 |
PDBsum entry 4zcg
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.2.3.2.2
- gamma-glutamyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
an N-terminal (5-L-glutamyl)-[peptide] + an alpha-amino acid = 5-L- glutamyl amino acid + an N-terminal L-alpha-aminoacyl-[peptide]
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
N-terminal (5-L-glutamyl)-[peptide]
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 45.45% similarity
|
+
|
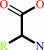 alpha-amino acid
alpha-amino acid
|
=
|
5-L- glutamyl amino acid
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 45.00% similarity
|
+
|
N-terminal L-alpha-aminoacyl-[peptide]
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.3.4.19.13
- glutathione gamma-glutamate hydrolase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
glutathione + H2O = L-cysteinylglycine + L-glutamate
|
|
2.
|
an S-substituted glutathione + H2O = an S-substituted L-cysteinylglycine + L-glutamate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
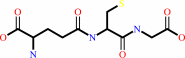 glutathione
glutathione
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
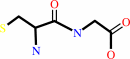 L-cysteinylglycine
L-cysteinylglycine
|
+
|
L-glutamate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
S-substituted glutathione
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
S-substituted L-cysteinylglycine
|
+
|
L-glutamate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 4:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.3.4.19.14
- leukotriene-C4 hydrolase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
leukotriene C4 + H2O = leukotriene D4 + L-glutamate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
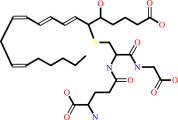 leukotriene C4
leukotriene C4
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
leukotriene D4
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
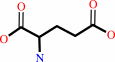 L-glutamate
L-glutamate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
290:17576-17586
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Human γ-Glutamyl Transpeptidase 1: STRUCTURES OF THE FREE ENZYME, INHIBITOR-BOUND TETRAHEDRAL TRANSITION STATES, AND GLUTAMATE-BOUND ENZYME REVEAL NOVEL MOVEMENT WITHIN THE ACTIVE SITE DURING CATALYSIS.
|
|
S.S.Terzyan,
A.W.Burgett,
A.Heroux,
C.A.Smith,
B.H.Mooers,
M.H.Hanigan.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
γ-Glutamyl transpeptidase 1 (GGT1) is a cell surface, N-terminal nucleophile
hydrolase that cleaves glutathione and other γ-glutamyl compounds. GGT1
expression is essential in cysteine homeostasis, and its induction has been
implicated in the pathology of asthma, reperfusion injury, and cancer. In this
study, we report four new crystal structures of human GGT1 (hGGT1) that show
conformational changes within the active site as the enzyme progresses from the
free enzyme to inhibitor-bound tetrahedral transition states and finally to the
glutamate-bound structure prior to the release of this final product of the
reaction. The structure of the apoenzyme shows flexibility within the active
site. The serine-borate-bound hGGT1 crystal structure demonstrates that
serine-borate occupies the active site of the enzyme, resulting in an
enzyme-inhibitor complex that replicates the enzyme's tetrahedral
intermediate/transition state. The structure of GGsTop-bound hGGT1 reveals its
interactions with the enzyme and why neutral phosphonate diesters are more
potent inhibitors than monoanionic phosphonates. These structures are the first
structures for any eukaryotic GGT that include a molecule in the active site
covalently bound to the catalytic Thr-381. The glutamate-bound structure shows
the conformation of the enzyme prior to release of the final product and reveals
novel information regarding the displacement of the main chain atoms that form
the oxyanion hole and movement of the lid loop region when the active site is
occupied. These data provide new insights into the mechanism of hGGT1-catalyzed
reactions and will be invaluable in the development of new classes of hGGT1
inhibitors for therapeutic use.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

