Ståhl,
and
Y.Lindqvist
(2009).
Crystal Structure of a Class XIB Phospholipase A2 (PLA2): RICE (ORYZA SATIVA) ISOFORM-2 PLA2 AND AN OCTANOATE COMPLEX.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
19371-19379.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Thireou,
V.Atlamazoglou,
M.Levakis,
E.Eliopoulos,
A.Hountas,
G.Tsoucaris,
and
K.Bethanis
(2007).
CrystTwiV: a webserver for automated phase extension and refinement in X-ray crystallography.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
35,
W718-W722.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Singh,
T.Jabeen,
S.Sharma,
R.K.Somvanshi,
S.Dey,
A.Srinivasan,
and
T.P.Singh
(2006).
Specific binding of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to phospholipase A2: structure of the complex formed between phospholipase A2 and diclofenac at 2.7 A resolution.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
62,
410-416.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.K.Singh,
N.Singh,
T.Jabeen,
S.Sharma,
S.Dey,
and
T.P.Singh
(2005).
Crystal structure of the complex of group I PLA2 with a group II-specific peptide Leu-Ala-Ile-Tyr-Ser (LAIYS) at 2.6 A resolution.
|
| |
J Drug Target,
13,
367-374.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.F.Scott,
G.G.Graham,
and
K.J.Bryant
(2003).
Secreted phospholipase A2 enzymes as therapeutic targets.
|
| |
Expert Opin Ther Targets,
7,
427-440.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.K.Singh,
P.Vikram,
J.Makker,
T.Jabeen,
S.Sharma,
S.Dey,
P.Kaur,
A.Srinivasan,
and
T.P.Singh
(2003).
Design of specific peptide inhibitors for group I phospholipase A2: structure of a complex formed between phospholipase A2 from Naja naja sagittifera (group I) and a designed peptide inhibitor Val-Ala-Phe-Arg-Ser (VAFRS) at 1.9 A resolution reveals unique features.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
42,
11701-11706.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
I.K.Mellinghoff,
and
C.L.Sawyers
(2002).
The emergence of resistance to targeted cancer therapeutics.
|
| |
Pharmacogenomics,
3,
603-623.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Sugiyama,
K.Ohtani,
M.Izuhara,
T.Koike,
K.Suzuki,
S.Imamura,
and
H.Misaki
(2002).
A novel prokaryotic phospholipase A2. Characterization, gene cloning, and solution structure.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
20051-20058.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Chandra,
J.Jasti,
P.Kaur,
S.Dey,
A.Srinivasan,
C.h.Betzel,
and
T.P.Singh
(2002).
Design of specific peptide inhibitors of phospholipase A2: structure of a complex formed between Russell's viper phospholipase A2 and a designed peptide Leu-Ala-Ile-Tyr-Ser (LAIYS).
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
58,
1813-1819.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.H.Pan,
B.Z.Yu,
A.G.Singer,
F.Ghomashchi,
G.Lambeau,
M.H.Gelb,
M.K.Jain,
and
B.J.Bahnson
(2002).
Crystal structure of human group X secreted phospholipase A2. Electrostatically neutral interfacial surface targets zwitterionic membranes.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
29086-29093.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Matoba,
Y.Katsube,
and
M.Sugiyama
(2002).
The crystal structure of prokaryotic phospholipase A2.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
20059-20069.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.A.Steiner,
H.J.Rozeboom,
A.de Vries,
K.H.Kalk,
G.N.Murshudov,
K.S.Wilson,
and
B.W.Dijkstra
(2001).
X-ray structure of bovine pancreatic phospholipase A2 at atomic resolution.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
57,
516-526.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
W.H.Lee,
M.T.da Silva Giotto,
S.Marangoni,
M.H.Toyama,
I.Polikarpov,
and
R.C.Garratt
(2001).
Structural basis for low catalytic activity in Lys49 phospholipases A2--a hypothesis: the crystal structure of piratoxin II complexed to fatty acid.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
40,
28-36.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Dessen
(2000).
Phospholipase A(2) enzymes: structural diversity in lipid messenger metabolism.
|
| |
Structure,
8,
R15-R22.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.G.Buckland,
and
D.C.Wilton
(2000).
The antibacterial properties of secreted phospholipases A(2).
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1488,
71-82.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.A.Six,
and
E.A.Dennis
(2000).
The expanding superfamily of phospholipase A(2) enzymes: classification and characterization.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1488,
1.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Hurt-Camejo,
G.Camejo,
and
P.Sartipy
(2000).
Phospholipase A2 and small, dense low-density lipoprotein.
|
| |
Curr Opin Lipidol,
11,
465-471.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Valentin,
F.Ghomashchi,
M.H.Gelb,
M.Lazdunski,
and
G.Lambeau
(2000).
Novel human secreted phospholipase A(2) with homology to the group III bee venom enzyme.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
275,
7492-7496.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.G.Hains,
K.L.Sung,
A.Tseng,
and
K.W.Broady
(2000).
Functional characteristics of a phospholipase A(2) inhibitor from Notechis ater serum.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
275,
983-991.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Le Maire,
E.Solito,
F.Russo-Marie,
A.Hernvann,
H.Le Marechal,
O.G.Ekindjian,
and
C.Aussel
(2000).
System A neutral amino acid transporter regulation by interleukin-1beta in human osteoarthritic synovial cells: evidence for involvement of prostaglandin E(2) as a second messenger.
|
| |
J Cell Physiol,
183,
65-73.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Zhao,
S.Song,
Z.Lin,
and
Y.Zhou
(1999).
Refined structure of basic phospholipase A2 from venom ofAgkistrodon halys Pallas in orthorhombic crystal form I at 0.25 nm resolution.
|
| |
Sci China C Life Sci,
42,
80-89.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Cupillard,
R.Mulherkar,
N.Gomez,
S.Kadam,
E.Valentin,
M.Lazdunski,
and
G.Lambeau
(1999).
Both group IB and group IIA secreted phospholipases A2 are natural ligands of the mouse 180-kDa M-type receptor.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
7043-7051.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.K.Han,
K.P.Kim,
R.Koduri,
L.Bittova,
N.M.Munoz,
A.R.Leff,
D.C.Wilton,
M.H.Gelb,
and
W.Cho
(1999).
Roles of Trp31 in high membrane binding and proinflammatory activity of human group V phospholipase A2.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
274,
11881-11888.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.G.Buckland,
A.R.Kinkaid,
and
D.C.Wilton
(1998).
Cardiolipin hydrolysis by human phospholipases A2. The multiple enzymatic activities of human cytosolic phospholipase A2.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1390,
65-72.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.M.Mounier,
T.M.Hackeng,
F.Schaeffer,
G.Faure,
C.Bon,
and
J.H.Griffin
(1998).
Inhibition of prothrombinase by human secretory phospholipase A2 involves binding to factor Xa.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
23764-23772.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Sekar,
C.Sekharudu,
M.D.Tsai,
and
M.Sundaralingam
(1998).
1.72 A resolution refinement of the trigonal form of bovine pancreatic phospholipase A2.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
54,
342-346.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Arbibe,
K.Koumanov,
D.Vial,
C.Rougeot,
G.Faure,
N.Havet,
S.Longacre,
B.B.Vargaftig,
G.Béréziat,
D.R.Voelker,
C.Wolf,
and
L.Touqui
(1998).
Generation of lyso-phospholipids from surfactant in acute lung injury is mediated by type-II phospholipase A2 and inhibited by a direct surfactant protein A-phospholipase A2 protein interaction.
|
| |
J Clin Invest,
102,
1152-1160.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Hurt-Camejo,
and
G.Camejo
(1997).
Potential involvement of type II phospholipase A2 in atherosclerosis.
|
| |
Atherosclerosis,
132,
1-8.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Tischfield
(1997).
A reassessment of the low molecular weight phospholipase A2 gene family in mammals.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
272,
17247-17250.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.M.Hackeng,
C.M.Mounier,
C.Bon,
P.E.Dawson,
J.H.Griffin,
and
S.B.Kent
(1997).
Total chemical synthesis of enzymatically active human type II secretory phospholipase A2.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
94,
7845-7850.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Tseng,
A.S.Inglis,
and
K.F.Scott
(1996).
Native peptide inhibition. Specific inhibition of type II phospholipases A2 by synthetic peptides derived from the primary sequence.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
271,
23992-23998.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Zhou,
and
K.Schulten
(1996).
Molecular dynamics study of phospholipase A2 on a membrane surface.
|
| |
Proteins,
25,
12-27.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Sartipy,
B.Johansen,
G.Camejo,
B.Rosengren,
G.Bondjers,
and
E.Hurt-Camejo
(1996).
Binding of human phospholipase A2 type II to proteoglycans. Differential effect of glycosaminoglycans on enzyme activity.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
271,
26307-26314.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Nakamura,
M.Nakai,
K.Nakashima,
T.Ogawa,
Y.Shimohigashi,
M.Ohno,
H.Kihara,
T.Yamane,
and
T.Ashida
(1996).
Roles of lysine-69 in dimerization and activity of Trimeresurus flavoviridis venom aspartate-49-phospholipase A2.
|
| |
J Mol Recognit,
9,
23-30.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.J.Lewis,
and
A.F.Keft
(1995).
A review on the strategies for the development and application of new anti-arthritic agents.
|
| |
Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol,
17,
607-663.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.van den Berg,
M.Tessari,
G.H.de Haas,
H.M.Verheij,
R.Boelens,
and
R.Kaptein
(1995).
Solution structure of porcine pancreatic phospholipase A2.
|
| |
EMBO J,
14,
4123-4131.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
C.L.Verlinde,
and
B.W.Dijkstra
(1995).
Drug or tool, design or serendipity?
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
2,
429-432.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Lambeau,
P.Ancian,
J.P.Nicolas,
S.H.Beiboer,
D.Moinier,
H.Verheij,
and
M.Lazdunski
(1995).
Structural elements of secretory phospholipases A2 involved in the binding to M-type receptors.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
270,
5534-5540.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.R.Burke,
K.R.Gregor,
and
K.M.Tramposch
(1995).
Mechanism of inhibition of human nonpancreatic secreted phospholipase A2 by the anti-inflammatory agent BMS-181162.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
270,
274-280.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Y.Lehtonen,
and
P.K.Kinnunen
(1995).
Phospholipase A2 as a mechanosensor.
|
| |
Biophys J,
68,
1888-1894.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
O.Ohara,
J.Ishizaki,
and
H.Arita
(1995).
Structure and function of phospholipase A2 receptor.
|
| |
Prog Lipid Res,
34,
117-138.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.W.Schevitz,
N.J.Bach,
D.G.Carlson,
N.Y.Chirgadze,
D.K.Clawson,
R.D.Dillard,
S.E.Draheim,
L.W.Hartley,
N.D.Jones,
and
E.D.Mihelich
(1995).
Structure-based design of the first potent and selective inhibitor of human non-pancreatic secretory phospholipase A2.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
2,
458-465.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Iwama,
T.Matsuda,
S.Katsumura,
T.Tani,
S.Fujii,
K.Ikeda,
and
H.Takehara
(1995).
New phospholipase A2 inhibitor: synthesis and inhibition mechanism of oxazolidinone phospholipid analog.
|
| |
Bioorg Med Chem,
3,
1397-1403.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.F.Bennett,
M.Y.Chiang,
L.Wilson-Lingardo,
and
J.R.Wyatt
(1994).
Sequence specific inhibition of human type II phospholipase A2 enzyme activity by phosphorothioate oligonucleotides.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
22,
3202-3209.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.L.Scott,
A.M.Mandel,
P.B.Sigler,
and
B.Honig
(1994).
The electrostatic basis for the interfacial binding of secretory phospholipases A2.
|
| |
Biophys J,
67,
493-504.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Angel,
F.Berenbaum,
C.Le Denmat,
T.Nevalainen,
J.Masliah,
and
C.Fournier
(1994).
Interleukin-1-induced prostaglandin E2 biosynthesis in human synovial cells involves the activation of cytosolic phospholipase A2 and cyclooxygenase-2.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
226,
125-131.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Dua,
and
W.Cho
(1994).
Inhibition of human secretory class II phospholipase A2 by heparin.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
221,
481-490.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Andersen,
W.Sjursen,
A.Laegreid,
G.Volden,
and
B.Johansen
(1994).
Elevated expression of human nonpancreatic phospholipase A2 in psoriatic tissue.
|
| |
Inflammation,
18,
1.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.H.Fremont,
D.H.Anderson,
I.A.Wilson,
E.A.Dennis,
and
N.H.Xuong
(1993).
Crystal structure of phospholipase A2 from Indian cobra reveals a trimeric association.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
90,
342-346.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Cordella-Miele,
L.Miele,
and
A.B.Mukherjee
(1993).
Identification of a specific region of low molecular weight phospholipases A2 (residues 21-40) as a potential target for structure-based design of inhibitors of these enzymes.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
90,
10290-10294.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Märki,
W.Breitenstein,
E.Beriger,
R.Bernasconi,
G.Caravatti,
J.E.Francis,
R.Paioni,
H.U.Wehrli,
and
R.Wiederkehr
(1993).
Differential inhibition of human secretory and cytosolic phospholipase A2.
|
| |
Agents Actions,
38,
202-211.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Stadel,
C.Jones,
G.P.Livi,
K.Hoyle,
J.Kurdyla,
A.Roshak,
M.M.McLaughlin,
D.A.Pfarr,
S.Comer,
and
J.Strickler
(1992).
Recombinant human secretory phospholipase A2: purification and characterization of the enzyme for active site studies.
|
| |
J Mol Recognit,
5,
145-153.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.P.Vernon,
and
J.D.Bell
(1992).
Membrane structure, toxins and phospholipase A2 activity.
|
| |
Pharmacol Ther,
54,
269-295.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.A.Franken,
L.Van den Berg,
J.Huang,
P.Gunyuzlu,
R.B.Lugtigheid,
H.M.Verheij,
and
G.H.De Haas
(1992).
Purification and characterization of a mutant human platelet phospholipase A2 expressed in Escherichia coli. Cleavage of a fusion protein with cyanogen bromide.
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
203,
89-98.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.M.Wang,
P.J.Lu,
C.L.Ho,
and
I.H.Tsai
(1992).
Characterization and molecular cloning of neurotoxic phospholipases A2 from Taiwan viper (Vipera russelli formosensis).
|
| |
Eur J Biochem,
209,
635-641.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

