 |
PDBsum entry 5fnh
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Native state mass spectrometry, surface plasmon resonance and x-ray crystallography correlate strongly as a fragment screening combination
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Carbonic anhydrase 2. Chain: a. Synonym: carbonate dehydratase ii, carbonic anhydrasE C, cac, carbonic anhydrase ii, ca-ii. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 511693.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.66Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.139
|
R-free:
|
0.180
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
L.A.Woods,O.Dolezal,B.Ren,J.H.Ryan,T.S.Peat,S.A.Poulsen
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
L.A.Woods
et al.
(2016).
Native State Mass Spectrometry, Surface Plasmon Resonance, and X-ray Crystallography Correlate Strongly as a Fragment Screening Combination.
J Med Chem,
59,
2192-2204.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
15-Nov-15
|
Release date:
|
02-Mar-16
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P00918
(CAH2_HUMAN) -
Carbonic anhydrase 2 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
260 a.a.
257 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.1
- carbonic anhydrase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
hydrogencarbonate + H+ = CO2 + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 hydrogencarbonate
hydrogencarbonate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
 CO2
CO2
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.4.2.1.69
- cyanamide hydratase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
urea = cyanamide + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
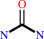 urea
urea
|
=
|
 cyanamide
cyanamide
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Med Chem
59:2192-2204
(2016)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Native State Mass Spectrometry, Surface Plasmon Resonance, and X-ray Crystallography Correlate Strongly as a Fragment Screening Combination.
|
|
L.A.Woods,
O.Dolezal,
B.Ren,
J.H.Ryan,
T.S.Peat,
S.A.Poulsen.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Fragment-based drug discovery (FBDD) is contingent on the development of
analytical methods to identify weak protein-fragment noncovalent interactions.
Herein we have combined an underutilized fragment screening method, native state
mass spectrometry, together with two proven and popular fragment screening
methods, surface plasmon resonance and X-ray crystallography, in a fragment
screening campaign against human carbonic anhydrase II (CA II). In an initial
fragment screen against a 720-member fragment library (the "CSIRO Fragment
Library") seven CA II binding fragments, including a selection of
nonclassical CA II binding chemotypes, were identified. A further 70 compounds
that comprised the initial hit chemotypes were subsequently sourced from the
full CSIRO compound collection and screened. The fragment results were extremely
well correlated across the three methods. Our findings demonstrate that there is
a tremendous opportunity to apply native state mass spectrometry as a
complementary fragment screening method to accelerate drug discovery.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

