- Course overview
- Search within this course
- Network analysis in biology
- Introduction to graph theory
- Types of biological networks
- The sources of data underlying biological networks
- Protein-protein interaction networks
- Building and analysing PPINs
- Summary
- Quiz: Check your learning
- Your feedback
- Learn more
- References
Types of biological networks
Biological networks
Different types of information can be represented in the shape of networks in order to model the cell (Figure 10). The meaning of the nodes and edges used in a network representation depends on the type of data used to build the network and this should be taken into account when analysing it.
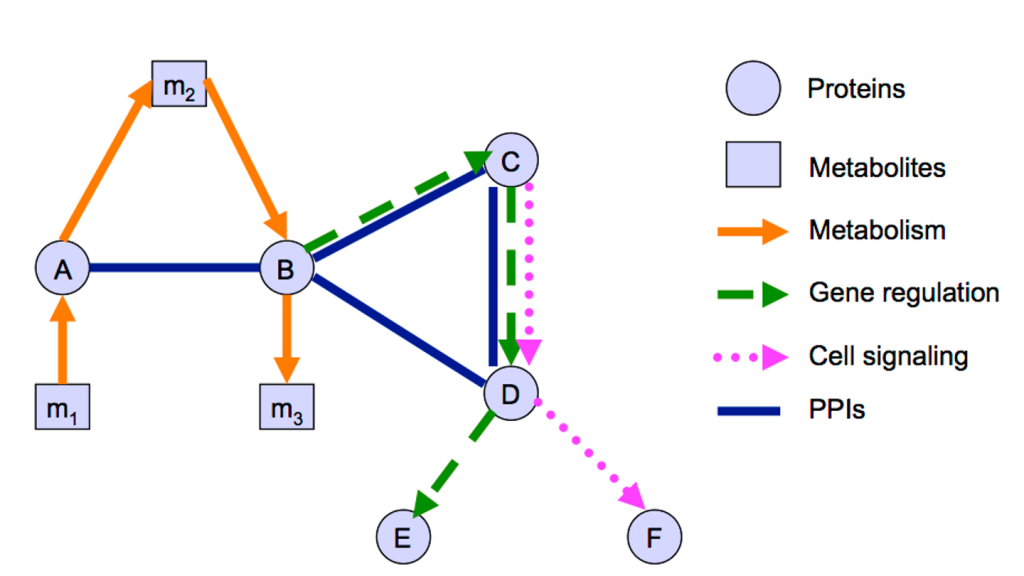
Different types of data will also produce different general network characteristics in terms of connectivity, complexity and structure, where edges and nodes potentially convey multiple layers of information.
Some of the most common types of biological networks are:
- Protein-protein interaction networks
- Metabolic networks
- Genetic interaction networks
- Gene / transcriptional regulatory networks
- Cell signalling networks
Slide the bar below to find further details (Figure 11-15):