 |
PDBsum entry 6imr

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Hydrolase/hydrolase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
6imr
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase/hydrolase inhibitor
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of pde4d complexed with a novel inhibitor
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Camp-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 4d. Chain: a, b. Synonym: pde4d, dpde3,pde43. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: pde4d, dpde3. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.50Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.212
|
R-free:
|
0.237
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
X.L.Zhang,H.X.Su,Y.C.Xu
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
X.Zhang
et al.
(2019).
Structure-Aided Identification and Optimization of Tetrahydro-isoquinolines as Novel PDE4 Inhibitors Leading to Discovery of an Effective Antipsoriasis Agent.
J Med Chem,
62,
5579-5593.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
23-Oct-18
|
Release date:
|
23-Oct-19
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q08499
(PDE4D_HUMAN) -
3',5'-cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase 4D from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
809 a.a.
325 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.4.53
- 3',5'-cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
3',5'-cyclic AMP + H2O = AMP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
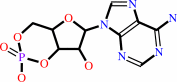 3',5'-cyclic AMP
3',5'-cyclic AMP
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
 AMP
AMP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Med Chem
62:5579-5593
(2019)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure-Aided Identification and Optimization of Tetrahydro-isoquinolines as Novel PDE4 Inhibitors Leading to Discovery of an Effective Antipsoriasis Agent.
|
|
X.Zhang,
G.Dong,
H.Li,
W.Chen,
J.Li,
C.Feng,
Z.Gu,
F.Zhu,
R.Zhang,
M.Li,
W.Tang,
H.Liu,
Y.Xu.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Psoriasis is a common, chronic inflammatory disease characterized by abnormal
skin plaques, and the effectiveness of phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor to
lessen the symptoms of psoriasis has been proved. Aiming to find a novel PDE4
inhibitor acting as an effective, safe, and convenient therapeutic agent, we
constructed a library consisting of berberine analogues, and compound 2 with a
tetrahydroisoquinoline scaffold was identified as a novel and potent hit. The
structure-aided and cell-based structure-activity relationship studies on a
series of tetrahydro-isoquinolines lead to efficient discovery of a qualified
lead compound (16) with the high potency and selectivity, well-characterized
binding mechanism, high cell permeability, good safety and pharmacokinetic
profile, and impressive in vivo efficacy on antipsoriasis, in particular with a
topical application. Thus, our study presents a prime example for efficient
discovery of novel, potent lead compounds derived from natural products using a
combination of medicinal chemistry, biochemical, biophysical, and
pharmacological approaches.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

