 |
PDBsum entry 4zvm

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase/oxidoreductase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4zvm
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.10.5.1
- ribosyldihydronicotinamide dehydrogenase (quinone).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
1-(beta-D-ribofuranosyl)-1,4-dihydronicotinamide + a quinone + H+ = beta-nicotinamide D-riboside + a quinol
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
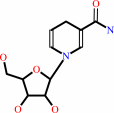 1-(beta-D-ribofuranosyl)-1,4-dihydronicotinamide
1-(beta-D-ribofuranosyl)-1,4-dihydronicotinamide
|
+
|
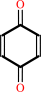 quinone
quinone
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
beta-nicotinamide D-riboside
|
+
|
quinol
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FAD; Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
FAD
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
FAD)
corresponds exactly
|
Zn(2+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
54:7438-7448
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Binding of DNA-Intercalating Agents to Oxidized and Reduced Quinone Reductase 2.
|
|
K.K.Leung,
B.H.Shilton.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Quinone reductase 2 (NQO2) is an enzyme that might have intracellular signaling
functions. NQO2 can exist in either an oxidized state or a reduced state, and
binding of compounds to one or both of these states inhibits enzymatic activity
and could also affect intracellular signaling. A wide range of planar aromatic
compounds bind NQO2, and we have identified three DNA-intercalating agents
[ethidium bromide, acridine orange (AO), and doxorubicin] as novel nanomolar
inhibitors of NQO2. Ethidium and AO, which carry a positive charge in their
aromatic ring systems, bound reduced NQO2 with an affinity 50-fold higher than
that of oxidized NQO2, while doxorubicin bound only oxidized NQO2.
Crystallographic analyses of oxidized NQO2 in complex with the inhibitors
indicated that the inhibitors were situated deep in the active site. The
aromatic faces were sandwiched between the isoalloxazine ring of FAD and the
phenyl ring of F178, with their edges making direct contact with residues lining
the active site. In reduced NQO2, ethidium and AO occupied a more peripheral
position in the active site, allowing several water molecules to interact with
the polar end of the negatively charged isoalloxazine ring. We also showed that
AO inhibited NQO2 at a nontoxic concentration in cells while ethidium was less
effective at inhibiting NQO2 in cells. Together, this study shows that reduced
NQO2 has structural and electrostatic properties that yield a preference for
binding of planar, aromatic, and positively charged molecules that can also
function as DNA-intercalating agents.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

