Small molecules
What are small molecules?
A small molecule (or metabolite) is a low molecular weight organic compound, typically involved in a biological process as a substrate or product. Metabolomics usually studies small molecules within a mass range of 50 – 1500 daltons (Da).
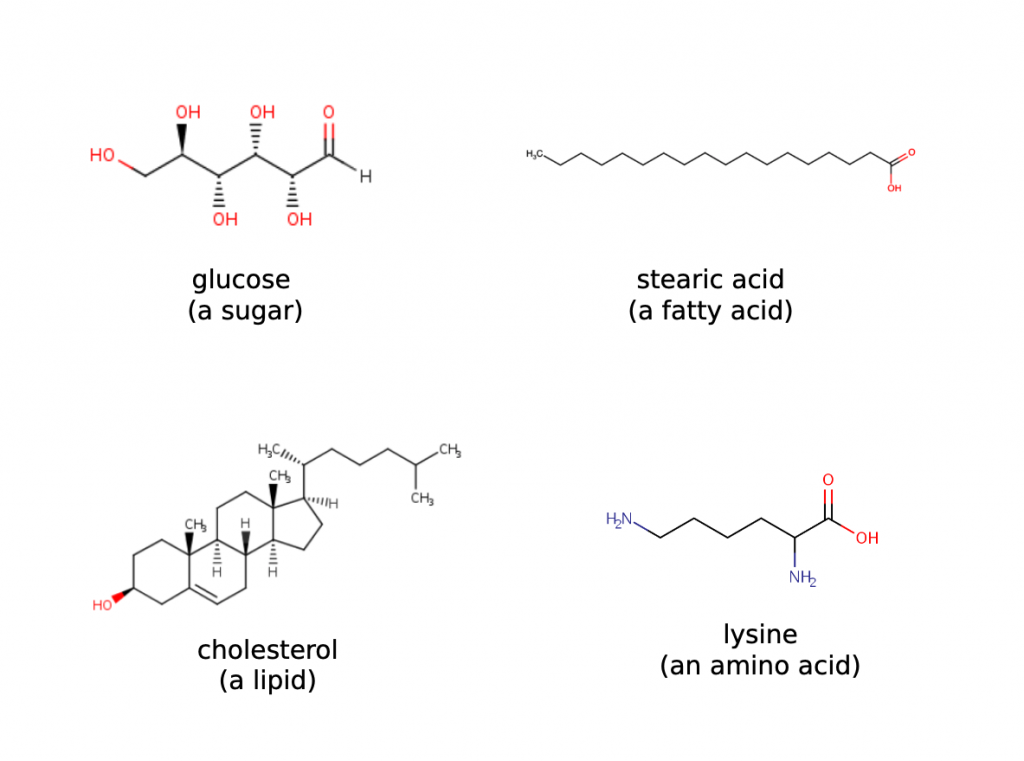
Examples of small molecules can be seen in Figure 2 and include:
- sugars
- lipids
- amino acids
- fatty acids
- phenolic compounds
- alkaloids
There is a great deal of variation in metabolites between species, it is estimated there are around 200,000 metabolites across the plant kingdom, and somewhere between 7,000 and 15,000 within an individual plant species (1, 2). By contrast, in humans, there are thought to be around 3,000 endogenous or common metabolites (3). These estimates are approximations that are likely to be underestimates because it is difficult to detect low-abundance molecules. Nonetheless, it can be concluded that plants are particularly biochemically rich by comparison with many other species. They also typically contain larger numbers of genes than other eukaryotes.